Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jul 15, 2025; 17(7): 105455
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.105455
Published online Jul 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.105455
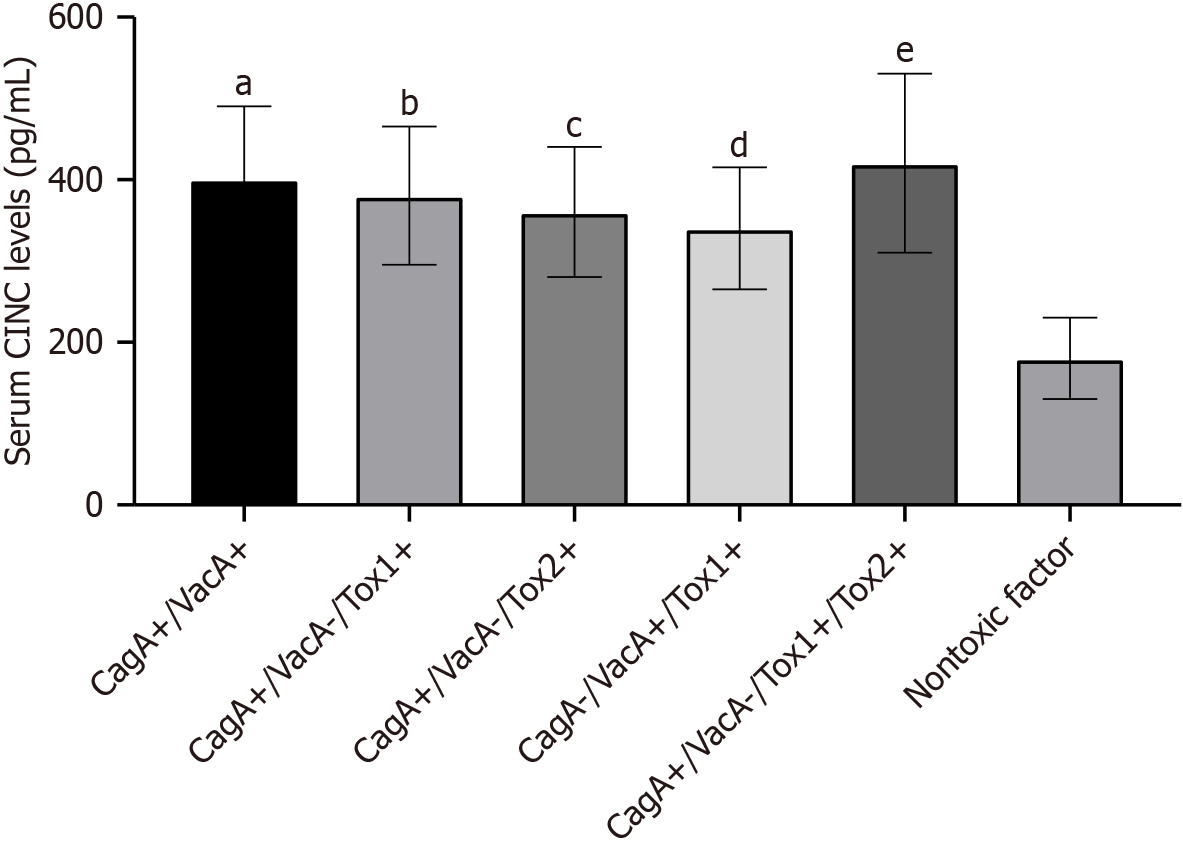
Figure 3 Cytotoxin-associated gene A/vacuolating cytotoxin -positive Helicobacter pylori strains enhance cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant production via NF-κB activation in gastric epithelial cells, promoting neutrophilic inflammation.
aP < 0.05, CagA+/VacA+ vs nontoxic control; bP < 0.01, CagA+/VacA−/Tox1+ vs nontoxic control; cP < 0.001, CagA+/VacA−/Tox2+ vs nontoxic control; dP < 0.0001, CagA−/VacA+/Tox1+ vs nontoxic control; eP < 0.00001, CagA−/VacA−/Tox1+/Tox2+ vs nontoxic control. CagA: Cytotoxin-associated gene A; VacA: Vacuolating cytotoxin; CINC: Cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant.
- Citation: Zhang HL, Niu XL, Wang N. Correlation of serum cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant levels with Helicobacter pylori infection and disease severity in gastric cancer patients. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(7): 105455
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i7/105455.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.105455