Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Biol Chem. Feb 26, 2016; 7(1): 188-205
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.188
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.188
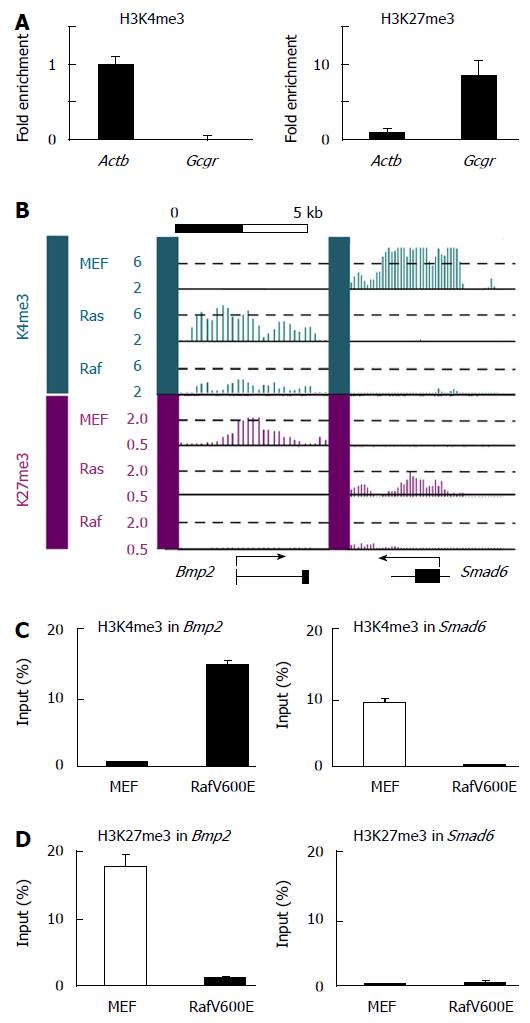
Figure 8 Epigenetic alteration of the Bmp2 and Smad6 locus in Raf-induced senescence.
A: Real-time ChIP-PCR for H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in RafV600E cells on day 7. Relative enrichment compared with Actb was shown, and it was confirmed that ChIP was performed properly. Actb was positive control region for H3K4me3 and Gcgr was positive control for H3K27me3; B: H3K4me3 and HK27me3 mapped by ChIP-sequencing. Y-axis, the number of mapped reads per 1000000 reads, within a window (300bp for H3K4me3 and 500bp for H3K27me3). The Bmp2 locus showed H3K27me3 mark, but no H3K4me3 mark, in MEF cells. Loss of H3K27me3 and gain of H3K4me3 were detected commonly in Ras- and Raf-induced senescence. The Smad6 locus showed H3K4me3 mark, but no H3K27me3 mark, in MEF cells. Loss of H3K4me3 was detected commonly in Ras- and Raf-induced senescence, but gain of H3K27me3 was detected specifically in Ras-induced senescence; C: Validation of the epigenetic status of the Bmp2 locus by ChIP-PCR. Loss of H3K27me3 and gain of H3K4me3 in RafV600E cells were confirmed. We repeated ChIP assay twice, and obtained the similar results by ChIP-PCR using those ChIP products; D: Validation of the epigenetic status of the Smad6 locus by ChIP-PCR. Loss of H3K4me3 and no gain of H3K27me3 in RafV600E cells were confirmed. We repeated ChIP assay twice, and obtained the similar results by ChIP-PCR using those ChIP products. MEF: Mouse embryonic fibroblast.
- Citation: Fujimoto M, Mano Y, Anai M, Yamamoto S, Fukuyo M, Aburatani H, Kaneda A. Epigenetic alteration to activate Bmp2-Smad signaling in Raf-induced senescence. World J Biol Chem 2016; 7(1): 188-205
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v7/i1/188.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.188