Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Jun 26, 2013; 5(6): 164-174
Published online Jun 26, 2013. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v5.i6.164
Published online Jun 26, 2013. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v5.i6.164
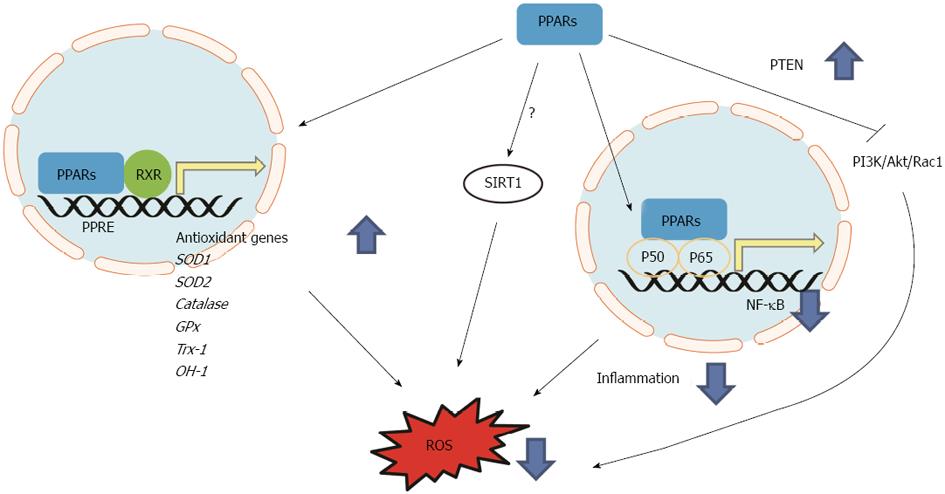
Figure 2 Antioxidant mechanisms of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors.
Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) activate antioxidant genes via transcriptional regulation by binding on PPAR response element (PPRE) of promoter region of target genes. PPARs suppress nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB)-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells via interaction with p50 and p65 resulting in decreased inflammatory response and oxidative stress. PPARs suppress phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/Rac1 signaling axis via activation of PTEN resulting in decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS). RXR: Retinoid X receptor. sod: Superoxide dismutase; trx: Thioredoxin; gpx: Glutathione peroxidase; ho: Heme oxygenase.
- Citation: Kim T, Yang Q. Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors regulate redox signaling in the cardiovascular system. World J Cardiol 2013; 5(6): 164-174
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v5/i6/164.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v5.i6.164