Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2024; 16(4): 1421-1436
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1421
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1421
Figure 1 Identification of dysregulated metabolic genes in tumor tissues.
A: Multi-step analysis of metabolic genes in this study; B: Volcano plot showing metabolic differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between tumor and adjacent tissues; C: Box plots showing the top ten metabolic DEGs based on the adjusted P-value; D: Bar plot showing top ten upregulated and downregulated Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes items; E: Pheatmap showing the consensus matrix (k = 3); F and G: Kaplan-Meier curves showing overall survival and progression free interval across three clusters. bP < 0.01. GO: Gene Ontology; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; NOX4: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4; FC: Fold change; OS: Overall survival; PFI: Progression free interval.
Figure 2 Construction and validation of the prediction model.
A-C: Kaplan-Meier curves showing the survival differences between high and low-risk groups in training, test datasets and our clinical cohort; D-F: Receiver operating characteristic curves showing the area under curve in training, test datasets and our clinical cohort. AUC: Area under curve.
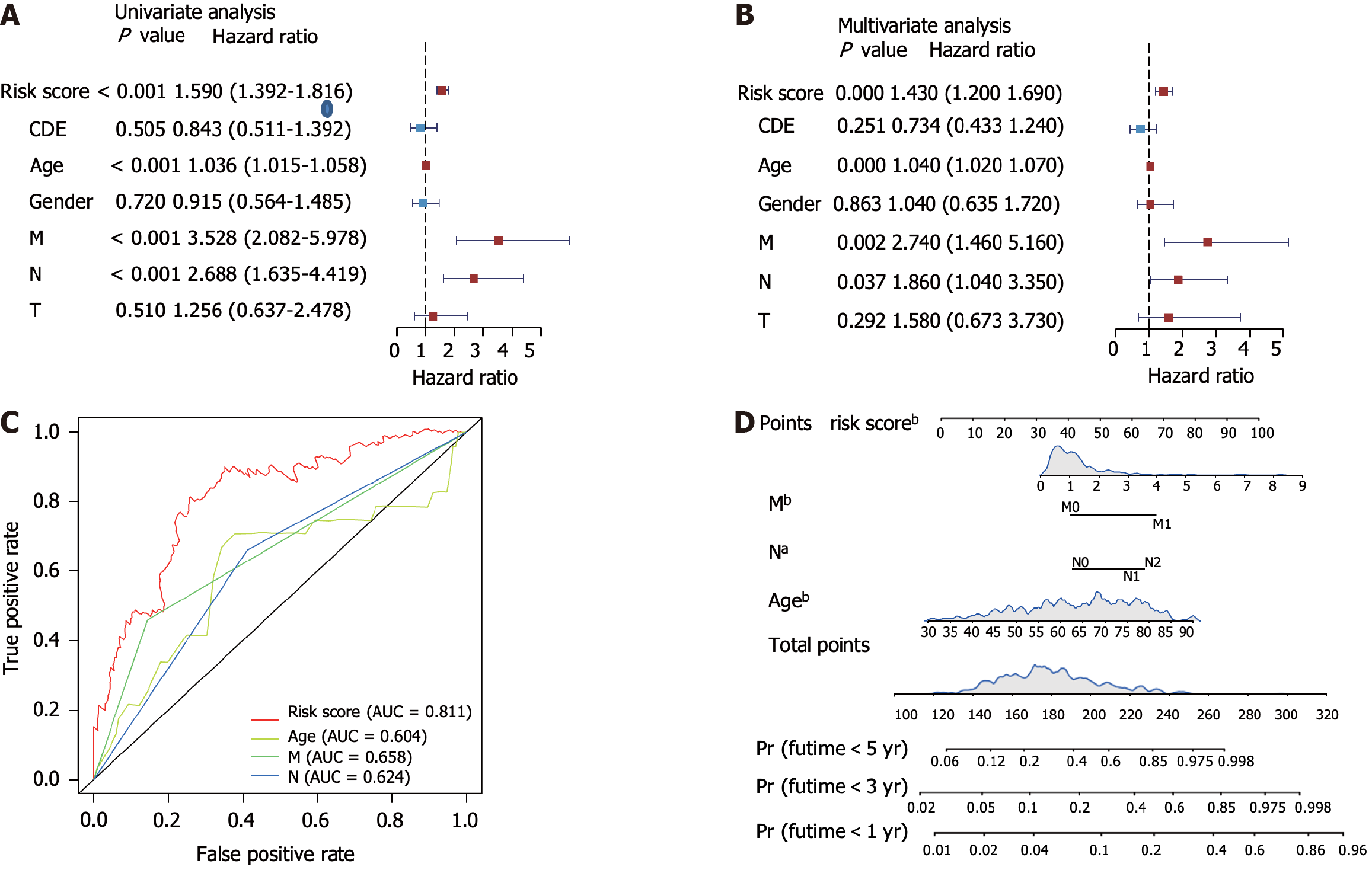
Figure 3 Validation of the risk score and survival prediction model.
A and B: Forest plots showing the univariate and multivariate analysis of risk scores and other clinical parameters; C: Receiver operating characteristic analysis showing the area under curve of each factor for predicting colorectal cancer overall survival; D: Construction of nomogram using the independent risk score. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. AUC: Area under curve.
Figure 4 Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 induces colorectal cancer progression.
A: Venn diagram showing the overlap of metabolic differentially expressed genes and genes correlated with poor prognosis; B: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 (NOX4) expression in tumor and adjacent normal tissues; C: Immunohistochemical representative images of NOX4 expression in colorectal cancer patient samples; D: Quantification of NOX4 expression in tumor and adjacent normal tissues in tumor samples; E: Kaplan-Meier curves showing the overall survival between high and low-NOX4 expression groups in our dataset; F and G: Clone and sphere formation was evaluated in NOX4-overexpressing RKO (RKO-OE) and wild-type (RKO-Ctrl) cells; H-J: Cell invasion and migration of RKO-OE and RKO-Ctrl cells were measured using the transwell chamber assay and scratch assay. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. DEG: Differentially expressed gene; NOX4: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4.
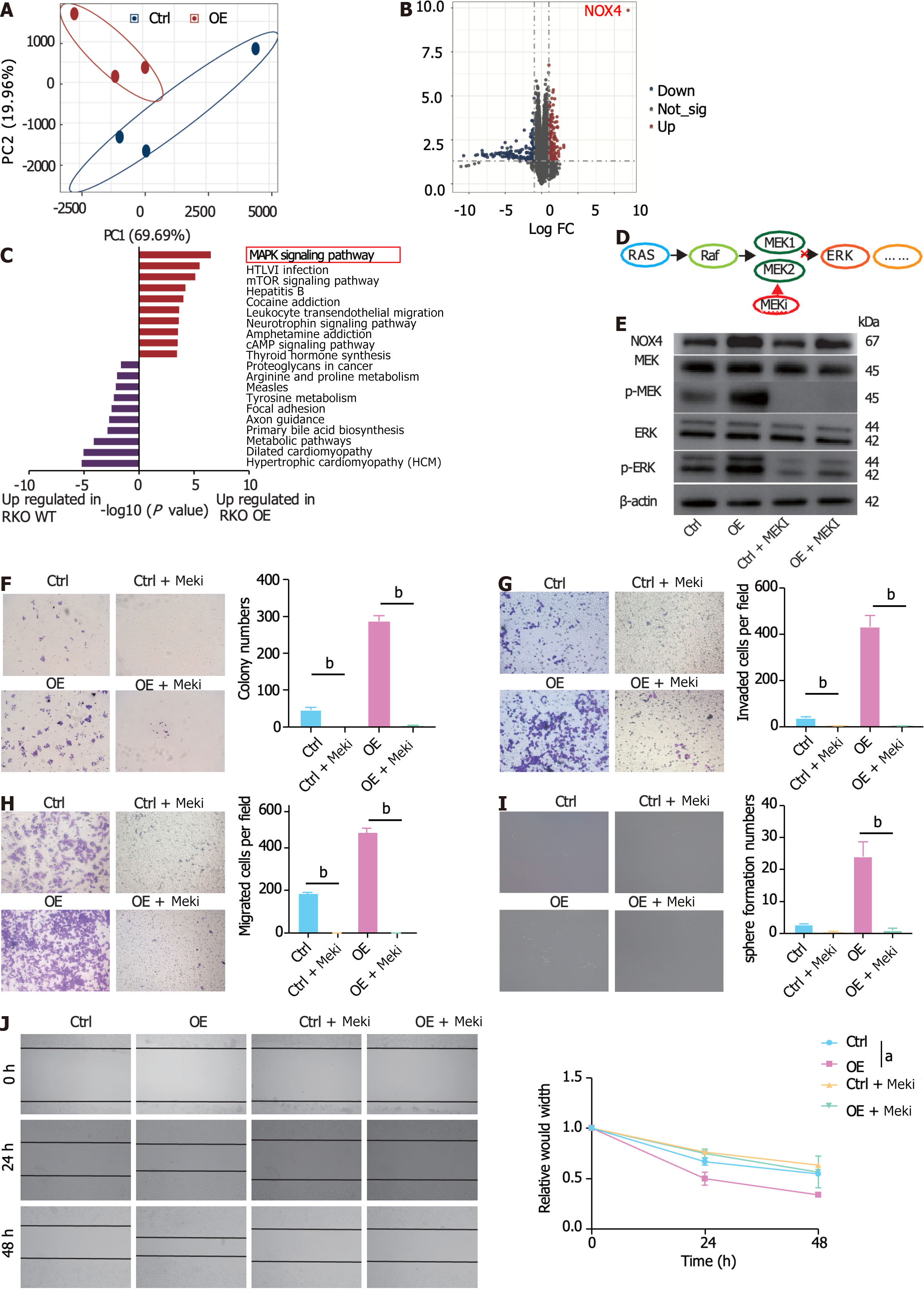
Figure 5 Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 promotes activation of mitogen-activated protein kina
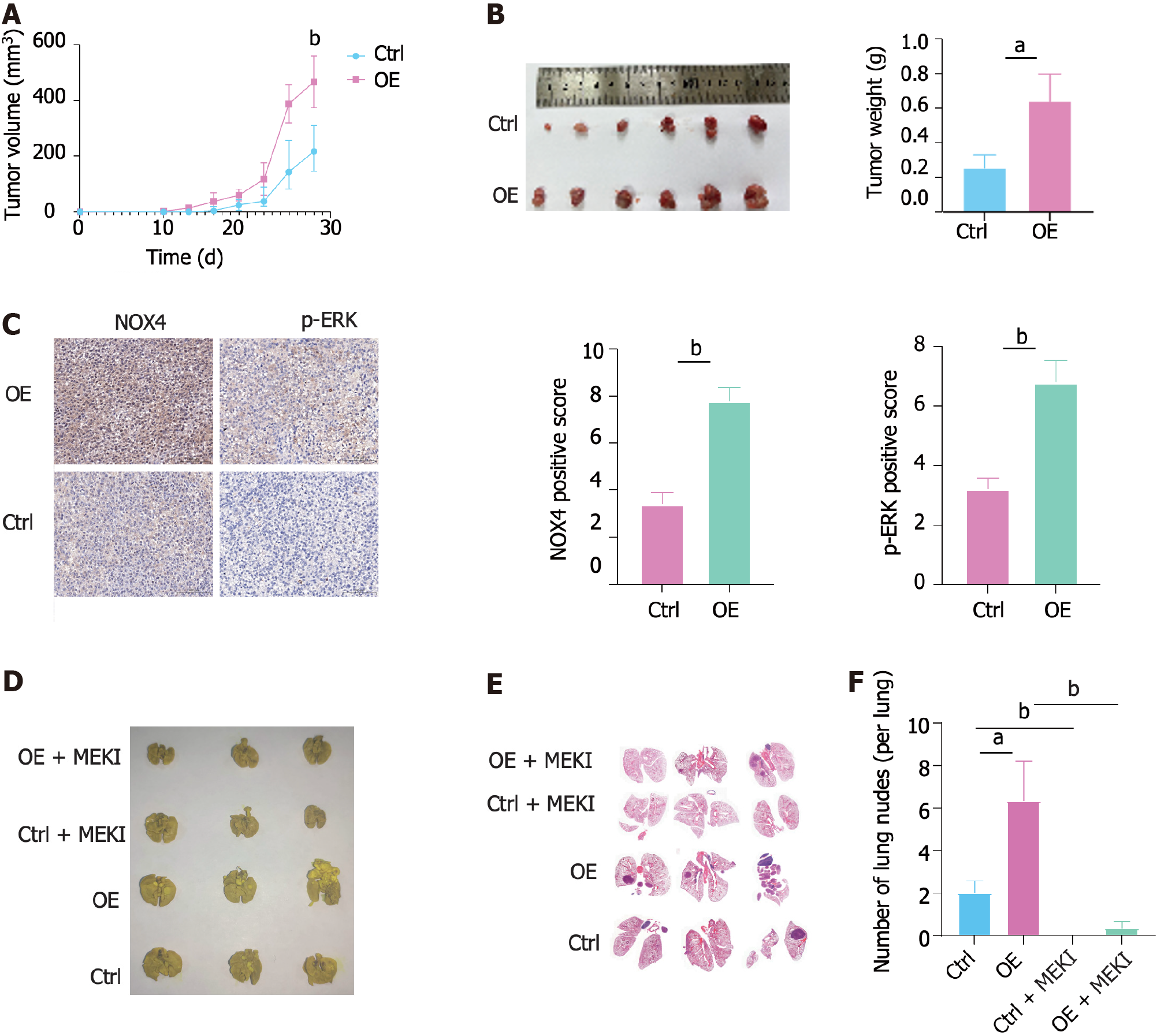
Figure 6 Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in vivo.
A: Volume of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 (NOX4)-overexpressing RKO and wild-type tumor and measured at indicated time points; B: The representative image of subcutaneous tumors at the end of the experiment (day 28); C: Immunohistochemical staining analysis showing NOX4 and pERK expression in two groups; D: The representative image of metastatic nodes in the mouse lung tissue; E: Hematoxylin-eosin staining of tumor metastasis in mouse lung tissues; F: Quantification of tumor metastasis in lung tissues. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. NOX4: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4.
- Citation: Xu YJ, Huo YC, Zhao QT, Liu JY, Tian YJ, Yang LL, Zhang Y. NOX4 promotes tumor progression through the MAPK-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 axis in colorectal cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(4): 1421-1436
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i4/1421.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1421