Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2025; 17(7): 107772
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.107772
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.107772
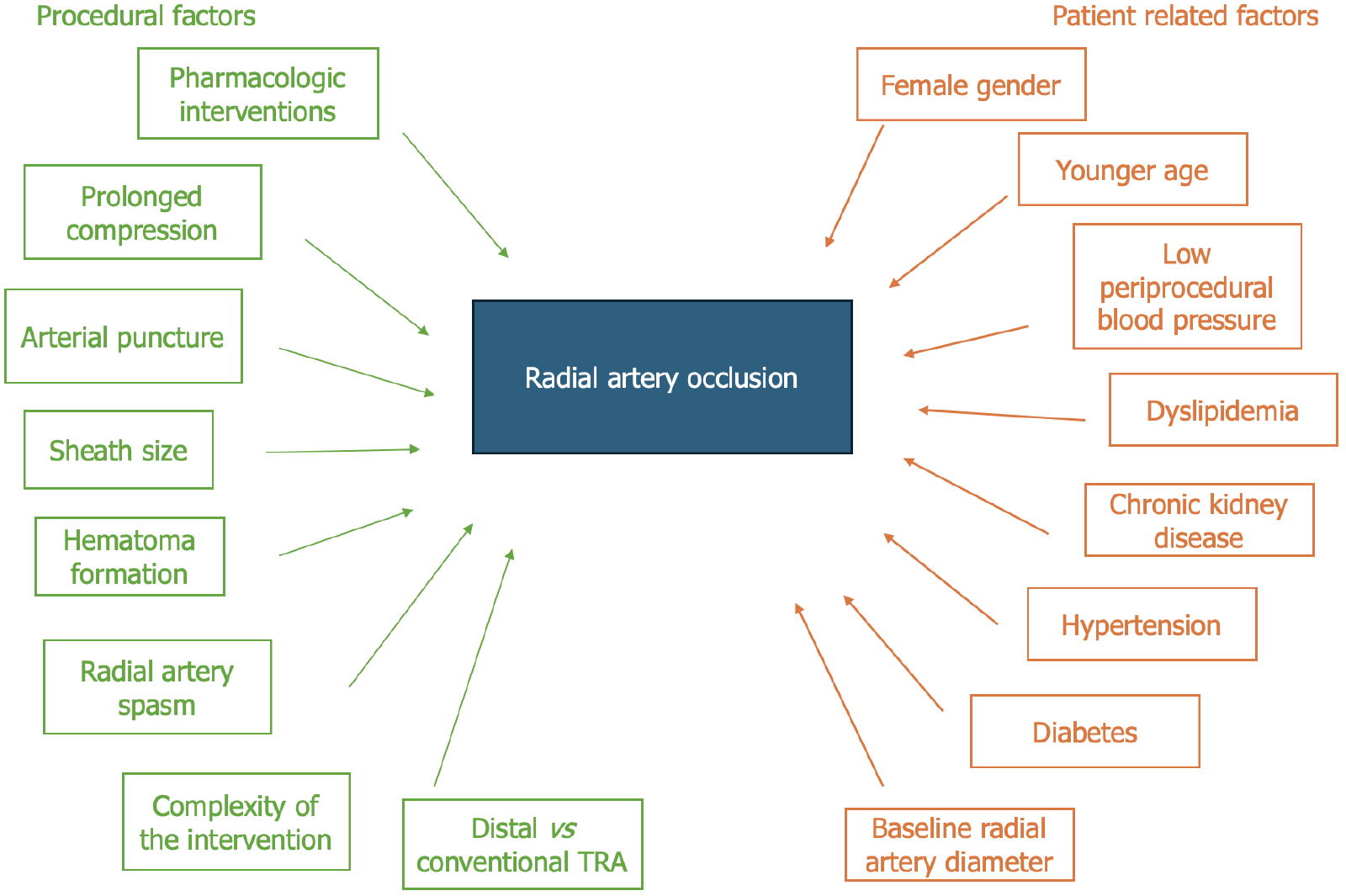
Figure 2 Procedural and patient-related factors associated with radial occlusion artery after transradial access.
Schematic representation of the factors contributing to radial occlusion artery (RAO) following transradial access (TRA). Procedural factors (green), including periprocedural pharmacologic interventions, prolonged compression, multiple arterial punctures, sheath size, hematoma formation, radial artery spasm, procedural complexity and choice of access site (distal vs conventional) impact the incidence of RAO. Patient-related factors (orange), such as female sex, younger age, low periprocedural blood pressure, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease, hypertension, diabetes, and baseline radial artery diameter, further predispose individuals to RAO. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing strategies to minimize RAO risk and preserve radial artery integrity. TRA: Transradial access.
- Citation: Sakellariou XM, Nikas DΝ, Papanagiotou P, Liberopoulos E, Florentin M, Bechlioulis A, Mastoridou EM, Kolettis TM. Structural radial artery modifications following transradial access: Mechanisms, clinical implications, and preventive strategies. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(7): 107772
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i7/107772.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.107772