Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Oct 15, 2015; 7(10): 184-203
Published online Oct 15, 2015. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v7.i10.184
Published online Oct 15, 2015. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v7.i10.184
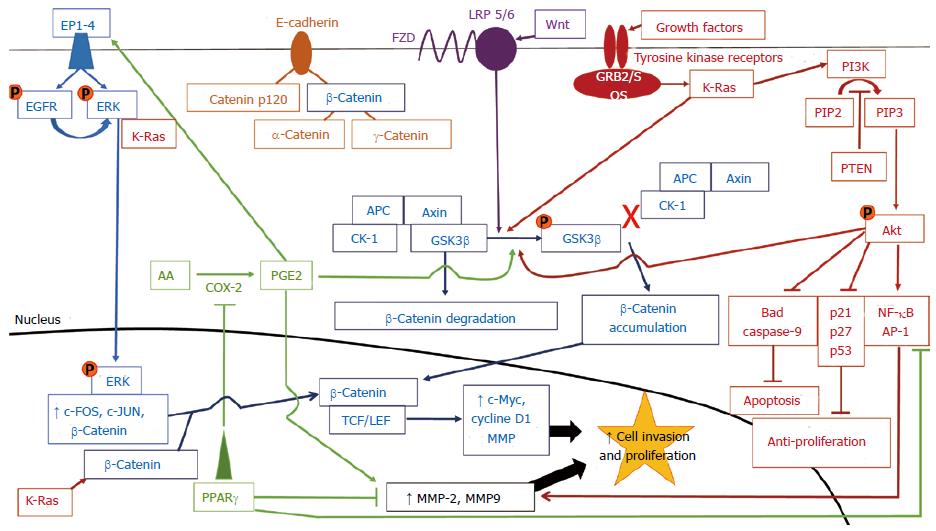
Figure 2 Crosstalk between signaling pathways that lead to colorectal cancer progression.
Each pathway is indicated by a specific color. Orange circles represent phosphate groups. β-Catenin is found at the cell membrane, complexed with E-cadherin, in the cytosol, and in the nucleus. Cytosolic β-catenin can be targeted for proteosomal degradation by GSK3β when GSK3β is not phosphorylated and is complexed with APC, Axin, and CK-1. Nuclear β-catenin induces gene transcription when complexed with TCF/LEF transcription factors. Ultimately, all pathways increase the transcription of genes favoring cellular proliferation (c-Myc, cyclin D1) and invasion (MMPs), most via increasing β-catenin-mediated gene transcription. CRC: Colorectal cancer; EP1-4: E-prostanoid receptor types 1-4; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; K-Ras: Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; FZD: Frizzled; LRP: Lipoprotein related receptor proteins 5/6; GRB2/SOS: Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2/son of sevenless; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; PIP2: Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3: Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; CK-1: Casein kinase 1; GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; COX2: Cyclooxygenase 2; AA: Arachidonic acid; PPARγ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; TCF/LEF: T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; AP-1: Activator protein 1.
- Citation: Applegate CC, Lane MA. Role of retinoids in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2015; 7(10): 184-203
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v7/i10/184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v7.i10.184