Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2012; 4(12): 238-249
Published online Dec 15, 2012. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v4.i12.238
Published online Dec 15, 2012. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v4.i12.238
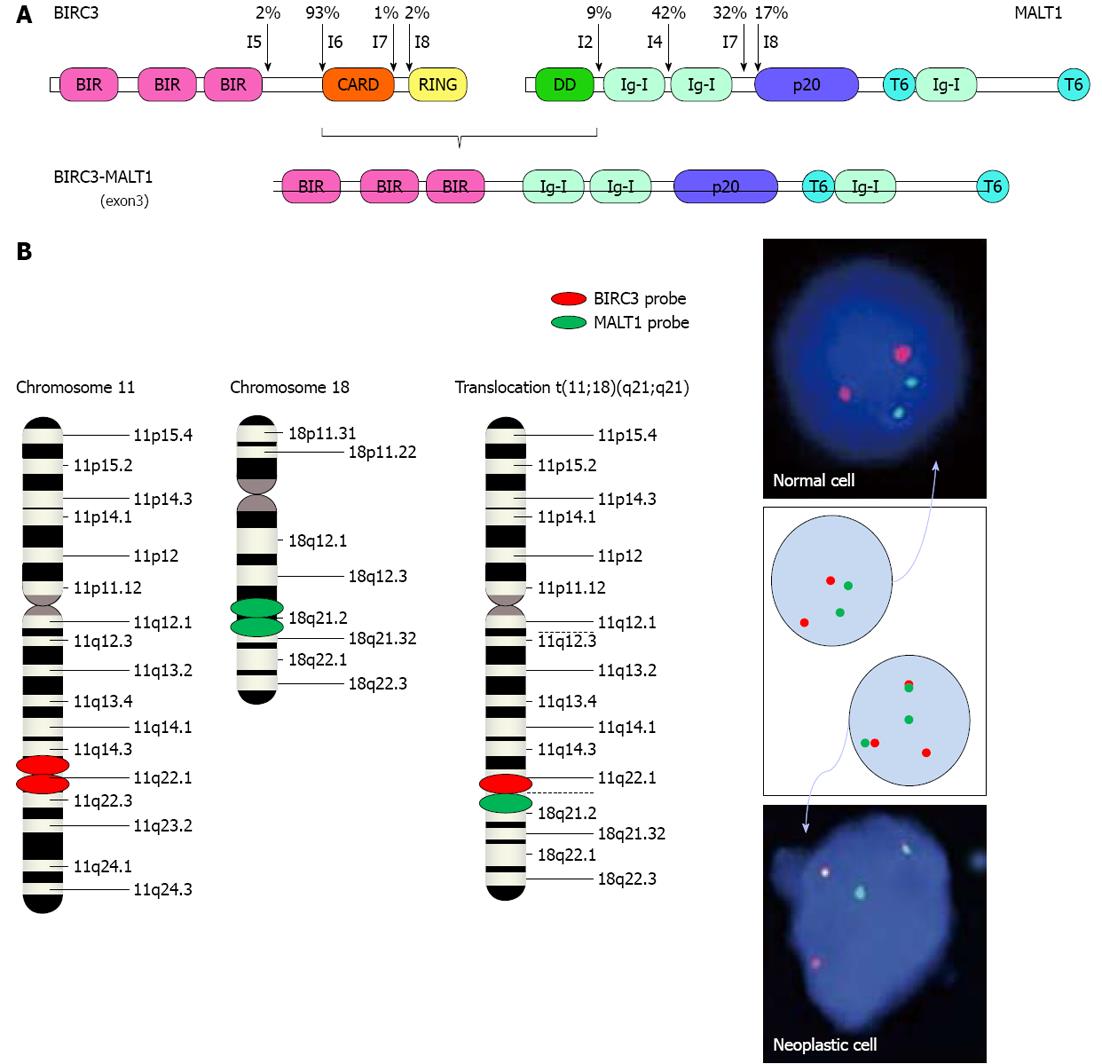
Figure 5 Fusion protein BIRC3-MALT1 in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas.
A: Known break points (arrows) in BIRC3 and MALT1 are shown with their frequencies. The break points within BIRC3 almost always occur in I6 (according to Ensembl Gene ENSG00000023445), whereas those within MALT1 are located in I2, I4, I7 and I8, which result in four possible versions of the BIRC3-MALT1 fusion gene: BIRC3(I6)-MALT1(I2), BIRC3(I6)-MALT1(I4), BIRC3(I6)-MALT1(I7) and BIRC3(I6)-MALT1(I8). The fusion gene depicted is the BIRC3(I6)-MALT1(I4) version. BIR: Baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis repeat; CARD: Caspase recruitment domain; DD: Death domain; I: Intron; Ig: Immunoglobulin-like; p20: Caspase-like p20 domain; RING: Really interesting new gene; T6: Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 binding site; B: Interphase FISH with dual-fusion probes results in 2 separate red and 2 separate green signals in normal lymphocytes, whereas t(11;18)(q21;q21)-positive MALT lymphoma cells will display 1 red and 1 green signal (that represent the normal loci) accompanied by 2 pathological fused red/green signals.
- Citation: Sagaert X, Tousseyn T, Yantiss RK. Gastrointestinal B-cell lymphomas: From understanding B-cell physiology to classification and molecular pathology. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2012; 4(12): 238-249
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v4/i12/238.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v4.i12.238