Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Jun 26, 2011; 2(6): 119-125
Published online Jun 26, 2011. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v2.i6.119
Published online Jun 26, 2011. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v2.i6.119
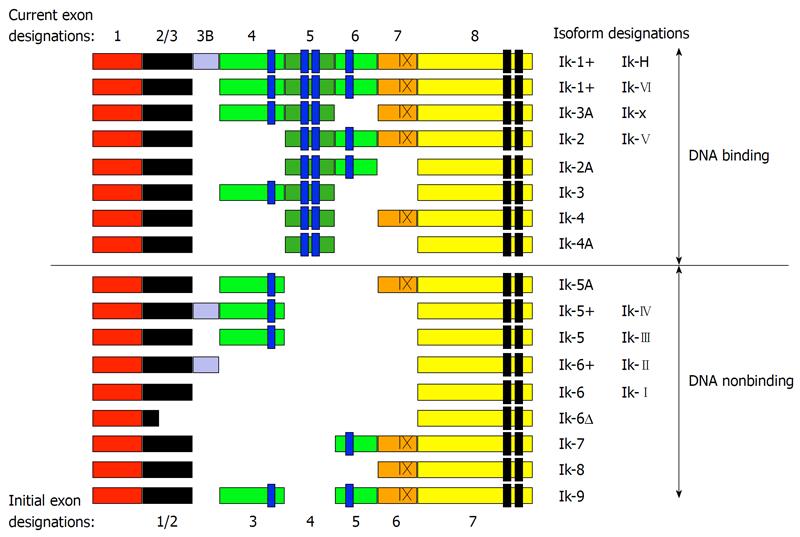
Figure 1 Ikaros isoforms.
The Ikaros gene in mice (Ikzf1) and humans (IKZF1) includes eight coding exons (exons 2-8 and 3B) and one upstream exon that is not translated (Figure 1). The untranslated exon (shown in red) has not been identified in initial reports, and the alternate exon designations that have appeared in early reports are shown at the bottom of the figure. Exon 3B is currently not identified as an exon in Genbank. Splice forms that include exon 3B have been designated as “plus” forms and many such splice forms, in addition to the ones shown, have been identified at the protein and/or mRNA level (i.e. Ik-x+, Ik-2+, Ik-4+, Ik-7+, Ik-8+) in humans and mice. An alternate splice site gives rise to splice forms that lack the last 30 bases of exon 7 (indicated with an X). Such splice variants have been designated minus forms (e.g. Ik-1- and Ik-x-). The four N-terminal zinc fingers (shown in blue) contribute to DNA binding and the two C-terminal zinc fingers (shown in black) are responsible for dimerization[1,2,19,47-53].
- Citation: Francis OL, Payne JL, Su RJ, Payne KJ. Regulator of myeloid differentiation and function: The secret life of Ikaros. World J Biol Chem 2011; 2(6): 119-125
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v2/i6/119.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v2.i6.119