Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2025; 17(6): 106161
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106161
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106161
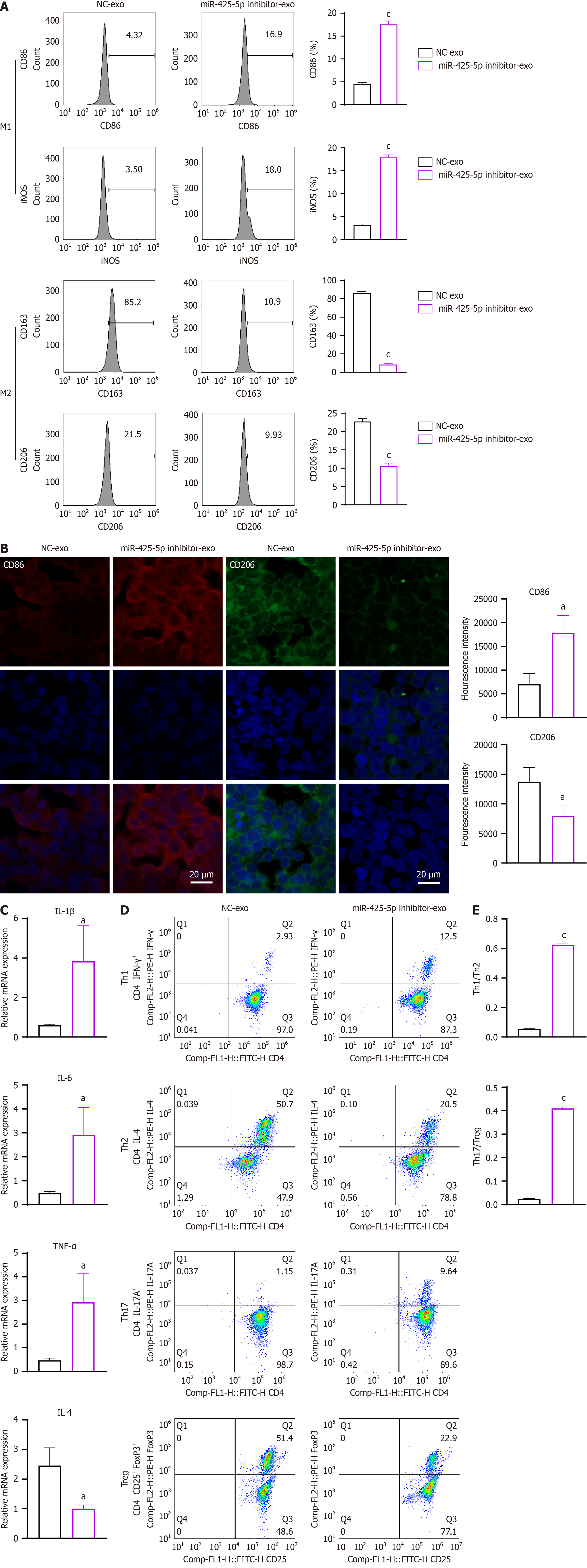
Figure 2 Exosomal miR-425-5p inhibition promotes macrophage M1-like polarization and proinflammatory T cell differentiation.
A: Flow cytometry analysis of CD86+iNOS+ and CD163+CD206+ cells ratio in THP-1 cells cultured with exosomes isolated from HTC116 cells transfected with negative control and miR-425-5p inhibitor; B: Immunofluorescent staining of CD86 (red) and CD206 (green) in THP-1 cells with DAPI nuclei (blue); C: Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of cytokine expression in CD4+ T cells cultured with exosomes; D and E: Flow cytometry analysis of CD4+ T cell subsets. aP < 0.05, cP < 0.001 vs negative control-exosome (n = 3 per group). NC-exo: Negative control-exosome; CD4: T-cell surface glycoprotein CD4; CD25: Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha; CD86: T-lymphocyte activation antigen CD86; CD163: Scavenger receptor cysteine-rich type 1 protein M130; CD206: Macrophage mannose receptor 1; FoxP3: Forkhead box protein P3; IFN-γ: Interferon gamma; IL-1β: Interleukin 1 beta; IL-4: Interleukin 4; IL-6: Interleukin 6; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; Th: T helper cells; TNF-α: Tumor necrotic factor alpha; Treg: Regulatory T cells.
- Citation: Feng CZ, Zhong SQ, Ye SW, Zheng Z, Sun H, Zhou SH. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-425-5p and miR-135b-3p enhance colorectal cancer progression through immune suppression and vascular permeability promotion. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(6): 106161
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i6/106161.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.106161