Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2025; 17(5): 104686
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.104686
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.104686
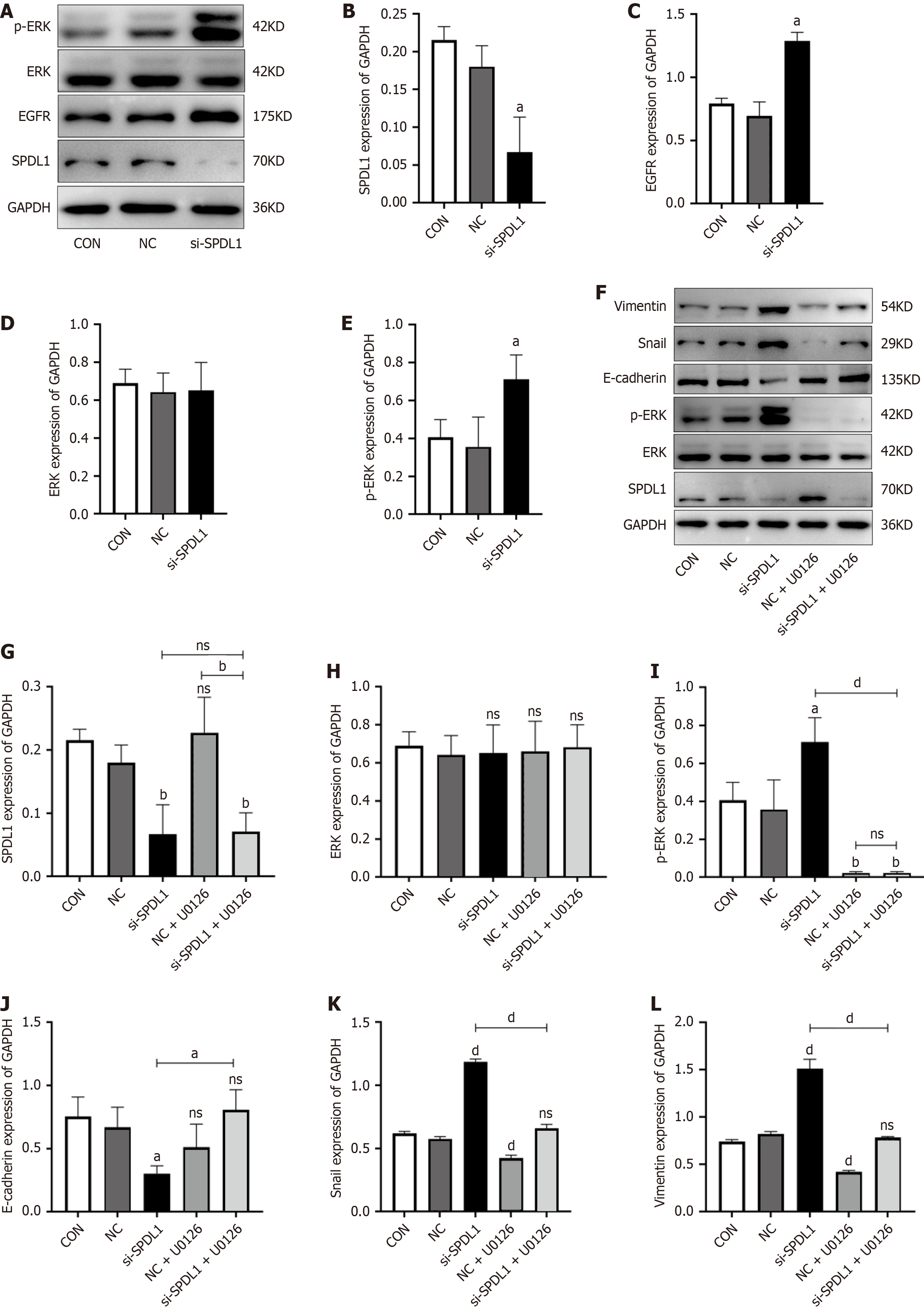
Figure 5 SPDL1 affects the expression of proteins related to epithelial-mesenchymal transition, epidermal growth factor receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway.
A: Representative Western blot images after SPDL1 knocked down in HCT116 cells; B-E: Quantification of Western blot data in (A); F: Representative Western blot images. Cells were treated with U0126 and analyzed by Western blot; G-L: Quantification of Western blot data in (F). Data are presented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.01. dP < 0.0001. ns: Not significant; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; p-ERK: Phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Con: Control; NC: Negative control; si-SPDL1: Small interfering RNA targeting SPDL1.
- Citation: Peng P, Sun J, Li MS, Cheng RX, Liu SQ, Qin MB, Zhang JX, Huang JA. SPDL1 inhibition enhances colorectal cancer progression via epidermal growth factor receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(5): 104686
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i5/104686.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.104686