Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2011; 2(5): 73-89
Published online May 26, 2011. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v2.i5.73
Published online May 26, 2011. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v2.i5.73
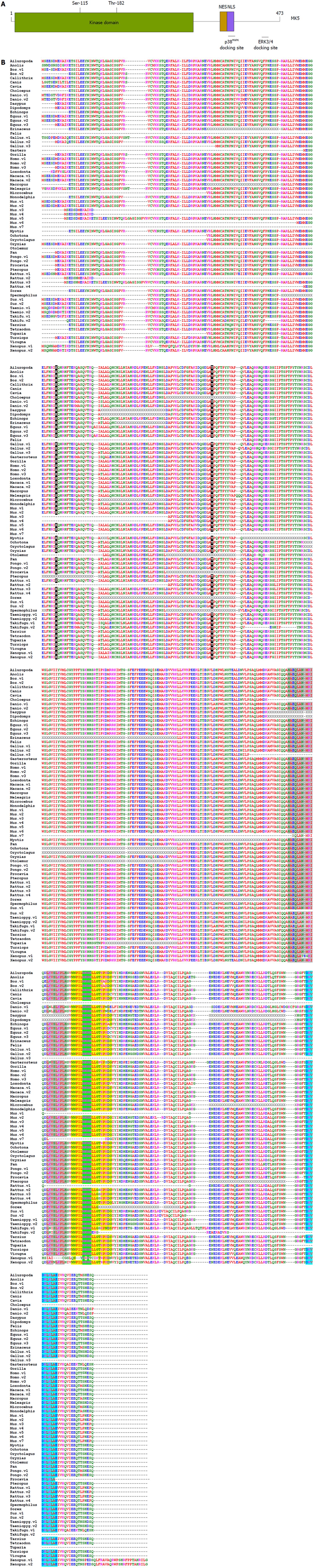
Figure 2 Structure of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 5.
A: Functional domains of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 5 (MK5); B: Primary sequence of annotated and proven MK5. The p38MAPK docking motif is in yellow, the nuclear localization signal (NLS) is shaded in green, the protein kinase A inhibitor (PKI)-like and REV-like nuclear export signal (NES) motifs are depicted in green, and the extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK)3/4 interaction domain is shaded in light blue. Notice that the NLS and p38MAPK docking site are overlapping. Threonine residue 182 in the activation loop and the protein kinase A phosphoacceptor site Ser-115 are highlighted in black. The one-letter amino acid code is used. Red represents small and hydrophobic amino acids (A, V, F, P, M, I, L, W), blue symbolizes acidic amino acids (D, E), magenta corresponds to basic amino acids (R, K), while green stands for hydroxyl, amine and basic amino acids (S, T, Y, C, N, G, Q, H). Non-annotated residues are indicated by X, while gaps are shown by dashed lines. The abbreviation v after the name of the organism refers to different isoforms. Clustal series of programs was used for multiple sequence alignment[67].
- Citation: Kostenko S, Dumitriu G, Lægreid KJ, Moens U. Physiological roles of mitogen-activated-protein-kinase-activated p38-regulated/activated protein kinase. World J Biol Chem 2011; 2(5): 73-89
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v2/i5/73.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v2.i5.73