Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Nov 15, 2023; 15(11): 1974-1987
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i11.1974
Published online Nov 15, 2023. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i11.1974
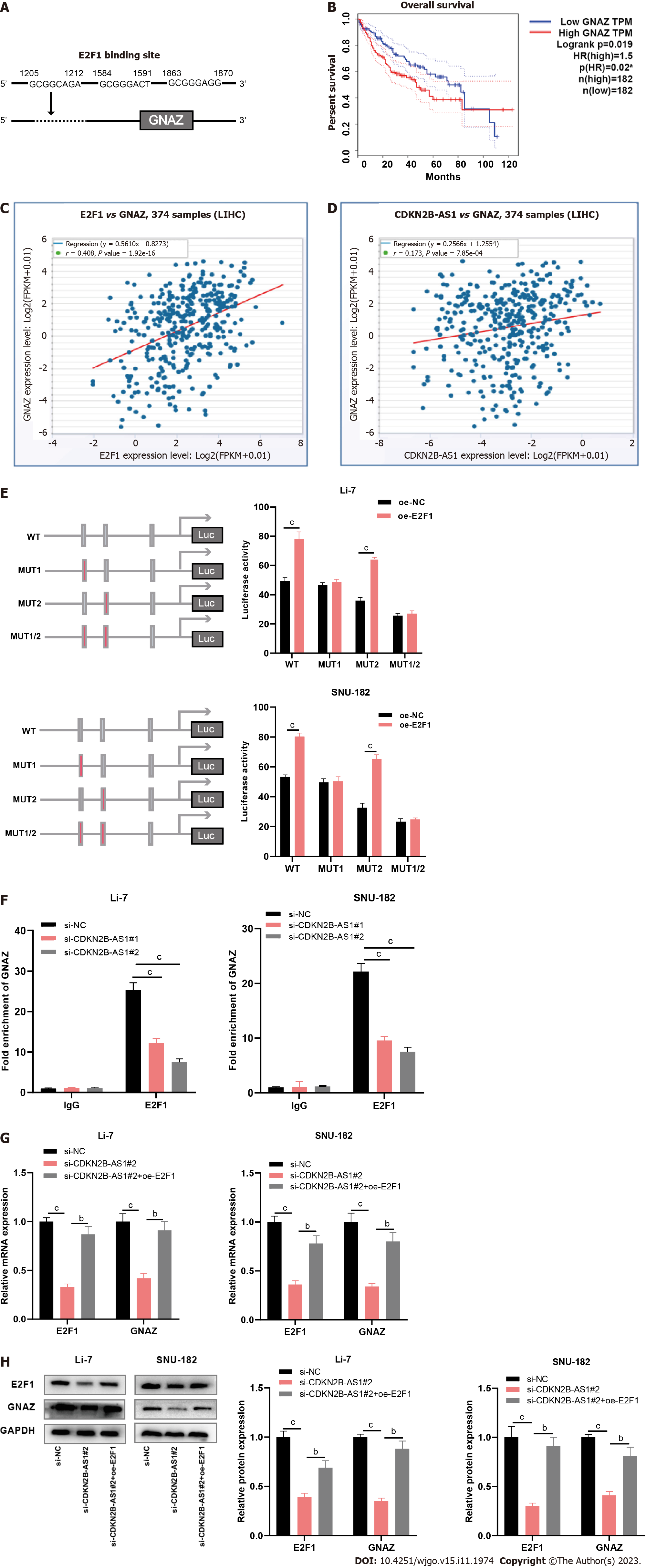
Figure 4 CDKN2B-AS1 promotes transcription of G protein subunit alpha Z by recruiting transcription factor E2F transcription factor 1.
A: Illustration of predicted binding site of E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1) on the G protein subunit alpha Z (GNAZ) promoter sequence generated from the PROMO database; B: Overall survival plot of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients grouped by GNAK expressions (high vs low). Red line represents the high expression group and blue line represents the low expression group; C and D: Correlation analyses between expressions of E2F1 and GNAZ (C), and expressions of CDKN2B-AS1 and GNAZ (D), respectively, in HCC tissues from StarBase database. P < 0.05 indicates a significant correlation; E: Dual-luciferase reporter gene assays were conducted to predict the specific site of binding of E2F1 protein to the GNAZ promoter. Bar charts summarize the luciferase activity in Li-7 and SNU-182 cell lines overexpressed with E2F1 with wild type and mutated form of GNAZ (MUT1, MUT2, MUT1/2); F: Bar charts showing the fold enrichment of GNAZ promoter from immunoglobulin G and E2F1, separately, in CDKN2B-AS1 silenced Li-7 and SNU-182 cells, detected by Chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments; G and H: Bar charts showing the expression levels of E2F1 and GNAZ in Li-7 and SNU-182 cells, after depletion of CDKN2B-AS1, examined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (G) and western blot assays (H). bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. E2F1: E2F transcription factor 1; GNAZ: G protein subunit alpha Z; IgG: Immunoglobulin G.
- Citation: Tao ZG, Yuan YX, Wang GW. Long non-coding RNA CDKN2B-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via E2F transcription factor 1/G protein subunit alpha Z axis. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2023; 15(11): 1974-1987
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v15/i11/1974.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v15.i11.1974