Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2025; 17(7): 108745
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.108745
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.108745
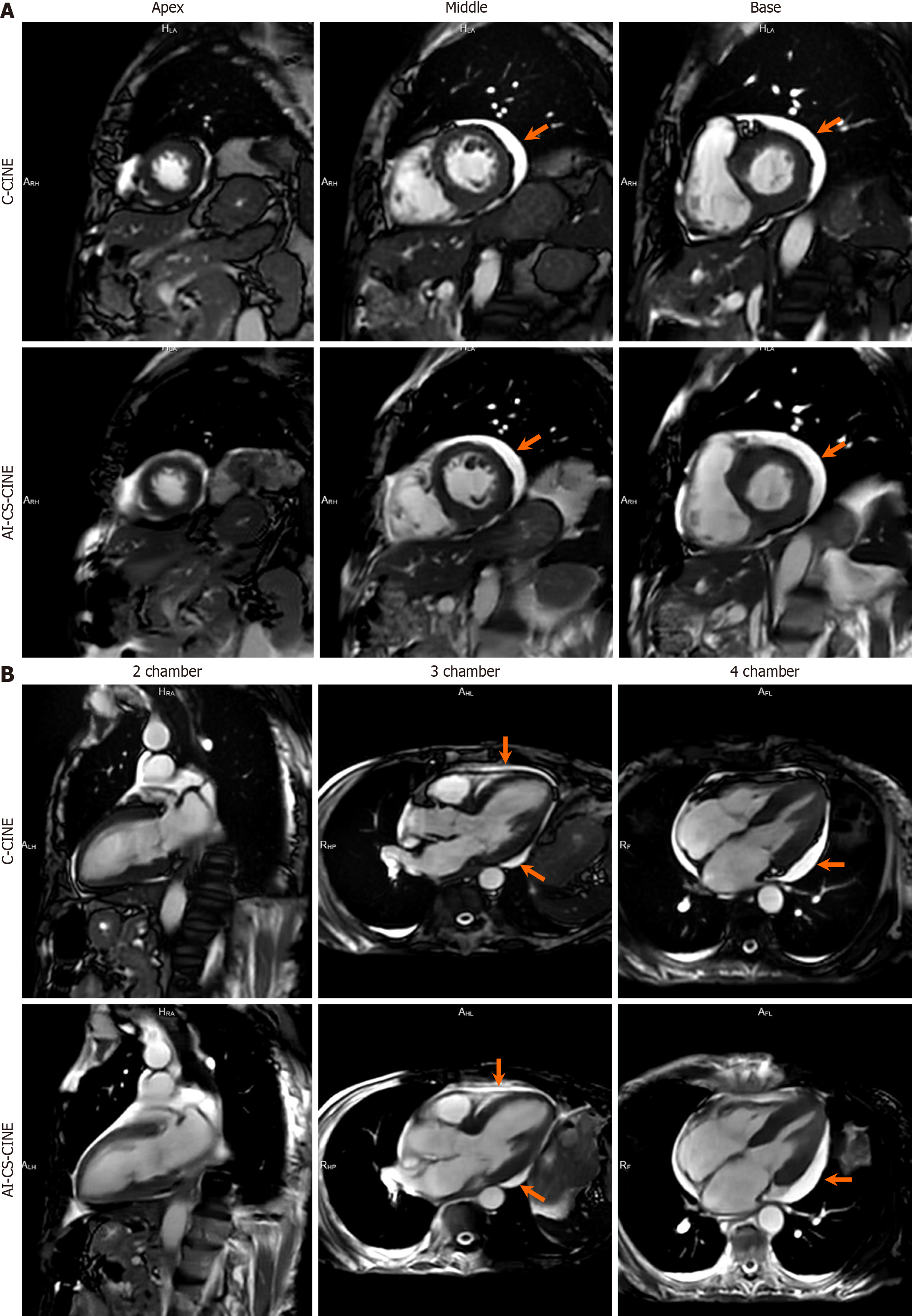
Figure 3 Exceptional alignment between conventional CINE and artificial-intelligence-assisted compressed sensing CINE is demon
- Citation: Wang H, Schmieder A, Watkins M, Wang P, Mitchell J, Qamer SZ, Lanza G. Artificial intelligence-assisted compressed sensing CINE enhances the workflow of cardiac magnetic resonance in challenging patients. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(7): 108745
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i7/108745.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.108745