Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2025; 17(8): 108362
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108362
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108362
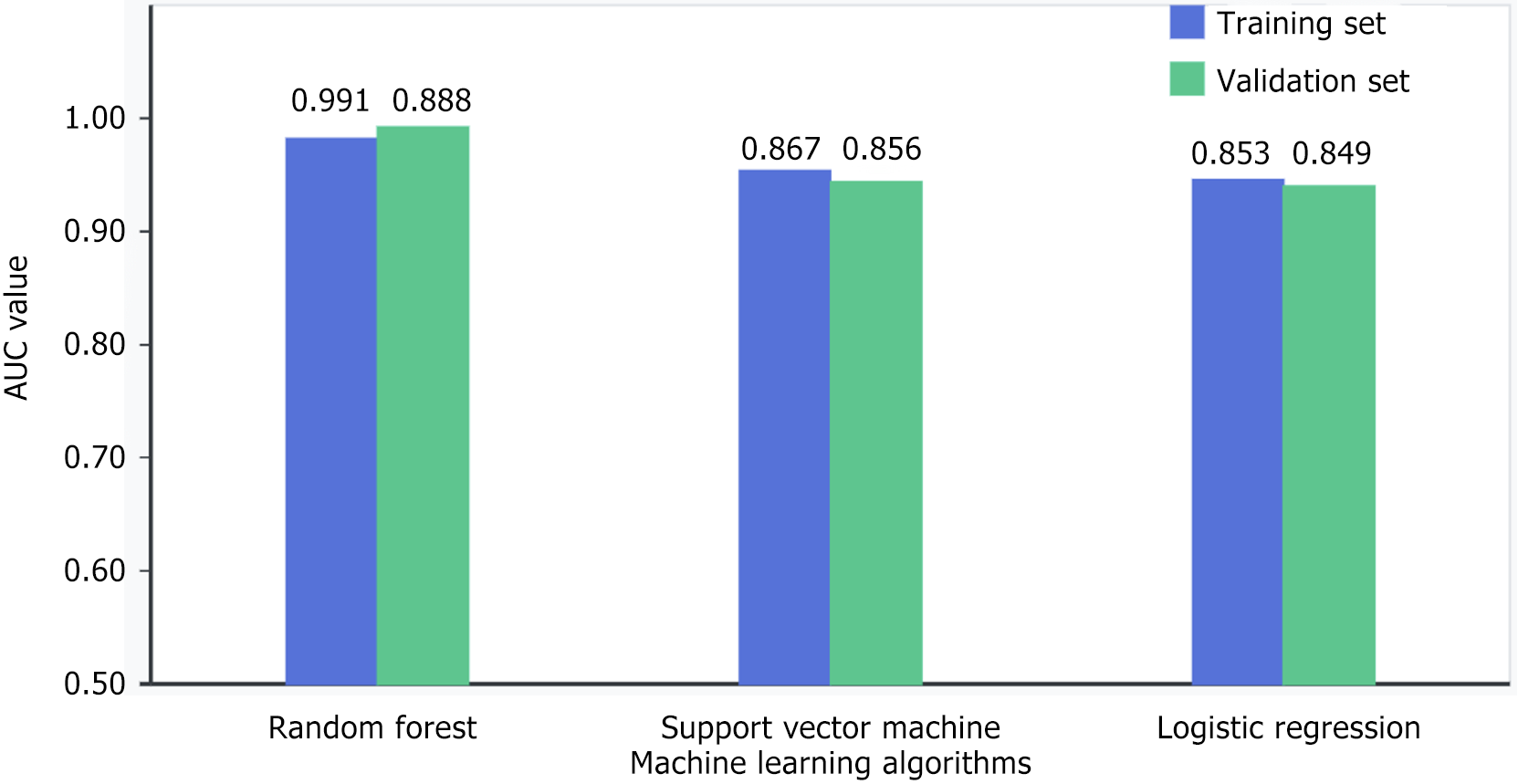
Figure 2 Comparative performance of different machine learning algorithms.
Random forest algorithm showed best performance in predicting microsatellite instability status with area under the curve values of 0.891 (training) and 0.896 (validation), outperforming support vector machine (0.867/0.858) and Logistic Regression (0.853/0.849). All models demonstrated good generalizability with statistically significant results (P < 0.001). AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Zheng CY, Zhang JM, Lin QS, Lian T, Shi LP, Chen JY, Cai YL. Noninvasive prediction of microsatellite instability in stage II/III rectal cancer using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging radiomics. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(8): 108362
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i8/108362.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108362