Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2025; 17(7): 107772
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.107772
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.107772
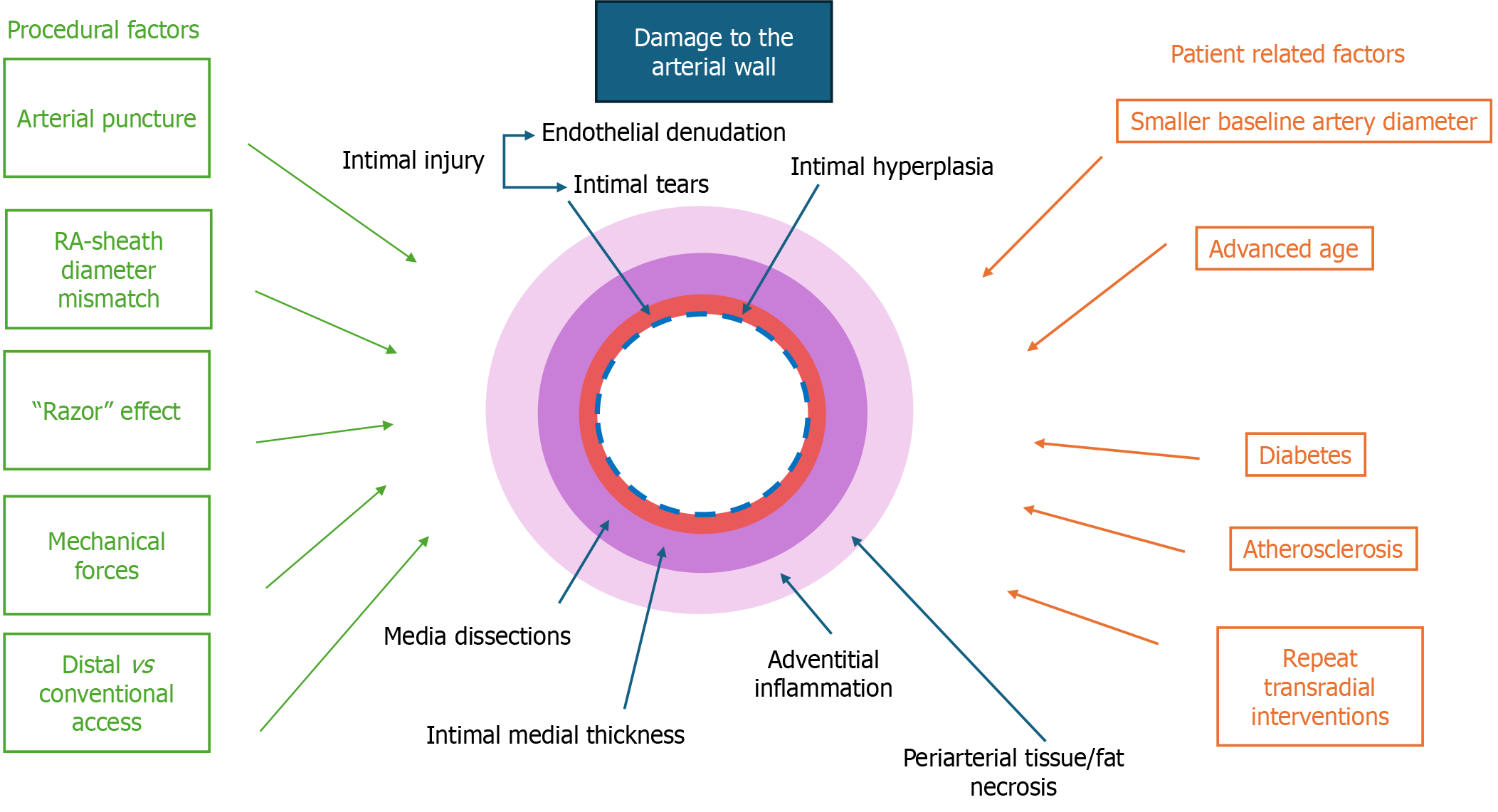
Figure 1 Mechanisms and factors contributing to radial artery wall damage following transradial access.
Schematic representation of the factors contributing to arterial wall damage following transradial access (TRA). Procedural factors (green) such as arterial puncture, sheath diameter mismatch, mechanical forces and choice of access site (distal vs conventional) contribute to intimal injury and hyperplasia, medial dissections, intimal-medial thickening and adventitial injury. Patient-related factors (orange), including smaller baseline artery diameter, advanced age, diabetes, atherosclerosis and repeat TRA interventions, further exacerbate arterial remodeling. These structural changes may not only impact long-term vascular integrity but also have implications for the radial artery’s suitability as a conduit for coronary artery bypass grafting.
- Citation: Sakellariou XM, Nikas DΝ, Papanagiotou P, Liberopoulos E, Florentin M, Bechlioulis A, Mastoridou EM, Kolettis TM. Structural radial artery modifications following transradial access: Mechanisms, clinical implications, and preventive strategies. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(7): 107772
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i7/107772.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.107772