Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 26, 2015; 6(4): 310-323
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.310
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.310
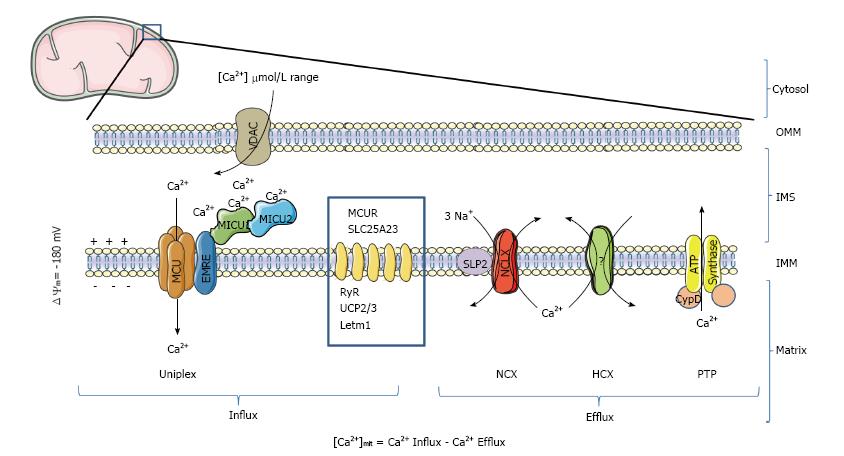
Figure 1 Ca2+ transport proteins of mitochondria.
In mammalian mitochondria, the uptake of Ca2+ is mediated by the Ca2+-selective channel MCU, which is part of a high molecular weight protein complex called Uniplex. At least 4 additional proteins (MCUb, MICU1, MICU2 and EMRE) regulate MCU activity. Ca2+ is then extruded by a sodium/calcium exchange (NCX) or proton/calcium exchange (HCX). If the protein NCLX has been confirmed to be the mitochondrial NCX, which is down-regulated by the protein SLP-2, the molecular nature of the mitochondrial HCX is still debated. Dimers of mitochondrial ATP synthase have been proposed to form the PTP, a mitochondrial channel regulated by CypD, that facilitates PTP opening by desensitizing PTP to Ca2+. Besides being activated by Ca2+, PTP has also been proposed to act as a reversible fast Ca2+ release channel. Other non-MCU mitochondrial proteins with an indirect or debated effect on Ca2+ transport are represented in the blue square (MCUR; SLC25A23; ryanodine receptor, RyR; UCP2; UCP3; LETM1). OMM: Outer mitochondrial membrane; IMS: Inter-membrane space; IMM: Inner mitochondrial membrane; VDAC: Mitochondrial porin; PTP: Permeability transition pore; CypD: Cyclophilin D; MCU: Mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter; MCUR1: Mitochondrial calcium uniporter regulator 1; MICU1: Mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake protein 1; MICU2: Mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake protein 2; EMRE: Essential MCU regulator.
- Citation: Santo-Domingo J, Wiederkehr A, De Marchi U. Modulation of the matrix redox signaling by mitochondrial Ca2+. World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(4): 310-323
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i4/310.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.310