Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2025; 16(6): 103616
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.103616
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.103616
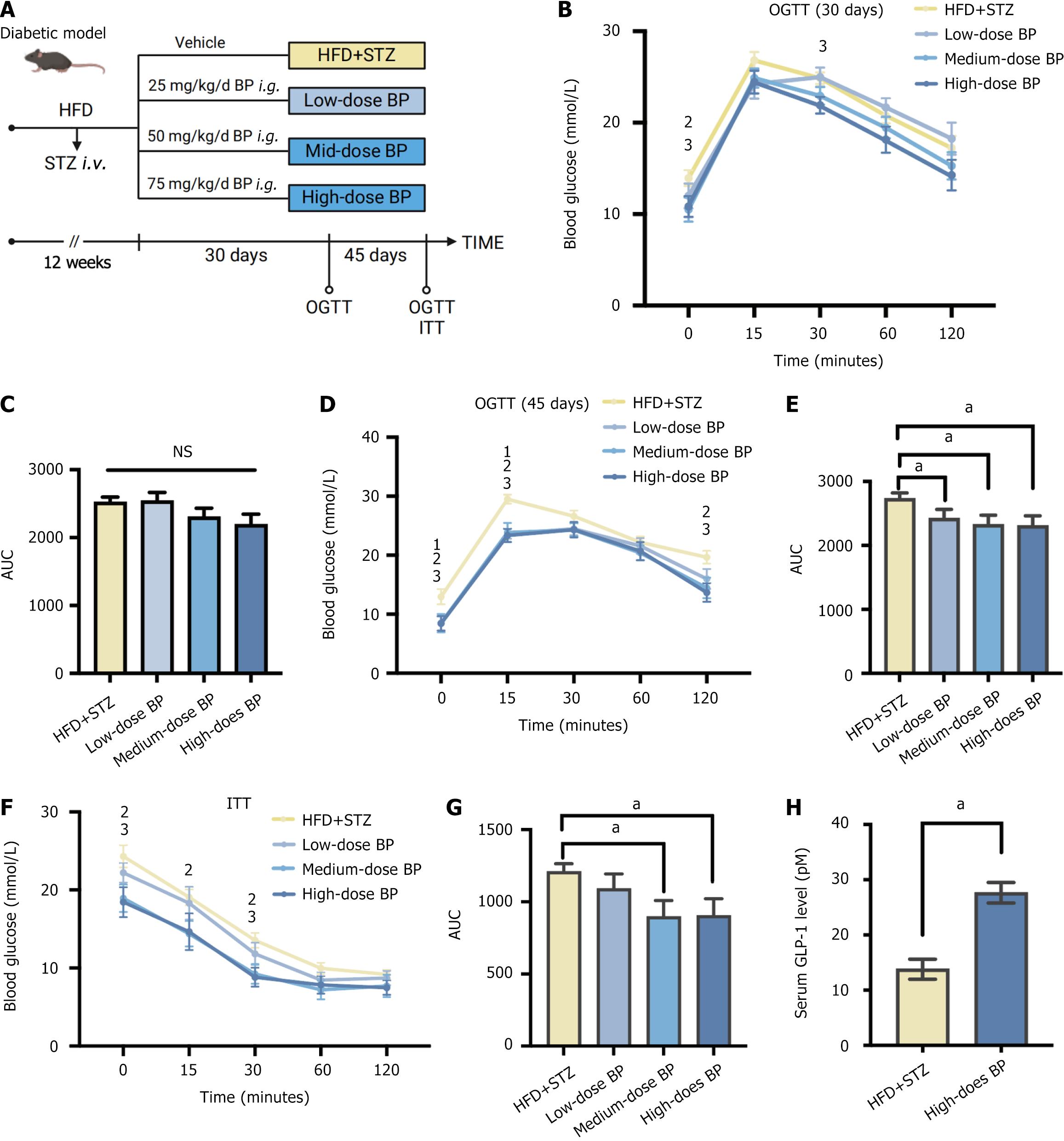
Figure 1 Bile powder improved blood glucose in a diabetic mouse model.
A: Schematic diagram. Mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for 6 weeks and were injected with streptozotocin (STZ) (50 mg/kg, intravenous) to induce blood glucose disorder. Mice continued a HFD for an additional 6 weeks. The mice were randomly divided into four groups (n = 5 per group) and treated with different doses of bile powder (BP): The HFD + STZ group (control group); The low-dose BP group (25 mg/kg/day, intragastric gavage); The medium-dose BP group (50 mg/kg/day, intragastric gavage); The high-dose BP group (75 mg/kg/day, intragastric gavage). The oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and insulin tolerance test (ITT) were performed after 30 days and 45 days of BP administration; B: OGTT after 30 days of BP treatment; C: Area under the curve (AUC) of the OGTT after 30 days of BP treatment; D: OGTT after 45 days of BP treatment; E: AUC of the OGTT after 45 days of BP treatment; F: ITT after 45 days of BP treatment; G: AUC of the ITT after 45 days of BP treatment; H: Serum glucagon-like peptide-1 levels in the HFD + STZ group and the high-dose BP group after 45 days of treatment. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. NS: Not significant (P > 0.05) compared between groups. Statistical analysis was performed using the Student’s t-test. aP < 0.05. 1High-fat diet + streptozotocin vs low-dose bile powder. 2High-fat diet + streptozotocin vs medium-dose bile powder. 3High-fat diet + streptozotocin vs high-dose bile powder. HFD: High-fat diet; STZ: Streptozotocin; BP: Bile powder; OGTT: Oral glucose tolerance test; ITT: Insulin tolerance test; AUC: Area under the curve; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1.
- Citation: Sun YM, Kuang JL, Zhang HH, Xia XX, Wang JY, Zheng D, Zhou KJ, Tang YJ, Zhao AH, Jia W, Xie GX, Zheng XJ. Pig bile powder maintains blood glucose homeostasis by promoting glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion via inhibiting farnesoid X receptor. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(6): 103616
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i6/103616.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.103616