Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Diabetes. Nov 15, 2016; 7(19): 483-514
Published online Nov 15, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i19.483
Published online Nov 15, 2016. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v7.i19.483
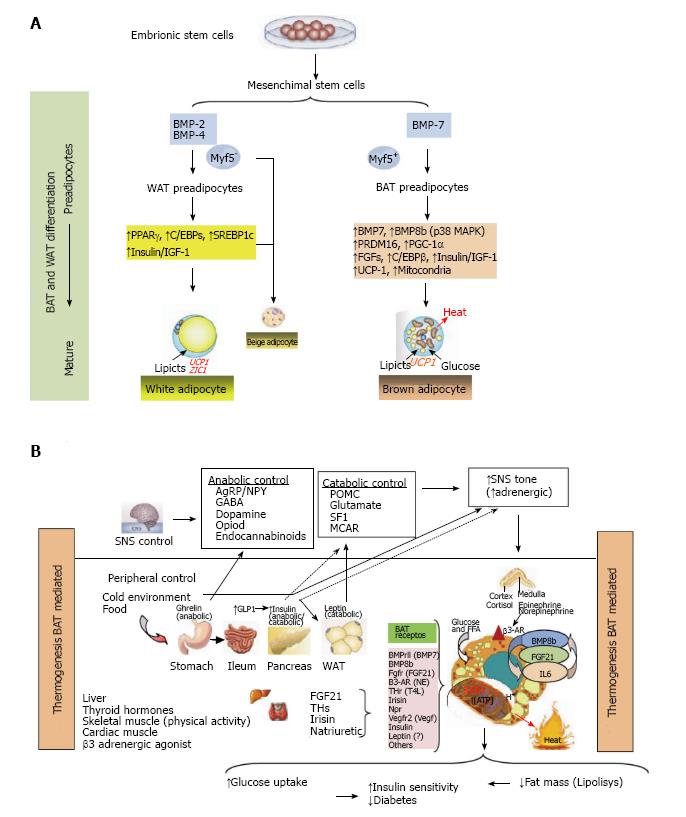
Figure 1 Thermogenesis brown adipose tissue (Bat) mediated.
A: Adipocytes were developed because non adipocytes cells are unable to store calories as fat to meet fuel needs during long periods without eating. If the energy intake is more than energy expenditure, WAT is expanded and leads to obesity. However, a second type of adipose tissue, called BAT was developed especially for energy expenditure (thermogenesis). Today, research in identifying the main genes that control differentiation, development and activation of BAT is highly active, because, activation of BAT, in detriment of WAT, could have anti-obesity effects, which can be utilized to keep the system of fat deposit balanced. In this research, PRDM16, PPAR-γ and PGC-1α, have been identified as the key nodes in the regulation of inducible BAT; B: The thermogenic potential of BAT is controlled by the SNS, which densely innervates brown fat depots. In addition, BAT is activated in response to cold temperatures, hormones and possibly diet. BAT content and activation is highest in children and decreases with age. BAT activation is decreased in fatness, and BAT activity has been inversely correlated to BMI, body fat, and visceral obesity. In humans, BAT amount and activation is higher in women than in men. Of clinical relevance, BAT activation is very low in diabetic patients in comparison with non-diabetic subjects. Thyroid hormones play a main role in control of BAT activation, therefore the cold-induced enhancement of the enzyme 5’-deiodinase type II activity, which deiodinates thyroxine (T4) to T3. Catecholamines such as norepinephrine binds to β-ARs and induce PGC1α through p38 MAPK and finally triggers expression of UCP1. Whereas β1-AR is considered important for proliferation of classical brown adipocyte precursors in response to norepinephrine, β3-AR plays a major role in thermogenic function of mature brown adipocytes. Another signal, Irisin hormone which comes from muscle to fat tissue, is able to induce a robust browning programme, and mediates the beneficial effects of exercise and could reduce diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. A more generalized program in the control of adipose tissue is conducted by FGF21 through regulating lipolysis in WAT as well as increasing substrate utilization by increasing fatty acid oxidation in the liver. Last, beige fat cell functions include either a like to “WAT” when energy balance is exceeded, or a like to “BAT” in response to many stimuli similar to BAT activation. WAT: White adipose tissue; BAT: Brown adipose tissue; PRDM16: PR domain containing 16; PPAR-γ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α; SNS: Sympathetic nervous system; BMI: Body mass index; FGF21: Fibroblast growth factor 21.
- Citation: Paniagua JA. Nutrition, insulin resistance and dysfunctional adipose tissue determine the different components of metabolic syndrome. World J Diabetes 2016; 7(19): 483-514
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v7/i19/483.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i19.483