Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2014; 5(2): 115-129
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.115
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.115
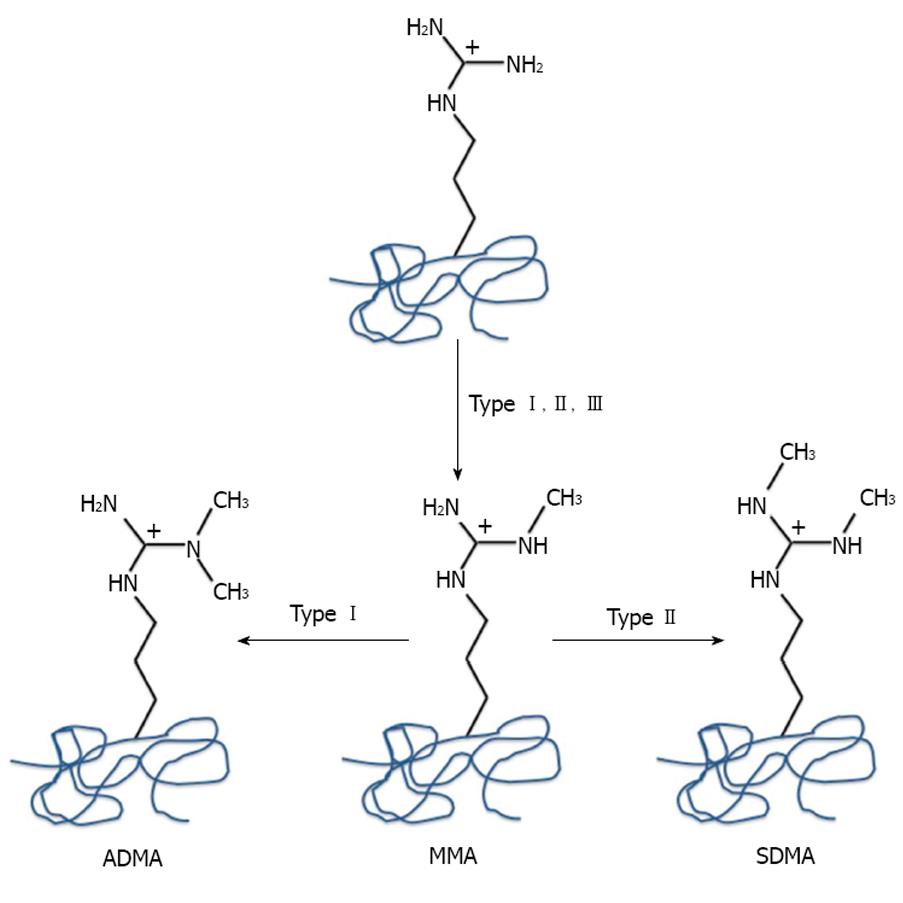
Figure 1 Arginine methylation reactions catalyzed by protein arginine methyltransferases.
Type I protein arginine methyltransferases catalyze the asymmetric dimethylation of arginine residues, Type II symmetrically dimethylated arginine and Type III monomethylated arginine residues.
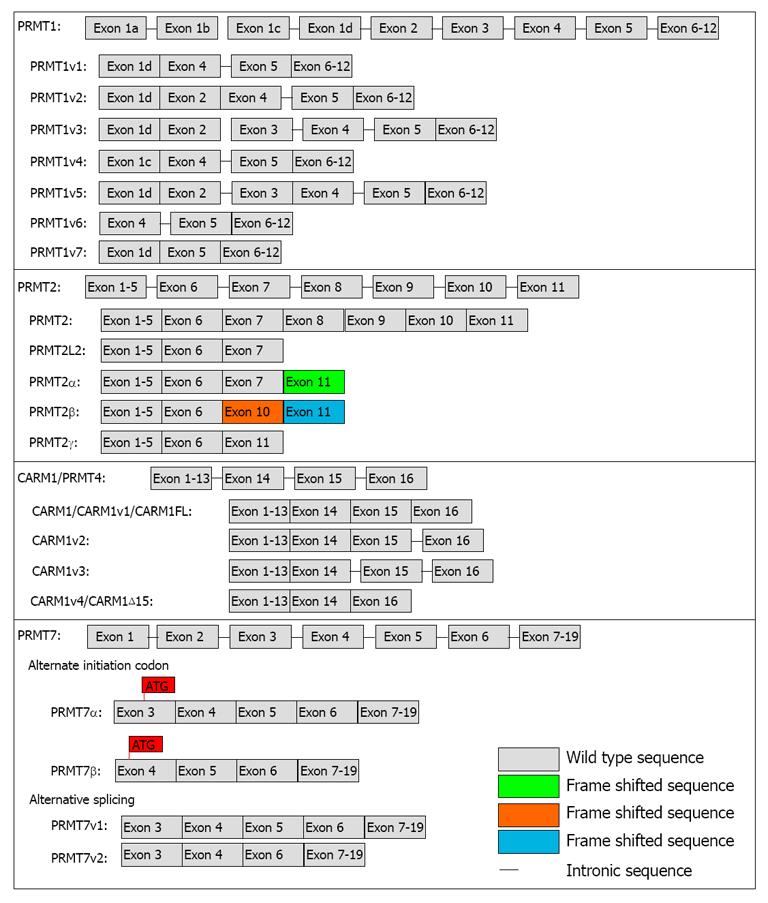
Figure 2 Protein arginine methyltransferase variant isoforms.
Schematic representation of the identified variant isoforms of protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) 1, PRMT2, CARM1/PRMT4 and PRMT7. The PRMT1 sequence has 12 exons. Exon organization of the seven identified PRMT1 isoforms are shown. The intronic sequences (-) that have been shown to be included in several of these alternative PRMT1 isoform transcripts are due to the splicing sites[21]. PRMT2 is made up of 11 exons. The PRMT2L2 transcript is produced as a result of alternative polyadenylation[72]. This silences the 5’ splice site on exon 7 and results in a transcript retains a significant portion of intron 7 and a premature termination codon. PRMT2α has a deletion of exons 8-10 with a frame shift that produces 12 new amino acids at the C-terminus (ν). The PRMT2β isoform has a deletion of exons 7, 8, 9 resulting in a frame shift that generates 83 alternate amino acids at the C-terminus (νν). PRMT2γ has an in frame deletion of exons 7 to 10. The full-length CARM1 gene, CARM1/CARM1v1/CARM1FL, consists of 16 exons. CARM1v2 is generated through retention of the intron 15 sequence; CARM1v3 is produced through the retention of introns 15 (-) and 16 (-). CARM1v4/CARM1Δ15 results from the skipping of exon 15[23,24]. The PRMT7 sequence consists of 19 exons. In Hamster cells, these two PRMT7 isoforms (α and β) are thought to be generated by the use of distinct 5’ translation initiation codons within the primary transcript. The PRMT7β isoform sequence contains 37 extra amino acids at the N-terminus. Alternatively, at least 2 alternatively spliced PRMT7 isoforms can be produced from the human PRMT7 gene. These two isoforms have the same N- and C-terminal regions but variant 2 (PRMT7v2) has an in frame deletion of exon 5.
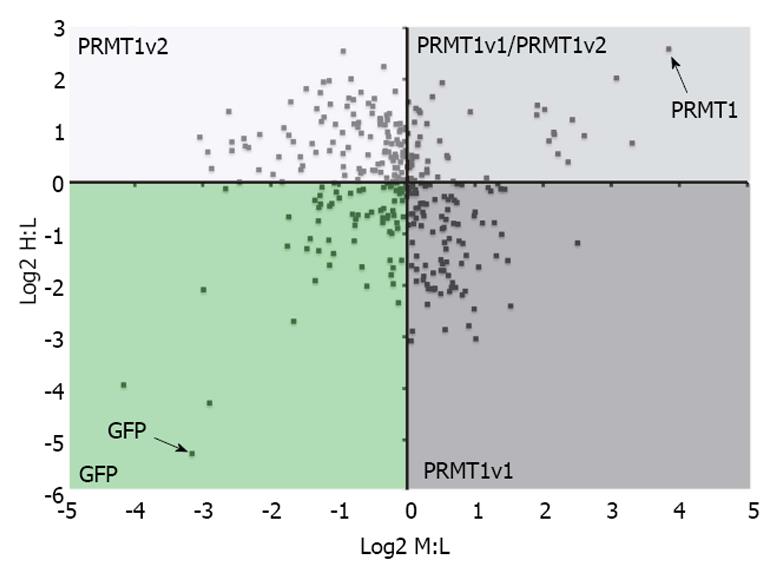
Figure 3 Protein arginine methyltransferase 1v1 and protein arginine methyltransferase 1v2 have potentially different interacting protein profiles.
Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) and mass spectrometry was used to identify protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) 1v1 protein binding partners and PRMT1v2 protein binding partners. Cells stably expressing GFP alone, GFP-tagged PRMT1v1 or GFP-tagged PRMT1v2 were grown independently in media containing light (L), medium (M) and heavy (H) isotopes of arginine and lysine residues, respectively. Protein lysates were collected, immunoprecipitated for GFP (isolation of PRMT1v1 and PRMT1v2 interacting protein), and subjected to mass spectrometry for peptide identification. The Log2 of the SILAC ratios for the peptides identified from this experiment are plotted on the scatter plot. The x-axis is the Log2 of the H:L SILAC ratio or PRMT1v2 interacting proteins. The y-axis is the Log2 of the M:L SILAC ratio or PRMT1v1 interacting proteins. Each data point represents a single protein that was identified in this experiment. The greater this ratio is for a protein, the higher the probability of the interaction being real. This revealed a protein interacting profile identifying PRMT1v1-specific interacting proteins (PRMT1v1 quadrant), PRMT1v2-specific interacting proteins (PRMT1v2 quadrant) and common interacting proteins (PRMT1v1/PRMT1v2 quadrant; unpublished data). These results require further validation.
- Citation: Baldwin RM, Morettin A, Côté J. Role of PRMTs in cancer: Could minor isoforms be leaving a mark? World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(2): 115-129
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i2/115.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.115