Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2025; 16(8): 107779
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i8.107779
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i8.107779
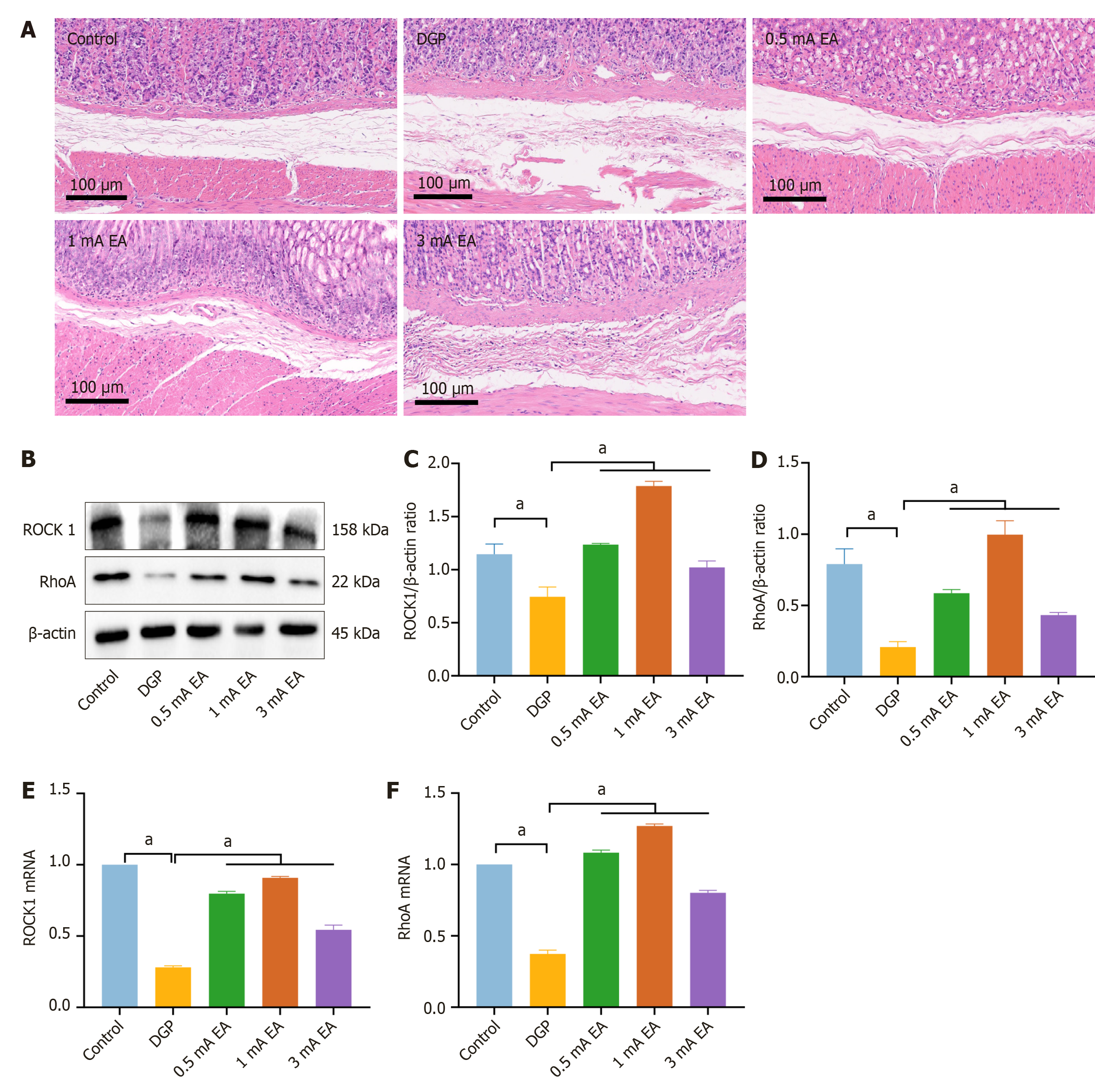
Figure 7 Electroacupuncture with different current intensities improves gastric smooth muscle dysfunction in rats with diabetic gastroparesis.
A: Hematoxylin-eosin staining (scale bar = 100 μm, n = 6); B-D: Western blotting and quantification of Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase 1 and Rho guanine nucleotide-binding protein A levels in gastric tissue; E and F: The mRNA levels of Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase 1 and Rho guanine nucleotide-binding protein A. aP < 0.05. DGP: Diabetic gastroparesis; EA: Electroacupuncture; ROCK: Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase; RhoA: Rho guanine nucleotide-binding protein A.
- Citation: Tang YW, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Peng YT, Zi Y, Wei YR, Yue ZH. Electroacupuncture with different current intensities can improve gastrointestinal motility in diabetic gastroparesis via vagal and sympathetic pathways. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(8): 107779
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i8/107779.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i8.107779