Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2025; 16(6): 105173
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.105173
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.105173
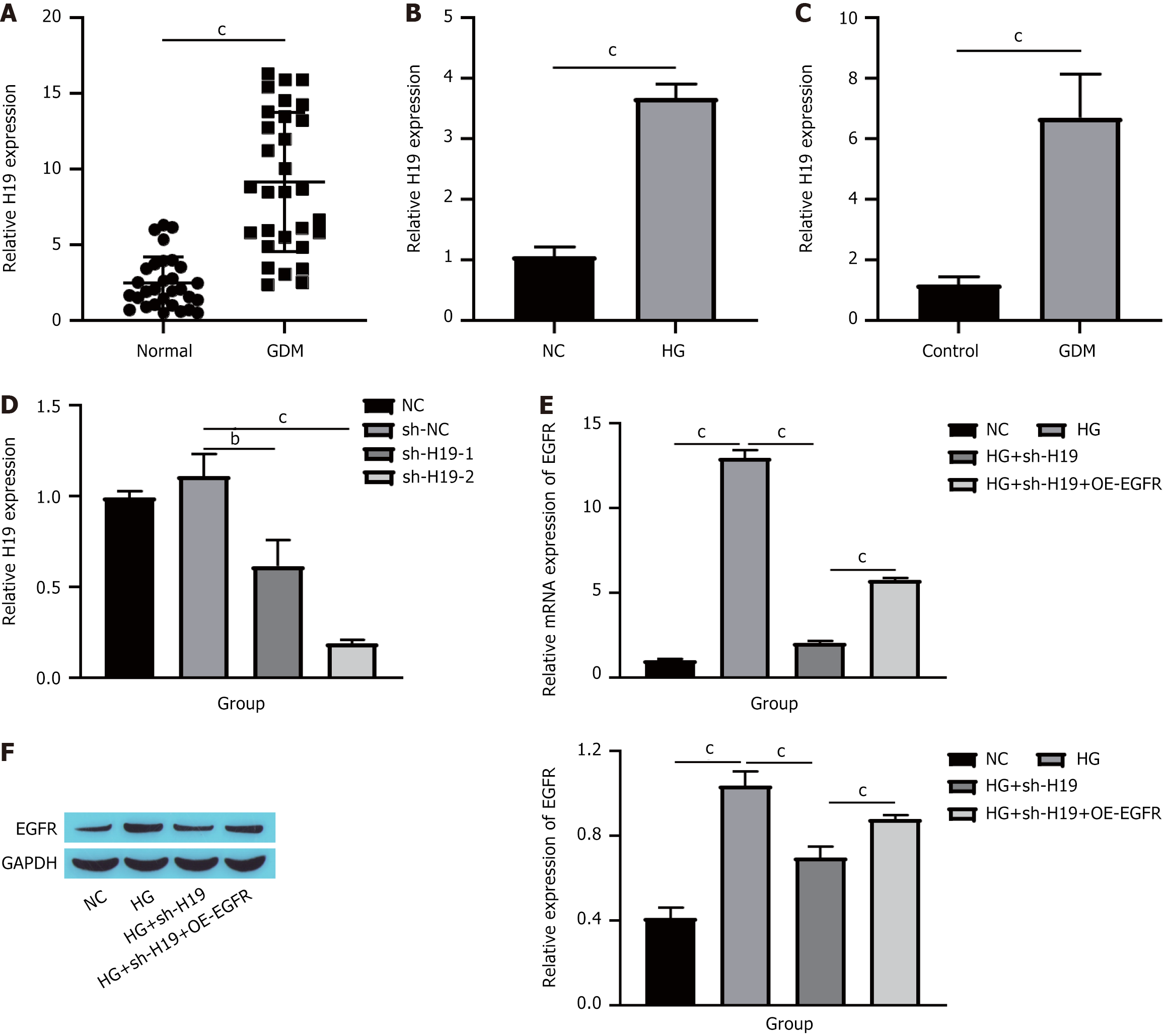
Figure 3 Epidermal growth factor receptor expression is regulated by long noncoding RNAs H19.
A: H19 expression in human placental tissue detected via quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR); B: H19 expression in cells detected via RT-qPCR; C: H19 expression in mouse placental tissue detected via RT-qPCR; D: H19 expression in cells detected via RT-qPCR; E: EGFR messenger RNA expression in cells detected via RT-qPCR; F: EGFR protein expression in cells detected via Western blotting. bP < 0.01. cP < 0.001. GDM: Gestational diabetes mellitus; NC: Normal control; HG: High glucose; sh-NC: Short hairpin-negative control; sh-H19: Short hairpin RNA targeting H19; OE-EGFR: Overexpression epidermal growth factor receptor; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Tang D, Wang CF, Wang J, Jing XT, Ma J. Mechanism of the epidermal growth factor receptor in promoting endothelial cell dysfunction in gestational diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(6): 105173
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i6/105173.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.105173