Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Diabetes. Feb 15, 2024; 15(2): 186-195
Published online Feb 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.186
Published online Feb 15, 2024. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.186
Figure 1 Comparative of negative emotions.
A: Before treatment, Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAMA) scores of the two groups were compared; B: After treatment, HAMA scores of the two groups were compared; C: Before treatment, Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD) scores of the two groups were compared; D: After treatment, HAMD scores of the two groups were compared. aP < 0.05, the difference between groups with statistical significance. HAMA: Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale; HAMD: Hamilton Depression Rating Scale.
Figure 2 Comparative of blood glucose indicators.
A: Comparison of fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level before and after treatment in control group; B: Comparison of FPG levels before and after treatment in the study group; C: Comparison of 2-h plasma glucose (2hPG) level in control group before and after treatment; D: Comparison of 2hPG levels before and after treatment in the study group; E: Comparison of hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level before and after treatment in control group; F: Comparison of HbA1c levels before and after treatment in the study group. aP < 0.05, the difference between groups with statistical significance. FPG: Fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c: Hemoglobin A1c; 2Hpg: 2-h plasma glucose.
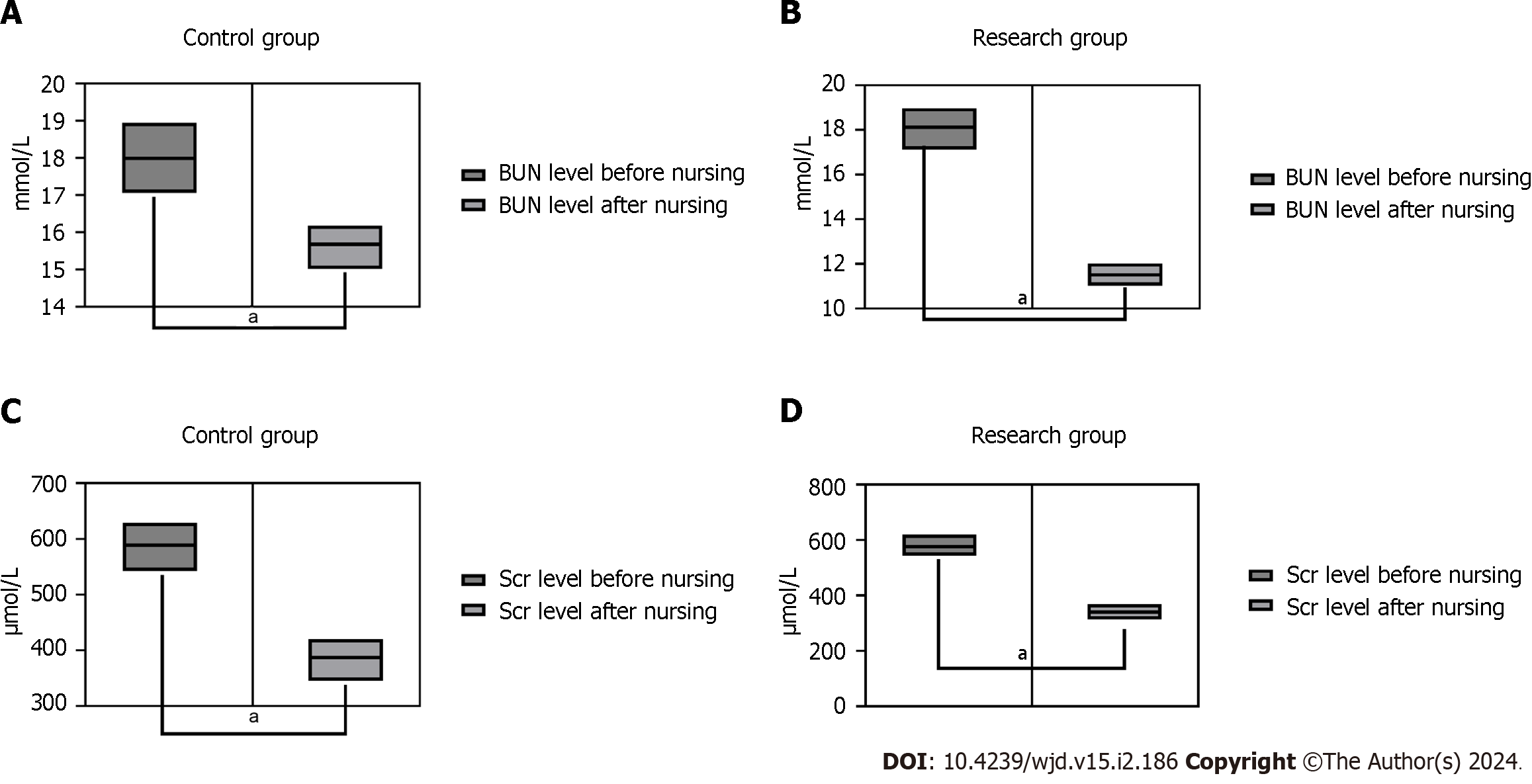
Figure 3 Comparative of renal function indicators.
A: Comparison of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels before and after treatment in control group; B: Comparison of BUN levels before and after treatment in the study group; C: Comparison of serum creatinine (SCr) level before and after treatment in control group; D: Comparison of SCr levels before and after treatment in the study group. aP < 0.05, the difference between groups with statistical significance.
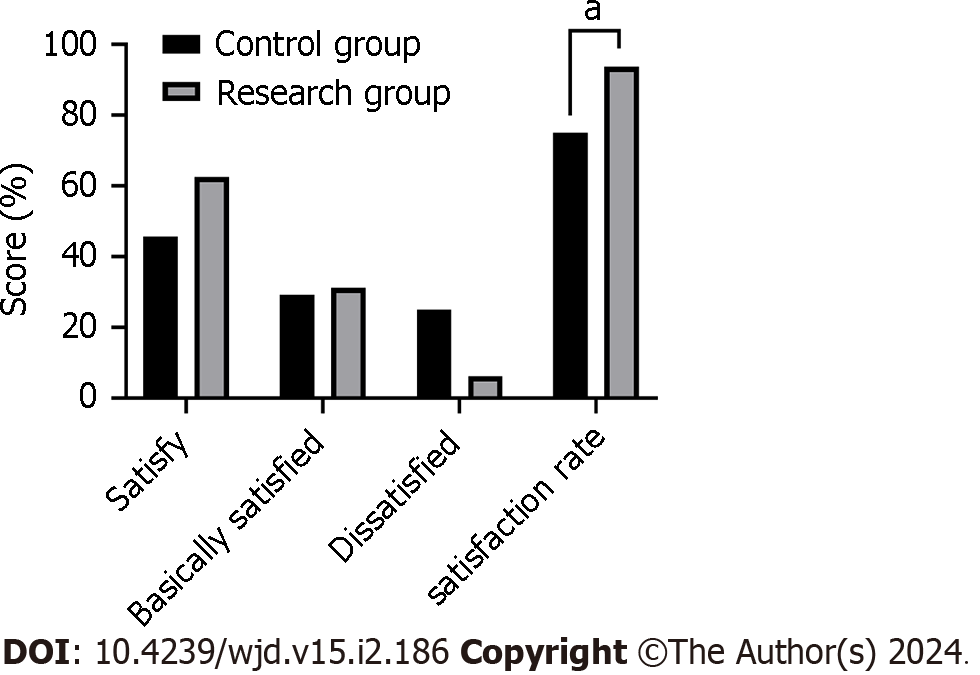
Figure 4 Comparative of nursing satisfaction rate.
aP < 0.05, the difference between groups with statistical significance.
- Citation: Chai XY, Bao XY, Dai Y, Dai XX, Zhang Y, Yang YL. Experience of humanistic nursing in hemodialysis nursing for patients with diabetic kidney disease. World J Diabetes 2024; 15(2): 186-195
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v15/i2/186.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v15.i2.186