Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2025; 17(7): 108455
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.108455
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.108455
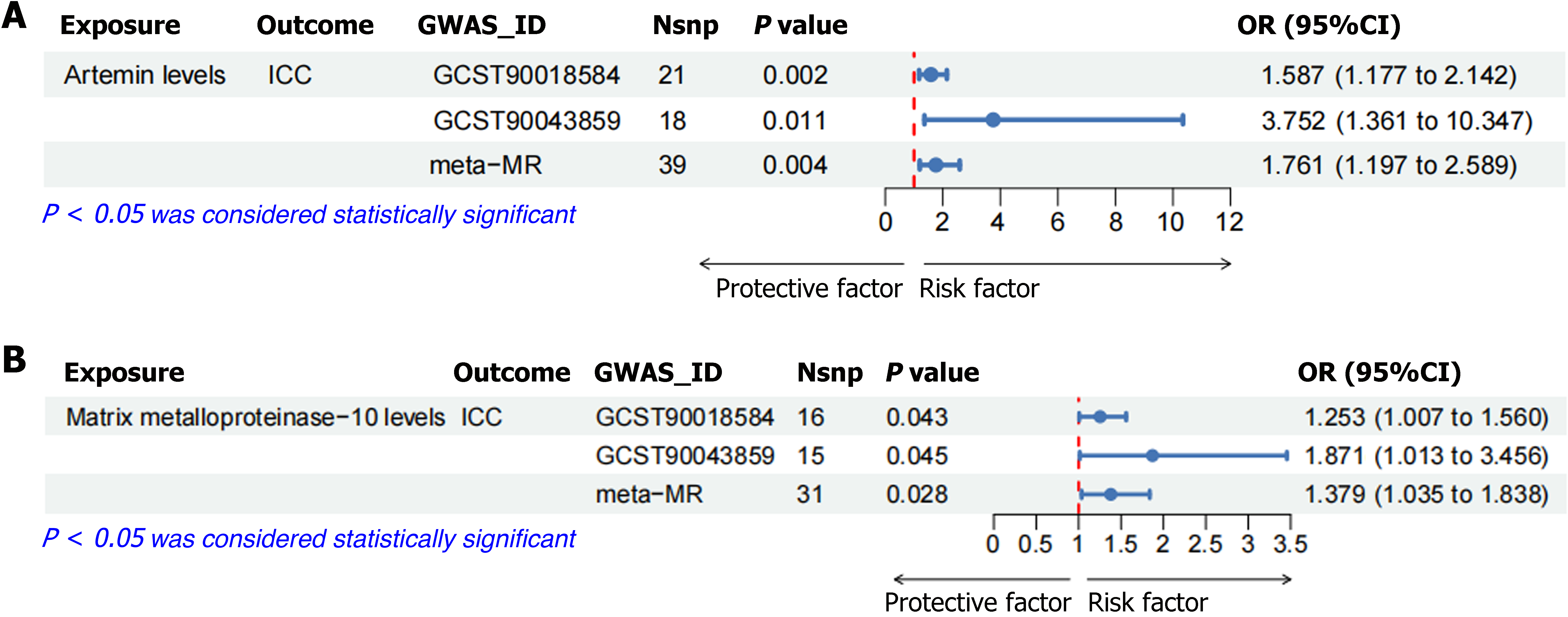
Figure 6 The meta-Mendelian randomization analysis was conducted to examine the association between artemin levels and matrix metalloproteinase-10 levels using data from both the training and validation sets.
A: Meta-Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis of artemin levels was conducted based on intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) data from both the training and validation sets; B: Meta-MR analysis of matrix metalloproteinase-10 levels was conducted based on ICC data from both the training and validation sets. ICC: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; OR: Odds ratio; GWAS: Genome-wide association studies; Nsnp: Number of SNPs.
- Citation: Chen B, Chen J, Chen ZT, Feng ZP, Lv HB, Jiang GP. Genetic evidence for the causal influence of inflammatory factors on intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma risk. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(7): 108455
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i7/108455.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.108455