Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jun 27, 2025; 17(6): 107351
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i6.107351
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i6.107351
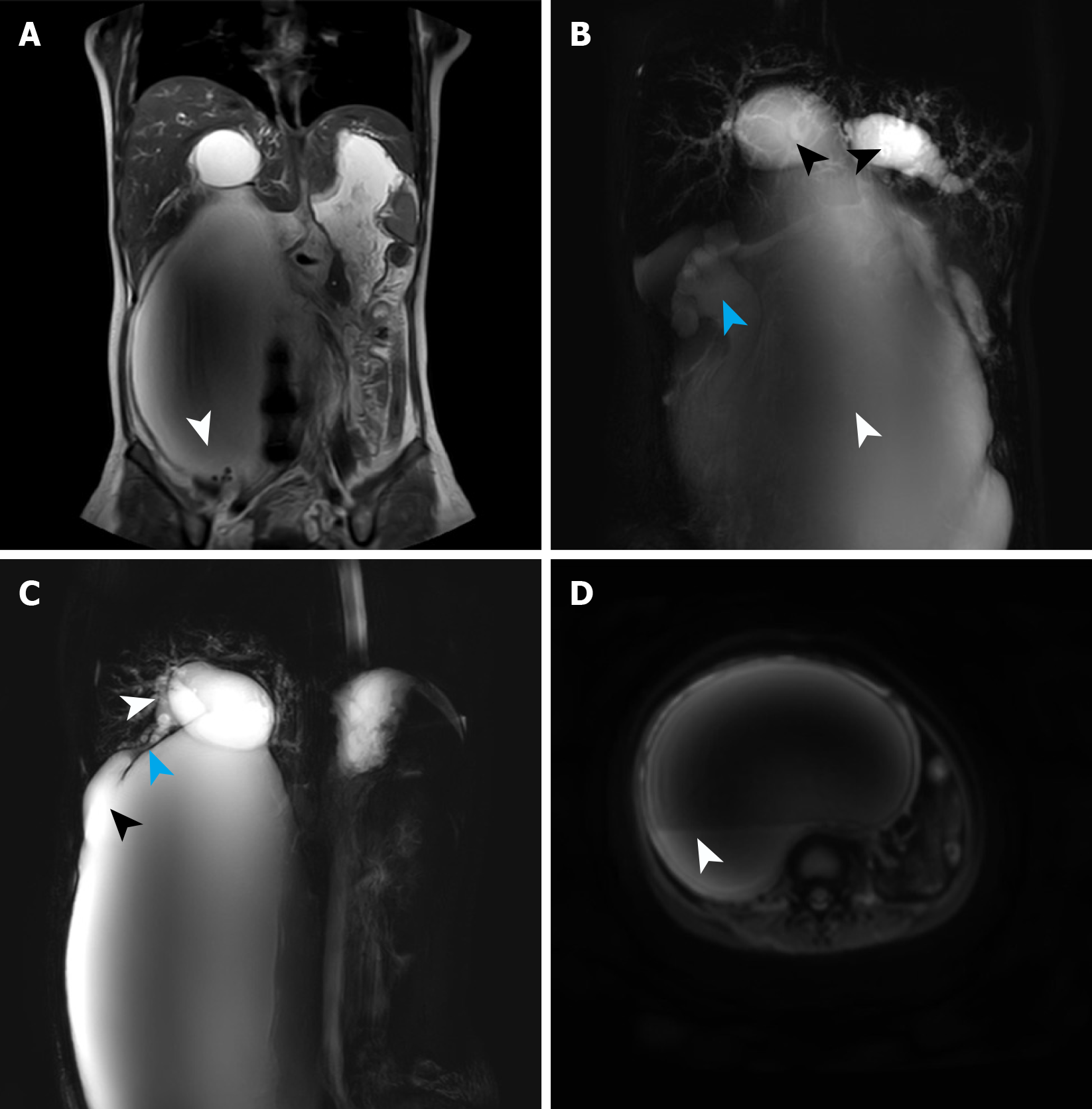
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography findings at first admission.
A: A round filling defect was detected at the base of the dilated bile duct, suggesting the presence of a stone (white arrow); B: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography revealed cystic dilation of the intrahepatic bile ducts (black arrow), accompanied with extreme dilation of the common hepatic duct and common bile duct (white arrows), presenting as a large cystic expansion. Hydronephrosis was also visualized (blue arrow); C: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography demonstrated gallbladder atrophy (white arrow), narrowing of the cystic duct (blue arrow), and dilatation at the junction of the cystic duct and common hepatic duct (black arrow); D: Diffusion-weighted imaging identified a layered appearance within the cyst, with the lower layer suggesting bile sludge deposition based on its location and shape (white arrow).
- Citation: Wang DD, Du YY, Li YZ, Wang W, Ma TL, Xu XC, Mi C, Wang SY, Cui F, She YH, Wang MC, Yang HT. Treatment of giant choledochal cysts with combined surgery and percutaneous transhepatic cholangial drainage: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(6): 107351
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i6/107351.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i6.107351