Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2021; 13(6): 509-535
Published online Jun 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.509
Published online Jun 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.509
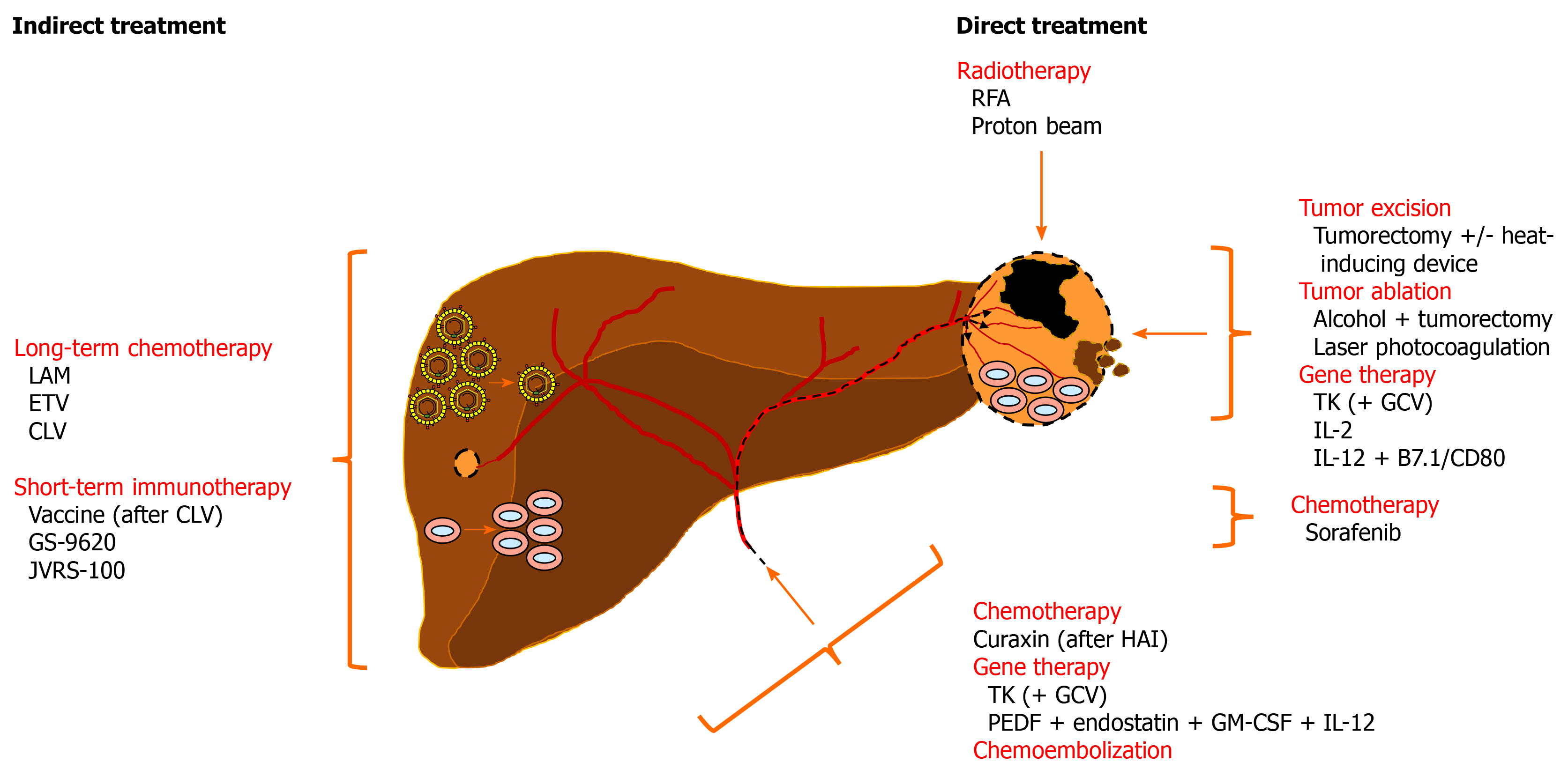
Figure 3 Overview of therapeutic interventions assessed in woodchucks with liver tumors for the treatment of human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Indirect treatment of chronic WHV carrier woodchucks with nucleos(t)ide analogs or immunomodulators reduces viremia or activates antiviral and anticancer immune responses, respectively, that delay or prevent HCC onset. Direct treatment of hepatic neoplasms by radiotherapy, excision and ablation, gene therapy, or chemotherapy induce apoptosis or necrosis of tumor cells and/or activate an intratumoral, anticancer immune response that result in partial tumor remission. Chemoembolization-mediated anticancer effects have not been evaluated in woodchucks so far. See text for more details. B7.1/CD80: Costimulatory molecule; CLV: Clevudine; ETV: Entecavir; GCV: Ganciclovir; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; GS-9620: Toll-like receptor 7 agonist; HAI: Hepatic artery infusion; IL-12: Interleukin 12; JVRS-100: Complex of non-coding plasmid DNA and cationic liposomes; LAM: Lamivudine; PEDF: Pigment epithelium-derived factor; RFA: Radiofrequency ablation; TK: Thymidine kinase.
- Citation: Suresh M, Menne S. Application of the woodchuck animal model for the treatment of hepatitis B virus-induced liver cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2021; 13(6): 509-535
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v13/i6/509.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v13.i6.509