Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. Dec 15, 2021; 12(12): 2036-2049
Published online Dec 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i12.2036
Published online Dec 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i12.2036
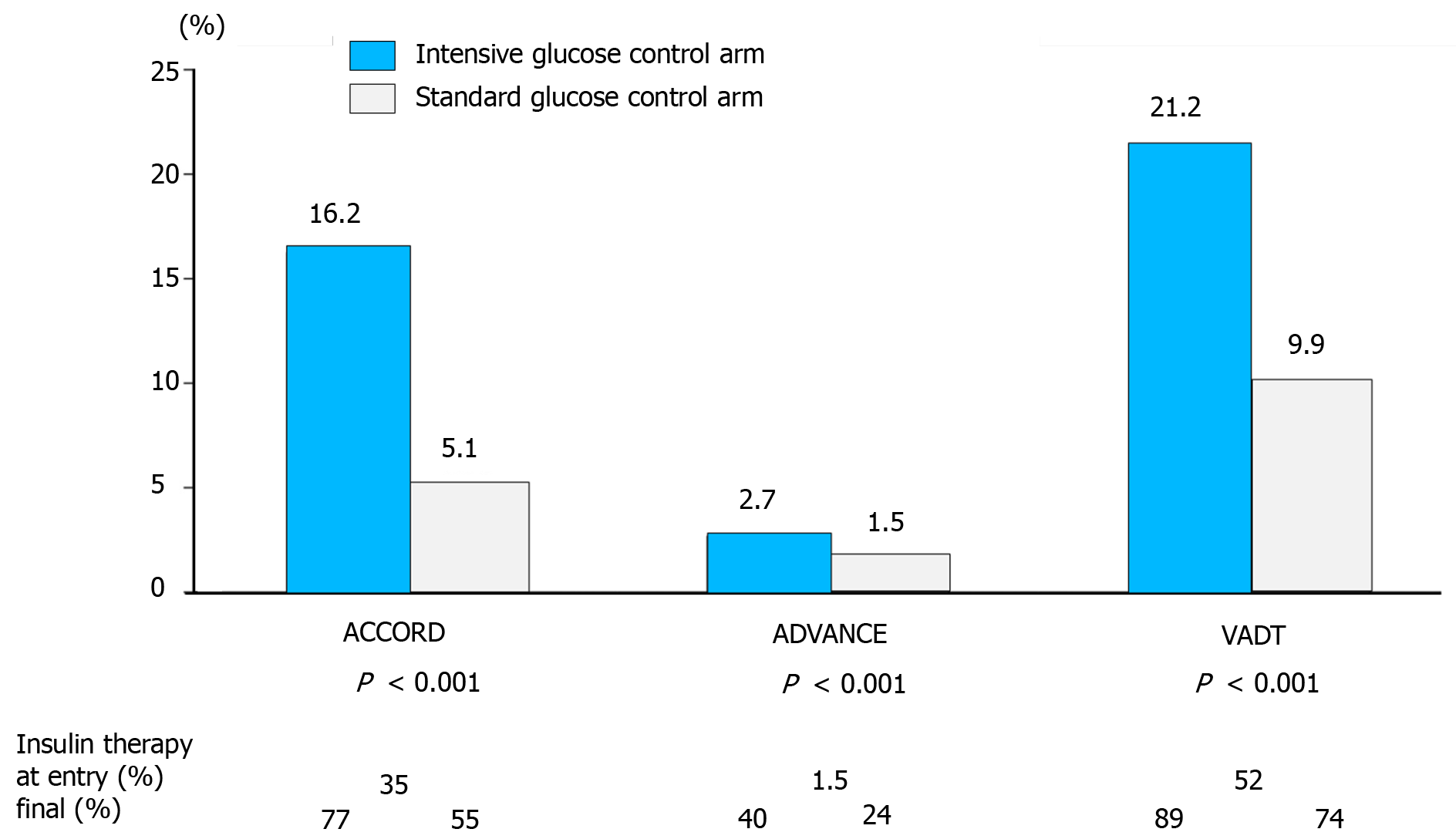
Figure 1 Percentage of severe hypoglycemic events in ACCORD, ADVANCE, and VADT.
Adapted from Frier et al[8] with permission from the American Diabetes Association. Citation: Frier BM, Schernthaner G, Heller SR. Hypoglycemia and cardiovascular risks. Diabetes Care 2011; 34 Suppl 2: S132-S137. Copyright ©The American Diabetes Association.
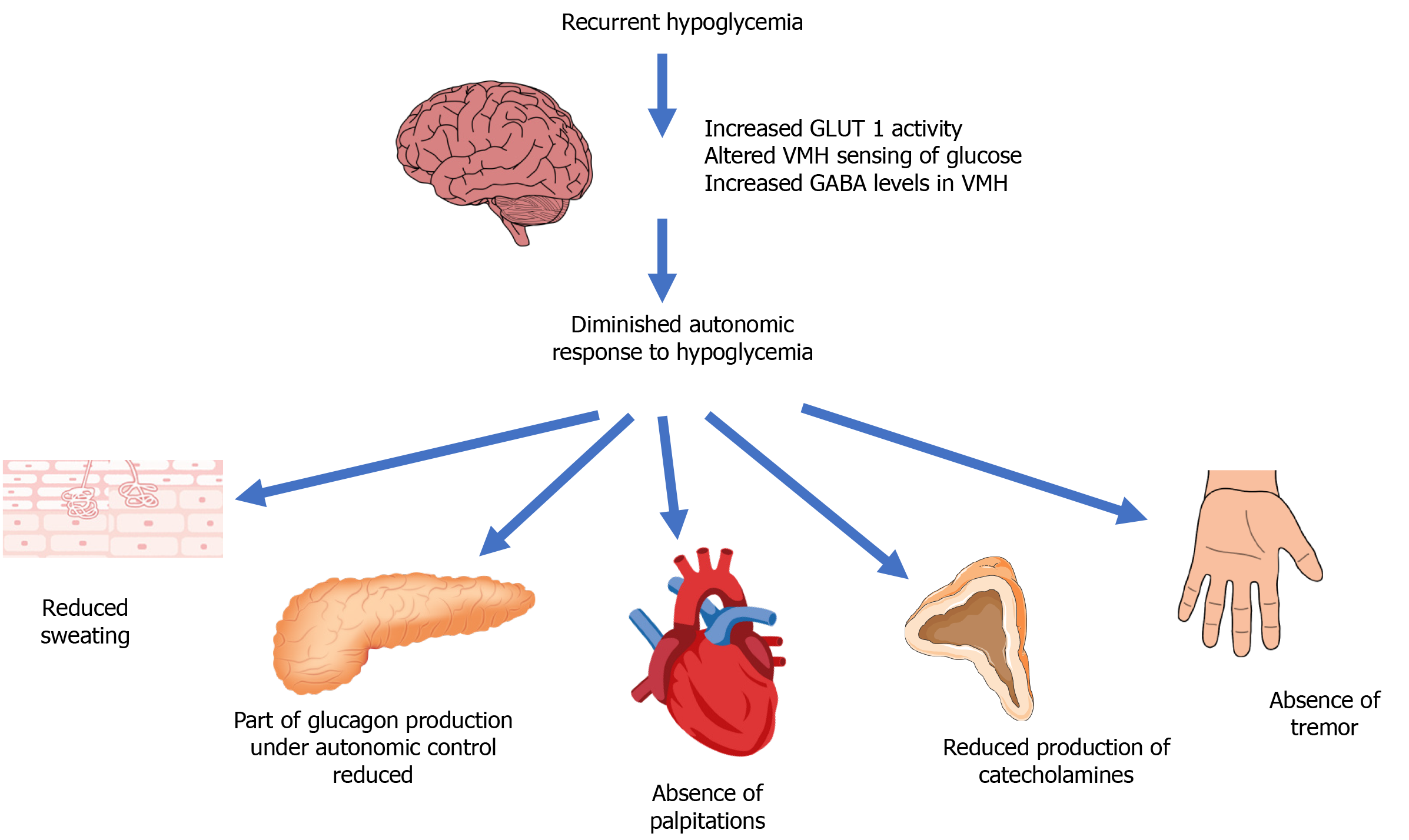
Figure 2 Putative mechanisms of hypoglycemia unawareness.
Recurrent hypoglycemia results in a reduced autonomic response to hypoglycemia with attenuation of autonomic warning symptoms. The maladaptive response in the brain is characterized by increased glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) activity in a bid to preserve brain function and alter glucose sensing in the ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH), mediated by elevated levels of gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA). Adapted from Iqbal et al[12] with permission from Elsevier. Citation: Iqbal A, Heller S. Managing hypoglycaemia. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016; 30: 413-430. Copyright © Elsevier.
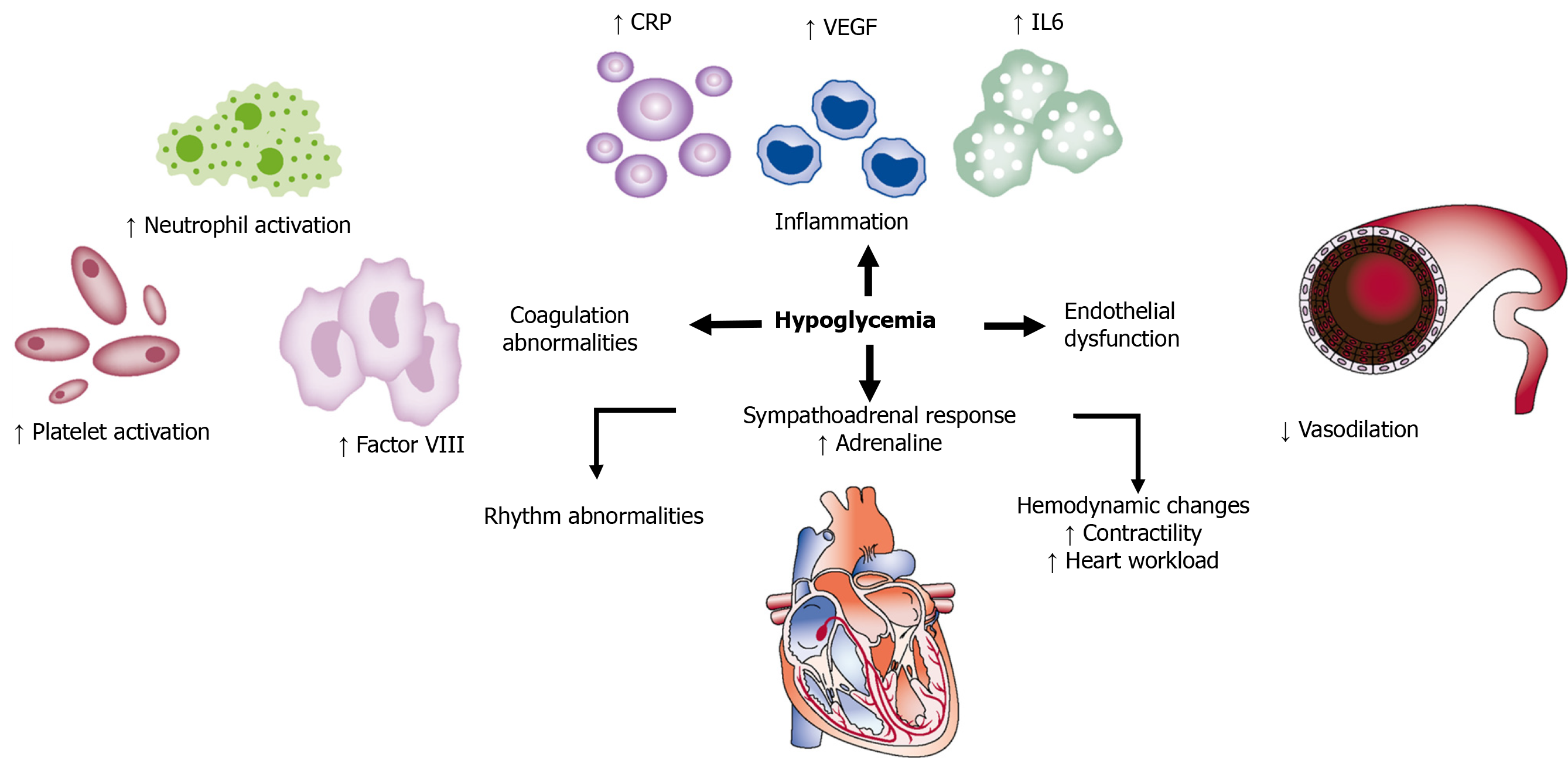
Figure 3 Mechanisms by which hypoglycemia may affect cardiovascular events.
Hypoglycemic events may induce inflammation by stimulating the release of C-reactive protein (CRP), IL-6, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Hypoglycemia also increases the activation of platelets and neutrophils. Sympathoadrenal response during hypoglycemia increases adrenaline release and may lead to arrhythmias and increased cardiac workload. Endothelial dysfunction may also contribute to cardiovascular risk. Adapted from Desouza et al[25] with permission from the American Diabetes Association. Citation: Desouza CV, Bolli GB, Fonseca V. Hypoglycemia, diabetes, and cardiovascular events. Diabetes Care 2010; 33: 1389-1394. Copyright ©The American Diabetes Association.
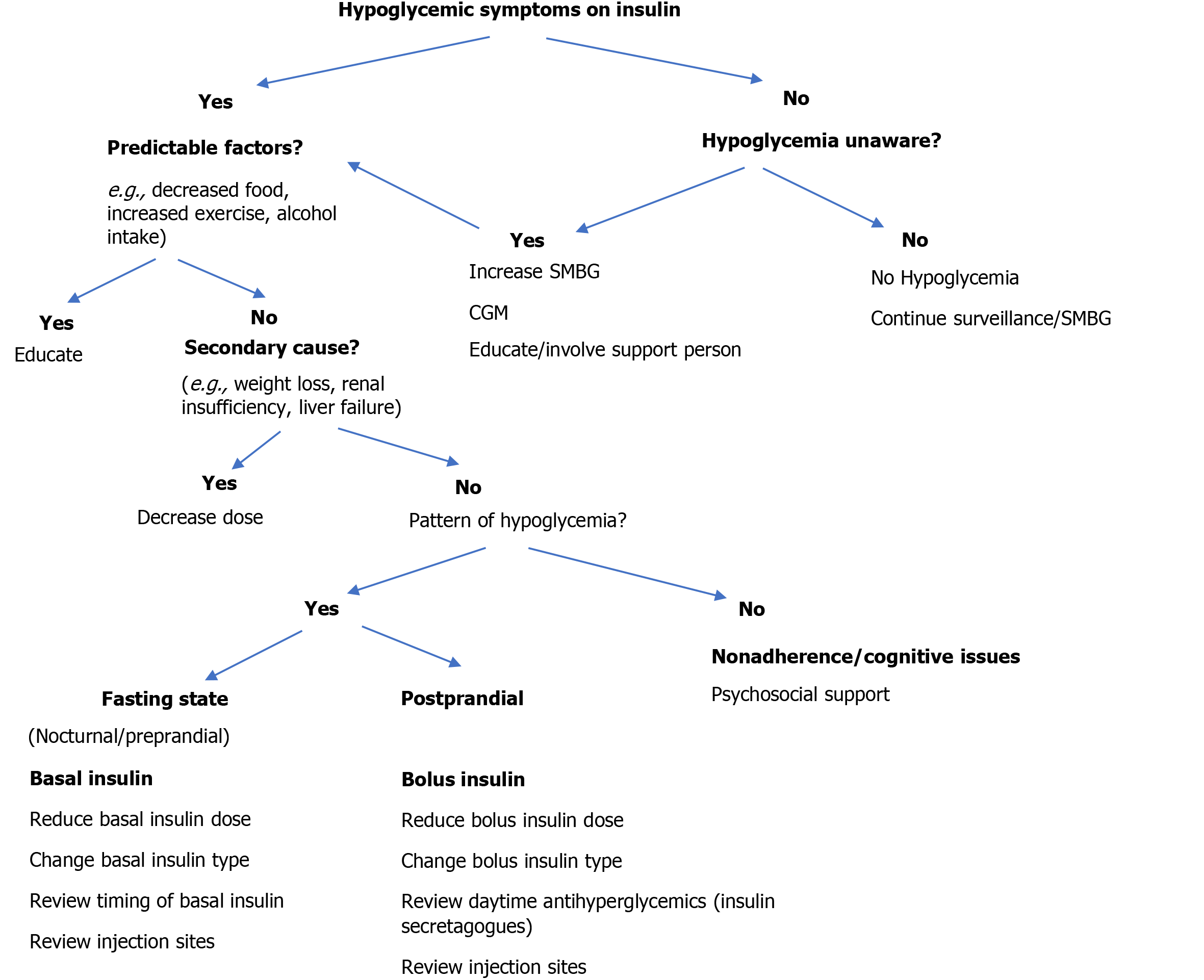
Figure 4 Algorithm of the approach to hypoglycemia.
CGM: Continuous glucose monitoring; SMBG: Self-monitoring of blood glucose. Adapted from Blumer et al[57] with permission from Elsevier. Citation: Blumer I, Clement M. Type 2 Diabetes, Hypoglycemia, and Basal Insulins: Ongoing Challenges. Clin Ther 2017; 39: S1-S11. Copyright © Elsevier.
- Citation: Nakhleh A, Shehadeh N. Hypoglycemia in diabetes: An update on pathophysiology, treatment, and prevention. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(12): 2036-2049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i12/2036.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i12.2036