Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2023; 14(12): 1824-1838
Published online Dec 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1824
Published online Dec 15, 2023. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1824
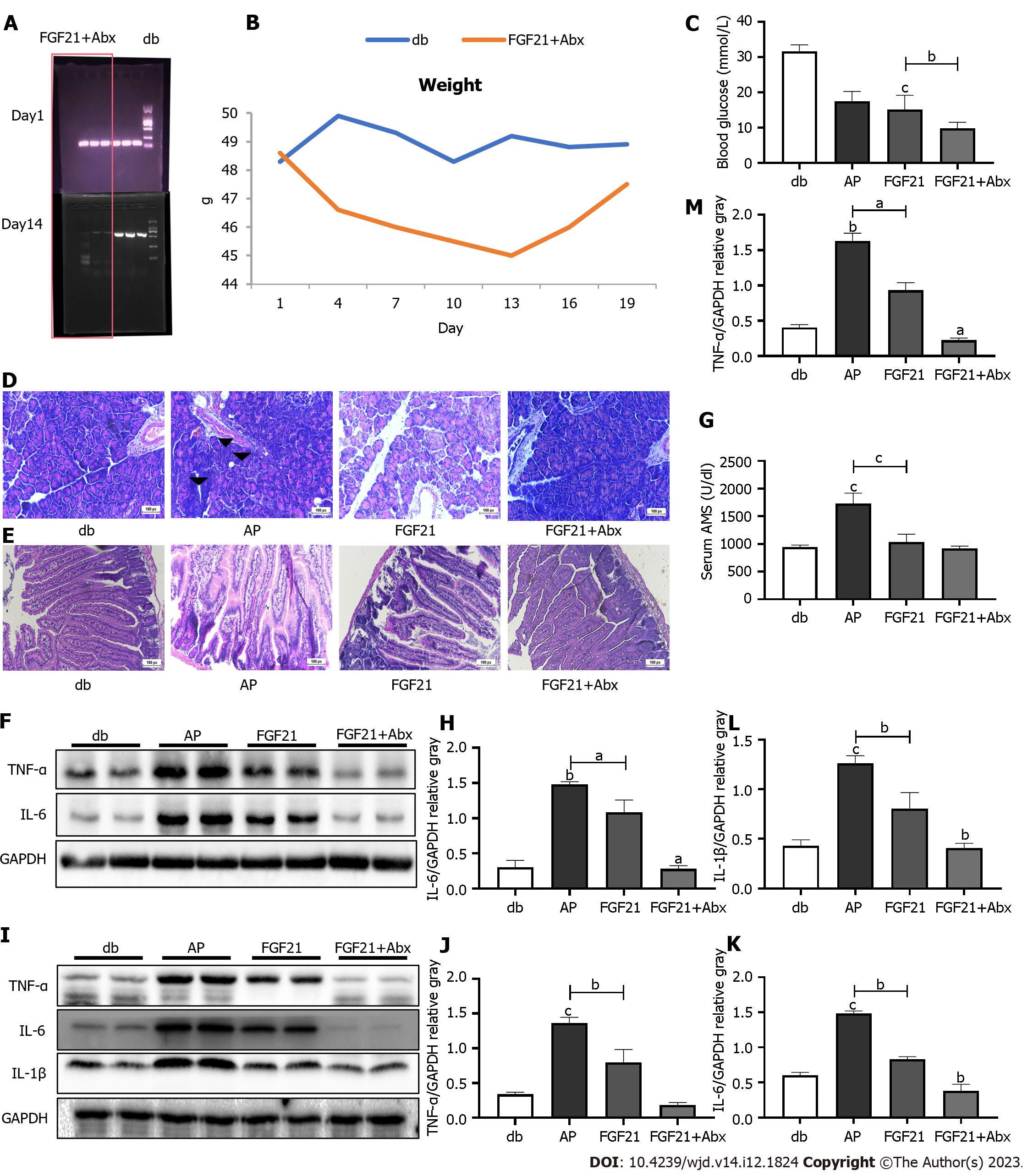
Figure 4 Combined therapy of Abx cocktail and fibroblast growth factor 21 significantly decreases the susceptibility to acute pancreatitis in diabetic mice.
A: Verification of the intestinal microbiota removal after feeding antibiotics; B: Following Abx cocktail treatment initiation, the body weight change of mice; C: Serum amylase levels of mice in each group; D: Pathological changes in pancreatic tissues of mice in each group, such as pancreatic edema, extensive intracellular vacuolation, and cellular necrosis (scale bar: 100 µm); E: Histological changes in the small intestine of mice in each group, characterized by tissue edema, increased villus width, and villus damage (scale bar: 100 µm); F-H: Representative immunoblots of inflammatory factors in mouse pancreatic tissue. Expression levels of interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha were quantified using densitometry, with GAPDH as a protein loading control; I-L: Representative immunoblots of inflammatory factors in mouse small intestinal tissue. Expression levels of IL-6, TNF- and IL-1 were quantified using densitometry, with GAPDH as a protein loading control. M: Changes in blood glucose in mice in different groups. Data are presented as mean ± SD, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. AP: Acute pancreatitis; db: Diabetic; IL: Interleukin; TNF-: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; FGF21: Fibroblast growth factor 21.
- Citation: Sun QY, Wang XY, Huang ZP, Song J, Zheng ED, Gong FH, Huang XW. Depletion of gut microbiota facilitates fibroblast growth factor 21-mediated protection against acute pancreatitis in diabetic mice. World J Diabetes 2023; 14(12): 1824-1838
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v14/i12/1824.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v14.i12.1824