Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Aug 15, 2025; 17(8): 108362
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108362
Published online Aug 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108362
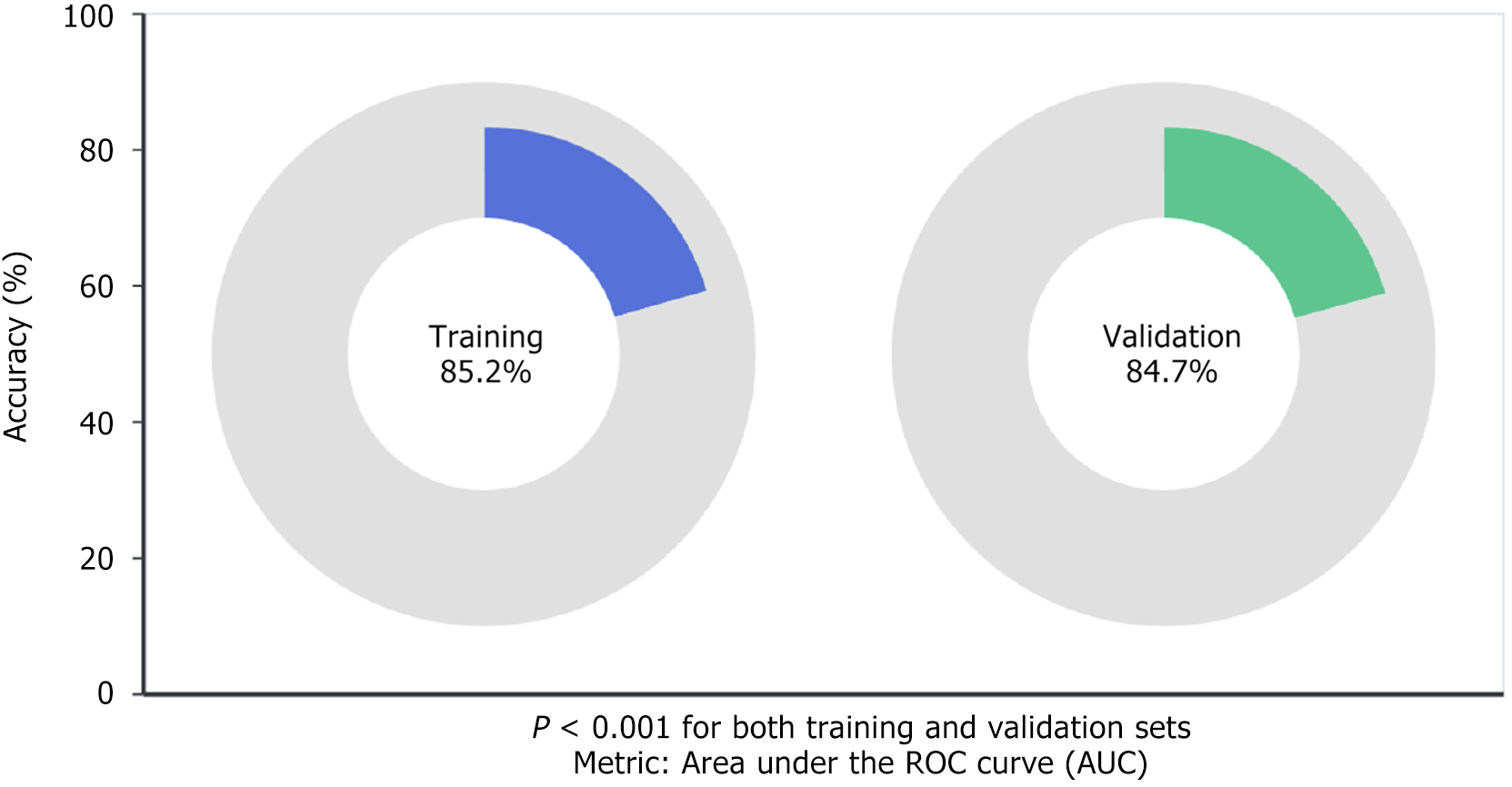
Figure 1 Machine learning models performance for microsatellite instability status prediction.
The models achieved 85.2% accuracy in training and 84.7% in validation (P < 0.001 for both), demonstrating good generalizability. This suggests radiomics-based machine learning approaches could serve as a valuable non-invasive tool for microsatellite instability assessment in clinical practice. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Zheng CY, Zhang JM, Lin QS, Lian T, Shi LP, Chen JY, Cai YL. Noninvasive prediction of microsatellite instability in stage II/III rectal cancer using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging radiomics. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(8): 108362
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i8/108362.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i8.108362