Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Jun 26, 2025; 17(6): 106147
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.106147
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.106147
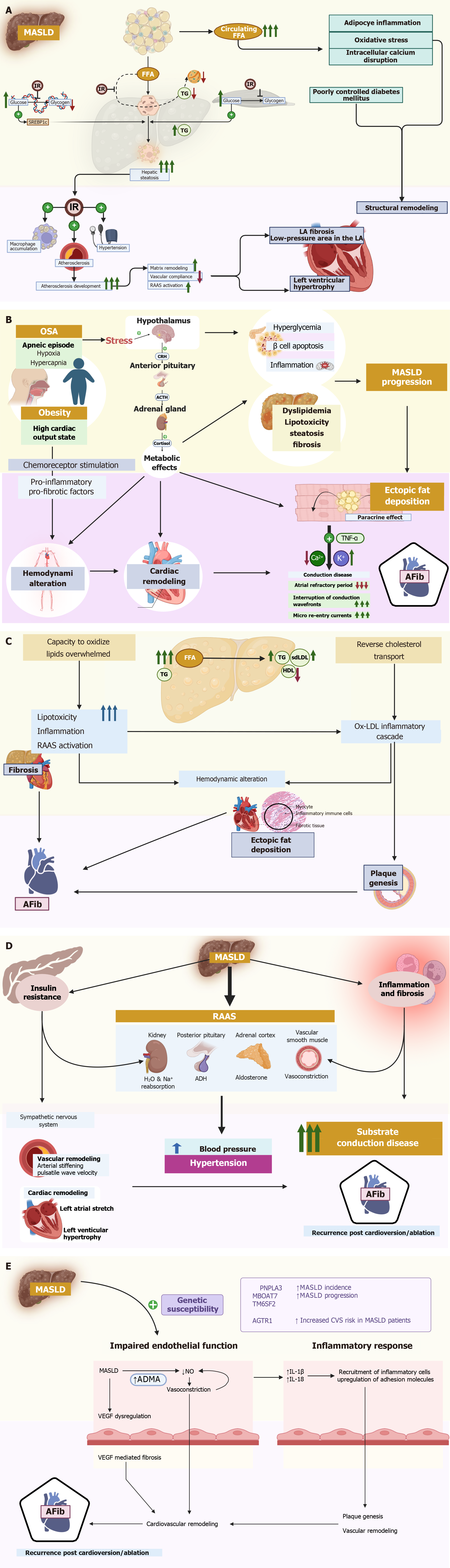
Figure 1 Role in atrial fibrillation and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
A: Insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus; B: Obesity and obstructive sleep apnea; C; Dyslipidemia; D: Hypertension; E: Proposed role of endothelial dysfunction. AF: Atrial fibrillation; AFib: Atrial fibrillation; FFA: Free fatty acid; IR: Insulin resistance; LA: Left atrium; RAAS: Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system; TG: Triglycerides; SREBP1c: Sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c; K: Potassium; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor-α; HDL: High desnity lipoprotein; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; Ox-LDL: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein; SdLDL: Small-density low-density lipoprotein; ADH: Antidiuretic hormone; ADMA: Asymmetric dimethylarginine; IL: Interleukin; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; Na: Sodium. Created in BioRender (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Bharaj IS, Brar AS, Kahlon J, Singh A, Hotwani P, Kumar V, Sohal A, Batta A. Metabolic-dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease and atrial fibrillation: A review of pathogenesis. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(6): 106147
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i6/106147.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i6.106147