Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. May 26, 2025; 17(5): 106567
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i5.106567
Published online May 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i5.106567
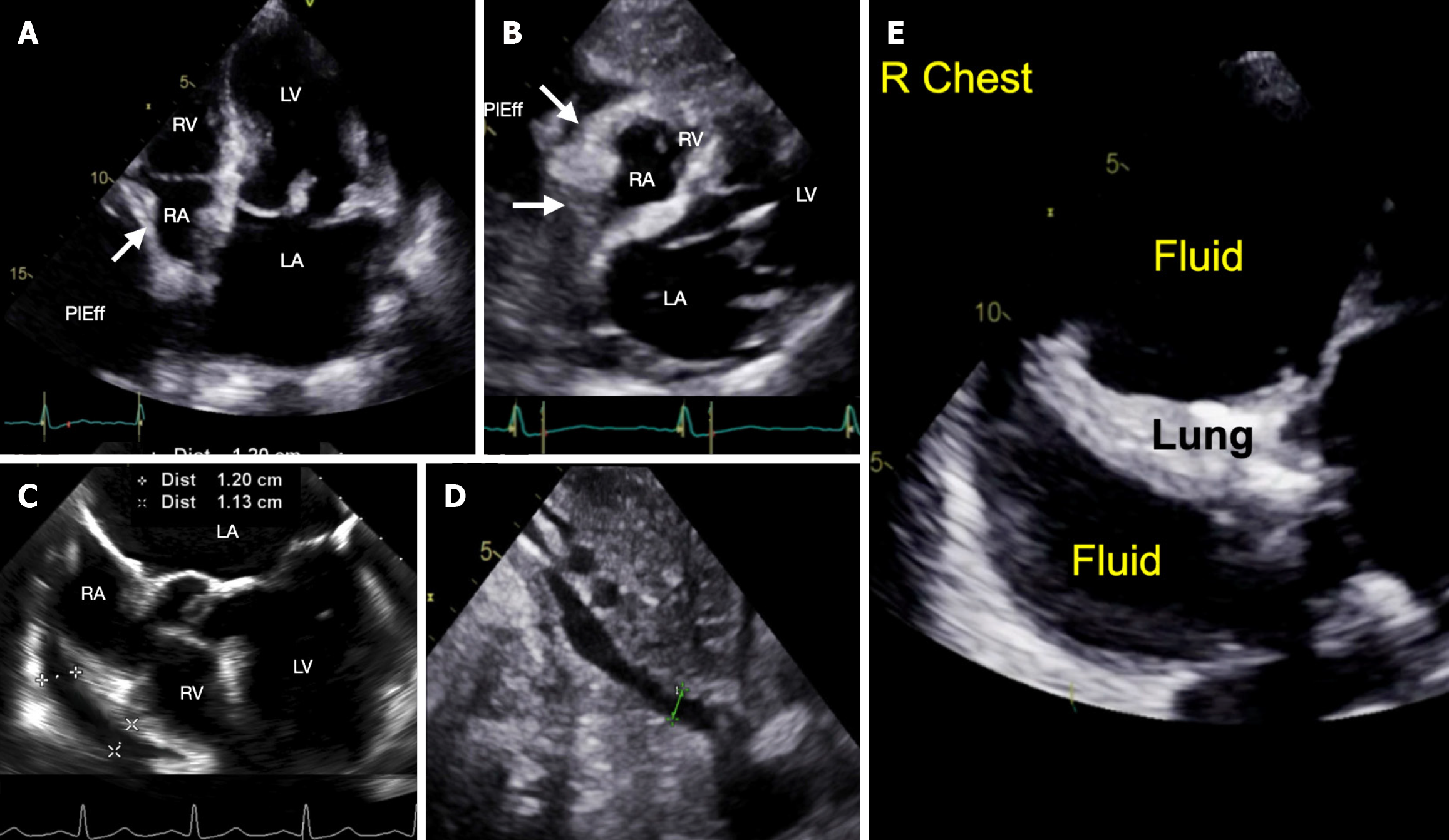
Figure 1 Point-of-care ultrasound exam.
A: Post-procedure cardiac apical four-chamber view showing large fluid collection posterior and lateral (PlEff) to the right atrium (RA) causing RA collapse (white arrow showing inward position of the RA wall) during ventricular systole (i.e., atrial diastole); B: Post-procedure cardiac subcostal view showing four chambers and RA collapse during atrial diastole (white arrows showing inward position of the RA wall) and a small right ventricle (RV); C: Transesophageal echocardiographic view, obtained during the procedure, showing pericardial effusion along the RA and right ventricular chambers (RV) measuring approximately 1.1 to 1.2 cm; D: Post-procedure subcostal view showing inferior cava diameter of 0.8 cm; E: Ultrasound of the right chest demonstrating collapsed lung and a large right chest fluid.
- Citation: Seidler N, Asher SR, Chen T, Gordon P, Sodha N, Maslow A. Low-pressure tamponade due to hemothorax after transcatheter edge-to-edge repair of the mitral valve. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(5): 106567
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i5/106567.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i5.106567