Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Jul 26, 2012; 3(7): 159-166
Published online Jul 26, 2012. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v3.i7.159
Published online Jul 26, 2012. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v3.i7.159
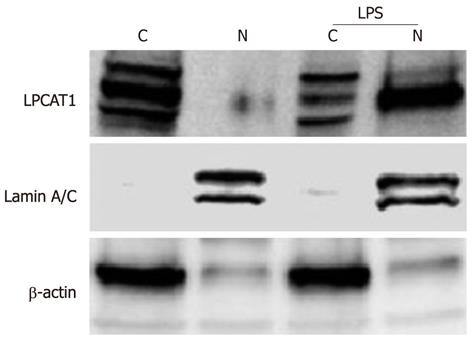
Figure 1 Lpcat1 shifts into the nucleus in lipopolysaccharide treated lung epithelia.
MLE cells were treated with 10 μg/mL of LPS for 2 h. The harvested cells were processed for cytosolic and nuclear protein fractionation and the fractions were subjected to immunoblotting with different antibodies as indicated. “C” donates to cytosolic fraction and “N” represents the nuclear fraction. Lamin A/C is used as a nuclear fraction protein marker and β-actin is the cytosolic fraction protein marker. The results represent three independent experiments. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
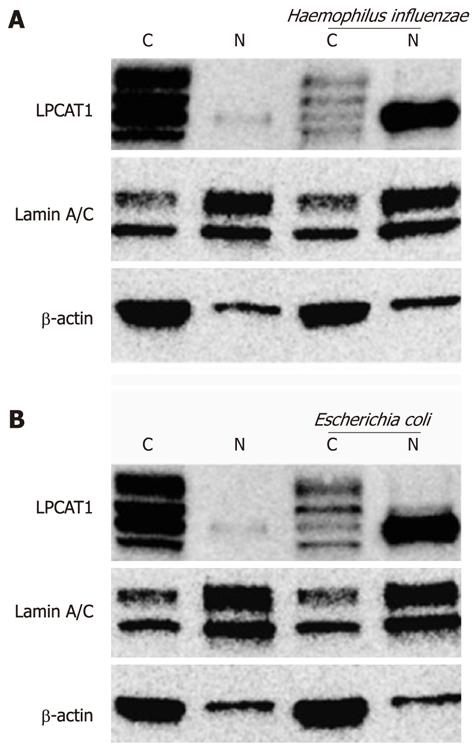
Figure 2 Haemophilus influenzae and Escherichia coli trigger Lpcat1 nuclear translocation.
MLE cells were exposed to LPS-containing bacteria at a concentration of 109/mL for 4 h. The infected cells were then washed and cytosolic and nuclear protein fractionations were prepared. Immunoblotting analysis was performed using antibodies as indicated. The results represent three independent experiments. “C” donates to cytosolic fraction and “N” represents the nuclear fraction. Lamin A/C is used as a nuclear fraction protein marker and β-actin is the cytosolic fraction protein marker. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
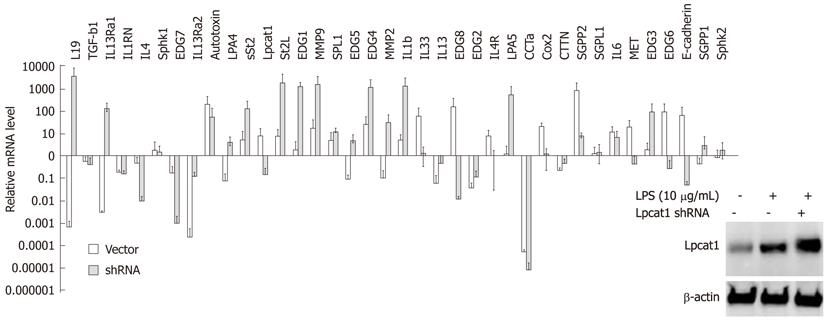
Figure 3 Lipopolysaccharide inducible gene expression profiles after Lpcat1 knockdown.
Protein levels were determined with Lpcat1 immunoblotting in wild type, LPS treated wild type, and LPS treated Lpcat1 knockdown MLE cells as showed in the imbedded image. Total cellular RNA was extracted from cells and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis was performed. The relative mRNA levels of the genes in LPS treated samples were normalized by the same gene from untreated MLE cells. The data represents the mean value (mean + SEM) from three independent experiments. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
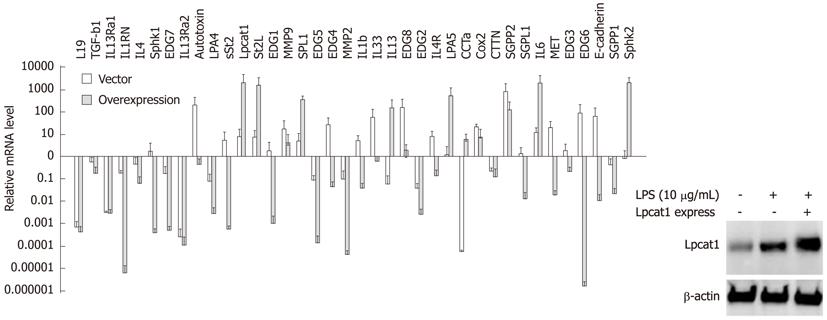
Figure 4 Overexpressed Lpcat1 suppresses lipopolysaccharide inducible gene expression.
Lpcat1 protein levels were determined by immunoblotting in wild type, LPS treated wild type, and LPS treated Lpcat1 overexpressed MLE cells as in the imbedded image. Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis was performed by using total cellular RNA extracted from wild type, LPS treated wild type, and LPS treated Lpcat1 overexpressed cells. The relative mRNA levels of the genes in LPS treated samples were normalized by the same gene from untreated MLE cells. The data represents the mean value (mean + SEM) from three independent experiments. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
- Citation: Ellis B, Kaercher L, Snavely C, Zhao Y, Zou C. Lipopolysaccharide triggers nuclear import of Lpcat1 to regulate inducible gene expression in lung epithelia. World J Biol Chem 2012; 3(7): 159-166
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v3/i7/159.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v3.i7.159