Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2025; 17(6): 106161
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106161
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106161
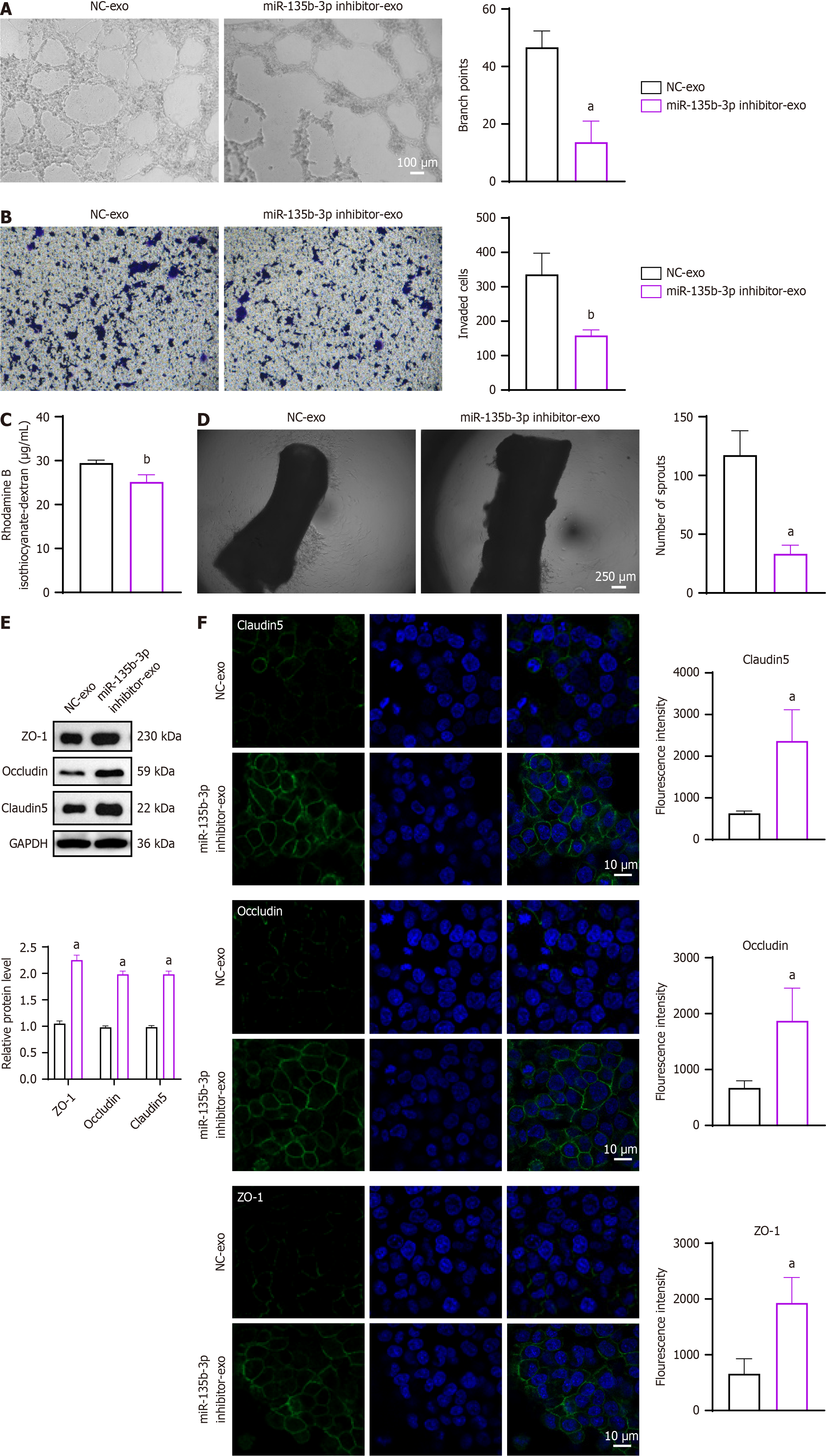
Figure 3 Exosomal miR-135b-3p enhances vascular permeability and angiogenesis in endothelial cells.
A: Representative images and branch points of microscopic observation of angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) cultured with exosomes from HCT116 cells transfected with miR-135b-3p inhibitor or negative control; B: Representative images and invaded cells of cell invasion assay; C: Permeability of the HUVEC monolayers to rhodamine–dextran (70 kDa) after exposure to exosomes for 72 hours; D: Representative images of the aortic ring and numbers of microvascular sprouts; E: Western blot analysis of tight junction proteins zonula occludens-1, occludin, and claudin-5 in HUVECs treated with exosomes; GAPDH as an internal control; F: Immunofluorescent staining of tight junction proteins zonula occludens-1, occludin, and claudin-5 (green) in HUVECs treated with DAPI nuclei (blue). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs negative control-exosome (n = 3 per group). NC-exo: Negative control-exosome; ZO-1: Zonula occludens-1.
- Citation: Feng CZ, Zhong SQ, Ye SW, Zheng Z, Sun H, Zhou SH. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-425-5p and miR-135b-3p enhance colorectal cancer progression through immune suppression and vascular permeability promotion. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(6): 106161
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i6/106161.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106161