Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Cardiol. Sep 26, 2016; 8(9): 534-546
Published online Sep 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i9.534
Published online Sep 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i9.534
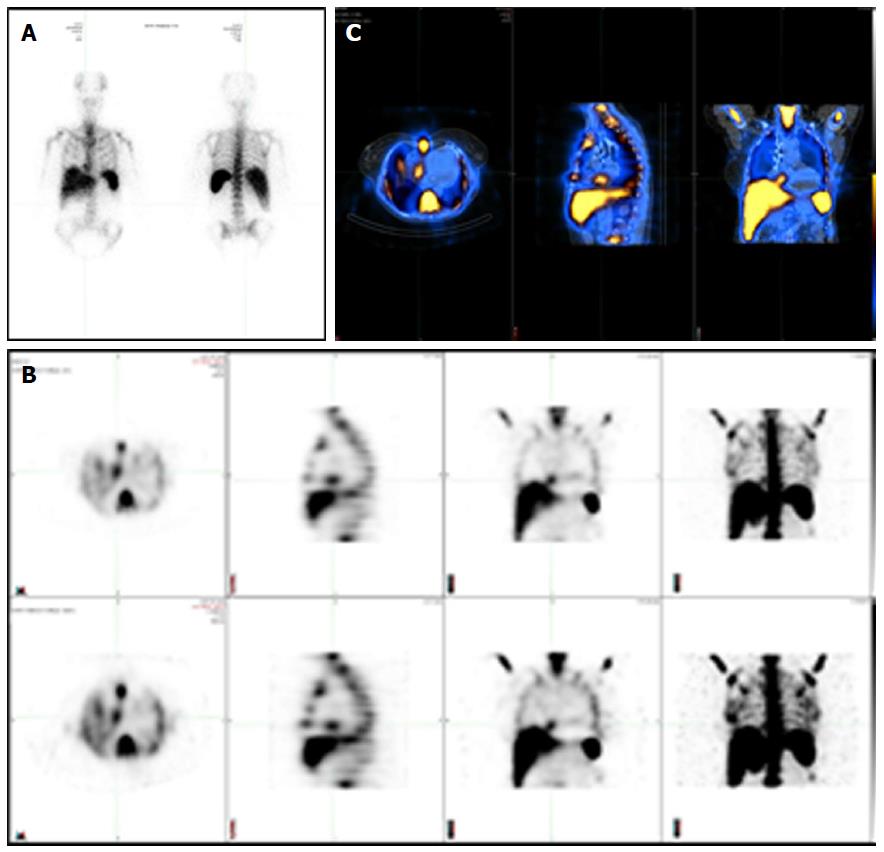
Figure 1 Different modalities in cardiac nuclear imaging.
A: Planar scintigraphy with a single two-dimensional image; B: Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) displayed as transverse, sagittal, coronal and MIP attenuation corrected (top row) and uncorrected images (bottom row); C: Hybrid SPECT/CT with precisely registered CT image.
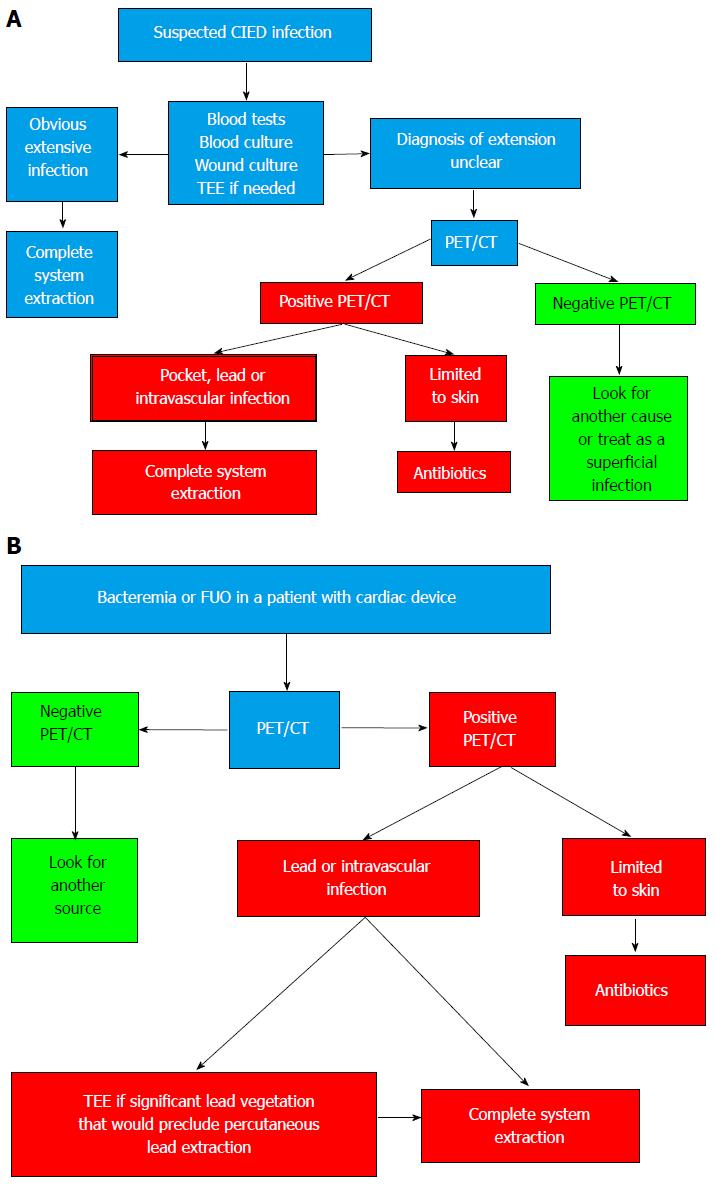
Figure 2 Proposed algorithms incorporating 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the evaluation and management of patients with possible device infection.
A: Initial CIED infection suspicion; B: Patients with cardiac device and bacteremia or fever of unknown origin (FUO) (Reprinted from Sarrazin JF, Philippon F, Tessier M, Guimond J, Molin F, Champagne J, Nault I, Blier L, Nadeau M, Charbonneau L, Trottier M, O’Hara G. Usefulness of fluorine-18 positron emission tomography/computed tomography for identification of cardiovascular implantable electronic device infections. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012; 59: 1616-1625, with permission from Elsevier). CIED: Cardiovascular implantable electronic device; PET/CT: Positron emission tomography/computed tomography; TEE: Transesophageal echocardiography.
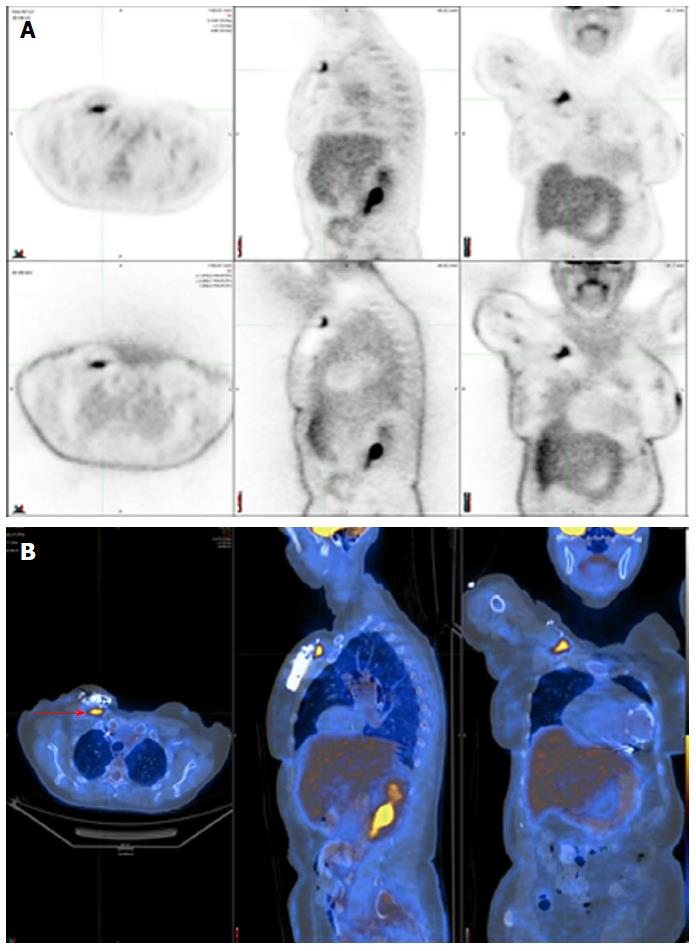
Figure 3 Positive 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in a patient with a deep pocket infection shown by focal 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake just underneath the generator (red arrow).
A: SPECT displayed as transverse, sagittal, and coronal attenuation corrected (top row) and uncorrected images (bottom row); B: Hybrid SPECT/CT displayed as transverse, sagittal, and coronal images. SPECT/CT: Single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography.
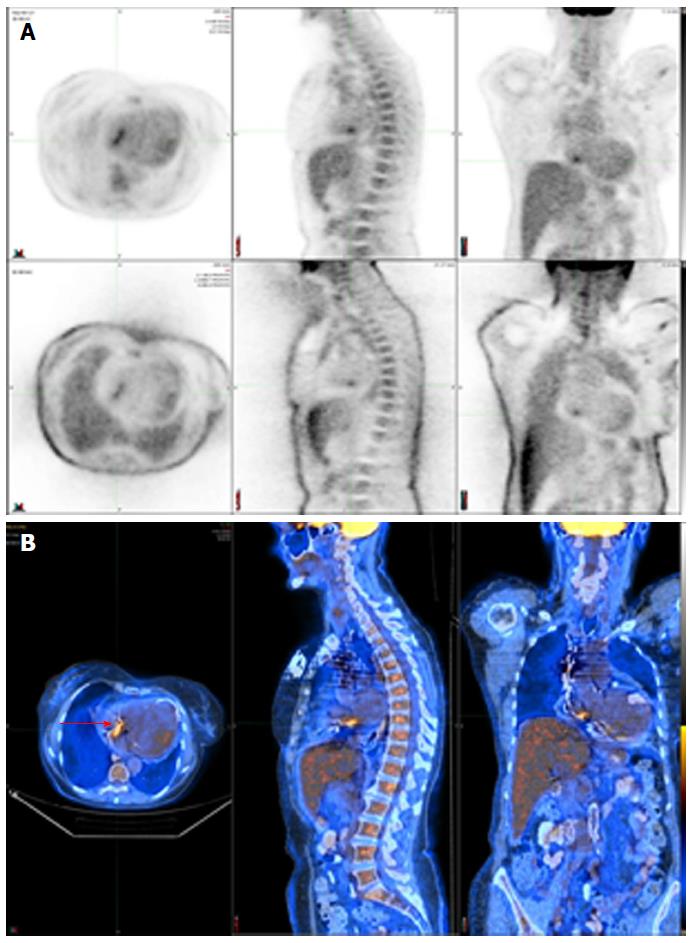
Figure 4 Positive 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in a patient with a lead infection (red arrow).
A: SPECT displayed as transverse, sagittal, and coronal attenuation corrected (top row) and uncorrected images (bottom row); B: Hybrid SPECT/CT displayed as transverse, sagittal, and coronal images. SPECT/CT: Single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography.
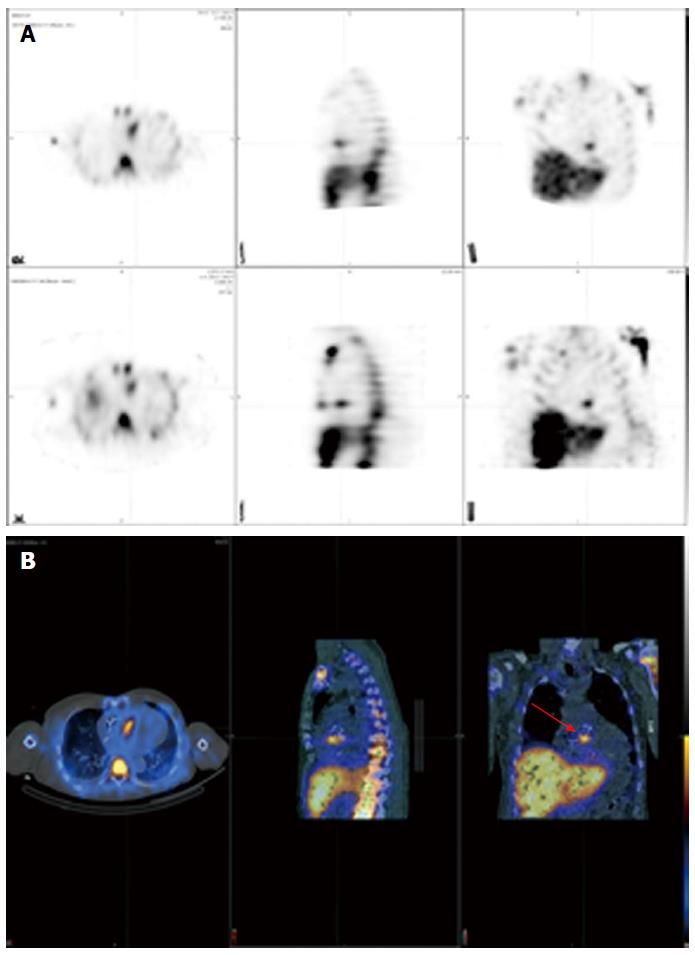
Figure 5 Positive 111In white blood cell single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography in a patient with endocarditis following an aortic valve replacement (red arrow).
A: SPECT displayed as transverse, sagittal, and coronal attenuation corrected (top row) and uncorrected images (bottom row); B: Hybrid SPECT/CT displayed as transverse, sagittal, and coronal images. SPECT/CT: Single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography.
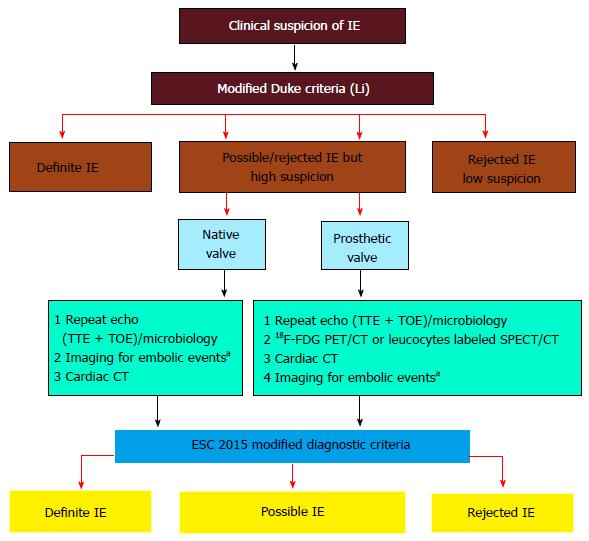
Figure 6 European Society of Cardiology 2015 algorithm for diagnosis of infective endocarditis.
Reprinted from Habib G, Lancelloti P, Antunes MJ, Bongiorni MG, Casalta JP, Del Zotti F, Dulgheru R, El Khoury G, Erba PA, Iung B, Miro JM, Mulder BJ, Plonska-Gosciniak E, Price S, Roos-Hesselink J, Snygg-Martin U, Thuny F, Tornos Mas P, Vilacosta I, Zamorano JL; Document Reviewers, Erol Ç, Nihoyannopoulos P, Aboyans V, Agewall S, Athanassopoulos G, Aytekin S, Benzer W, Bueno H, Broekhuizen L, Carerj S, Cosyns B, De Backer J, De Bonis M, Dimopoulos K, Donal E, Drexel H, Flachskampf FA, Hall R, Halvorsen S, Hoen B, Kirchhof P, Lainscak M, Leite-Moreira AF, Lip GY, Mestres CA, Piepoli MF, Punjabi PP, Rapezzi C, Rosenhek R, Siebens K, Tamargo J, Walker DM. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: The Task Force for the Management of Infective Endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, the European Association of Nuclear Medicine. Eur Heart J 2015; 36: 3075-3128. Reprinted by permission of Oxford University Press (UK)© European Society of Cardiology, http://www.escardio.org/. This image/content is not covered by the terms of the Creative Commons license of this publication. For permission to reuse, please contact the rights holder). aMay include cerebral MRI, whole body CT, and/or PET/CT; CT: Computed tomography; FDG: Fluorodeoxyglucose IE: Infective endocarditis; PET: Positron emission tomography; SPECT: Single-photon emission computed tomography; TTE: Transthoracic echocardiography; 18F-FDG PET/CT: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography.
- Citation: Sarrazin JF, Philippon F, Trottier M, Tessier M. Role of radionuclide imaging for diagnosis of device and prosthetic valve infections. World J Cardiol 2016; 8(9): 534-546
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v8/i9/534.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v8.i9.534