Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Mar 15, 2024; 16(3): 659-669
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.659
Published online Mar 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.659
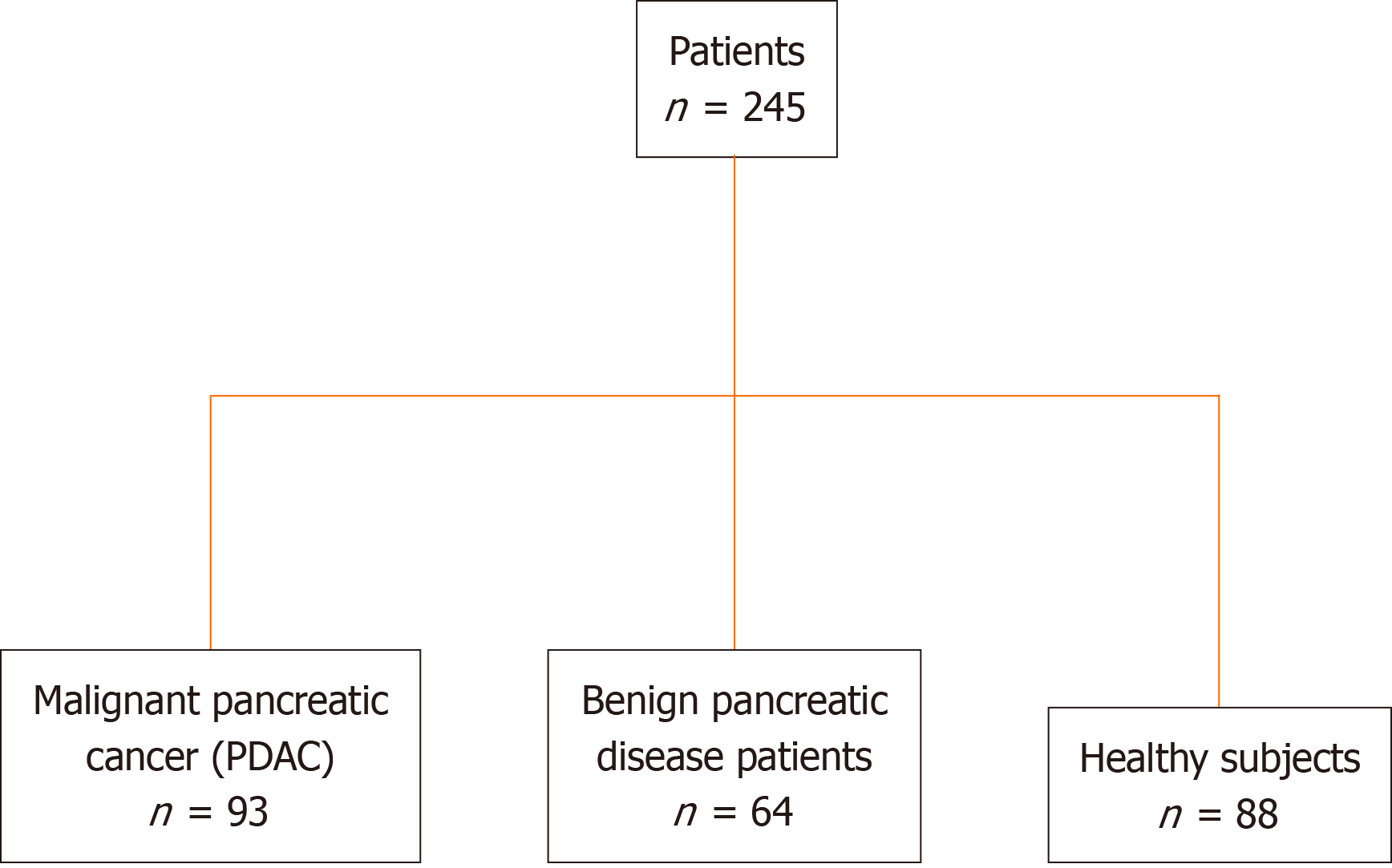
Figure 1 Overview of study design and patient cohort.
PDAC: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
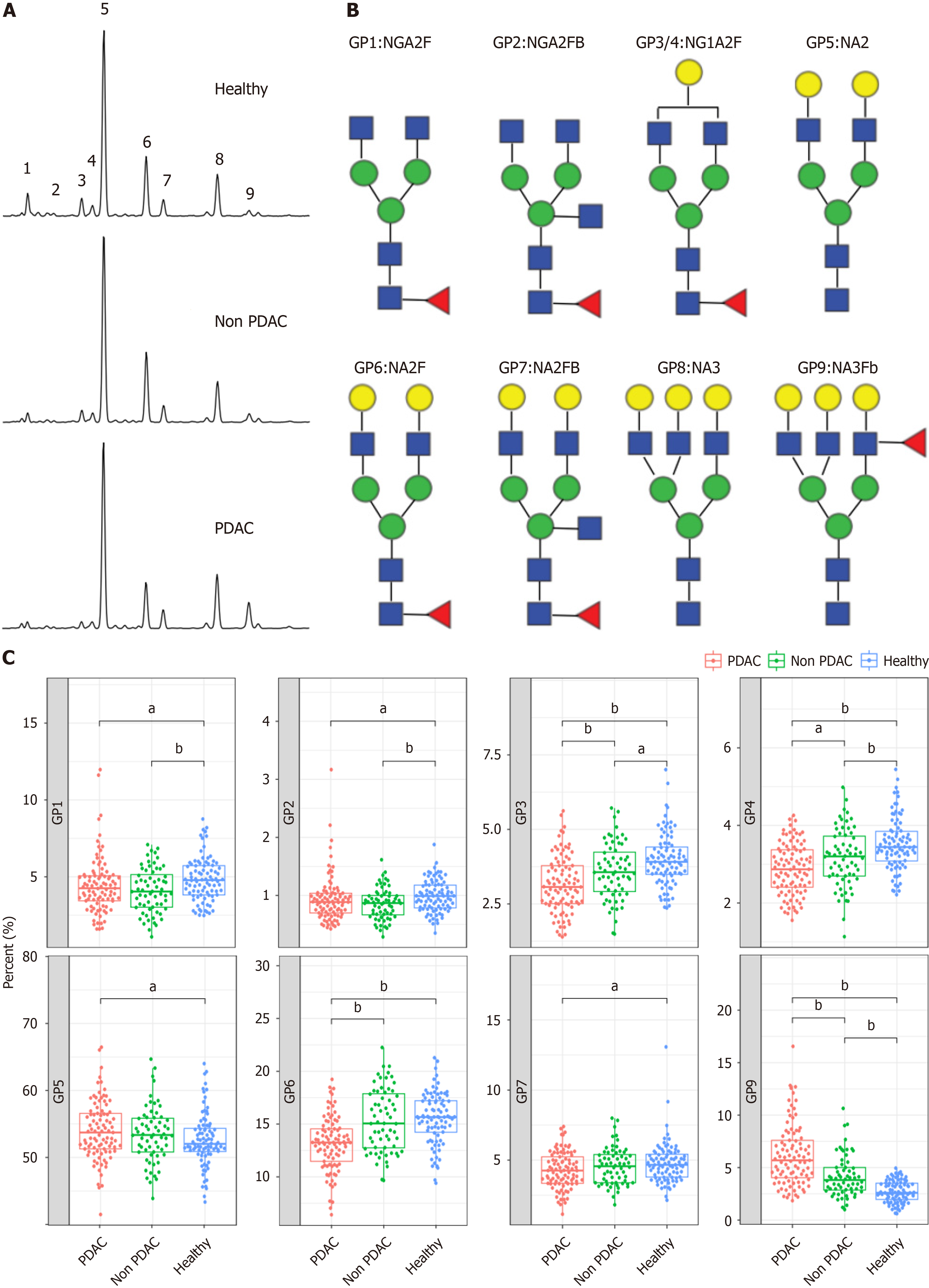
Figure 2 N-glycome profile from desialylated serum.
A: Typical desialylated N-glycan profiles from the total serum protein in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), patients without PDAC, and healthy participants; B: Structure of nine N-glycan peaks (GPs). GP1 indicates an agalacto core α-1,6 fucosylated biantennary glycan (NGA2F), GP2 indicates an agalacto core α-1,6 fucosylated bisecting bian tennary glycan (NGA2FB), GP3 and GP4 indicate a single agalacto core α-1,6 fucosylated biantennary glycan (NG1A2F), GP5 indicates a bigalacto biantennary glycan (NA2), GP6 indicates a bigalacto core α-1,6 fucosylated biantennary glycan (NA2F), GP7 indicates a bigalacto core α-1,6 fucosylated bisecting biantennary glycan (NA2FB), GP8 indicates a triantennary glycan (NA3), and GP9 indicates a branching α-1,3 fucosylated triantennary glycan (NA3Fb); C: N-glycan analysis in the three groups of patients. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. GPs: Glycan peaks; PDAC: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
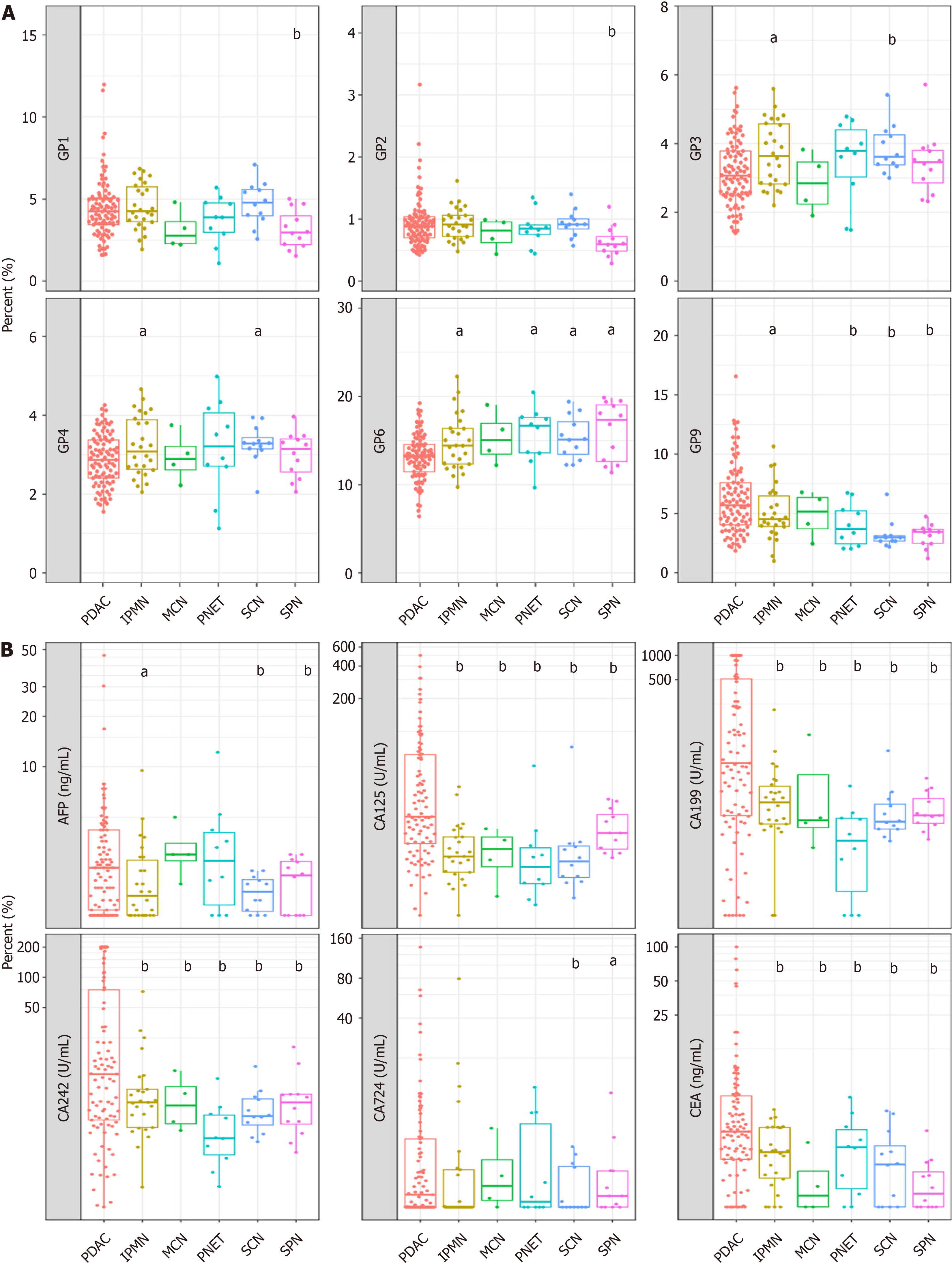
Figure 3 Verification of N-glycan peaks for distinguishing malignant pancreatic cancer (pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma) from non-pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cases.
A: N-glycan analysis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and non-PDAC (intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, mucinous cyst neoplasm, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, serous cyst adenoma, solid pseudopapillary neoplasm) groups; B: Tumor markers analysis in PDAC and non-PDAC groups. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. GPs: Glycan peaks; PDAC: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; SPN: Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm; PNET: Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; SCN: Serous cyst adenoma; IPMN: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; MCN: Mucinous cyst neoplasm; AFP: Alpha fetoprotein; CEA: Carcinoembryonic antigen; CA19-9: Cancer antigen 19-9.
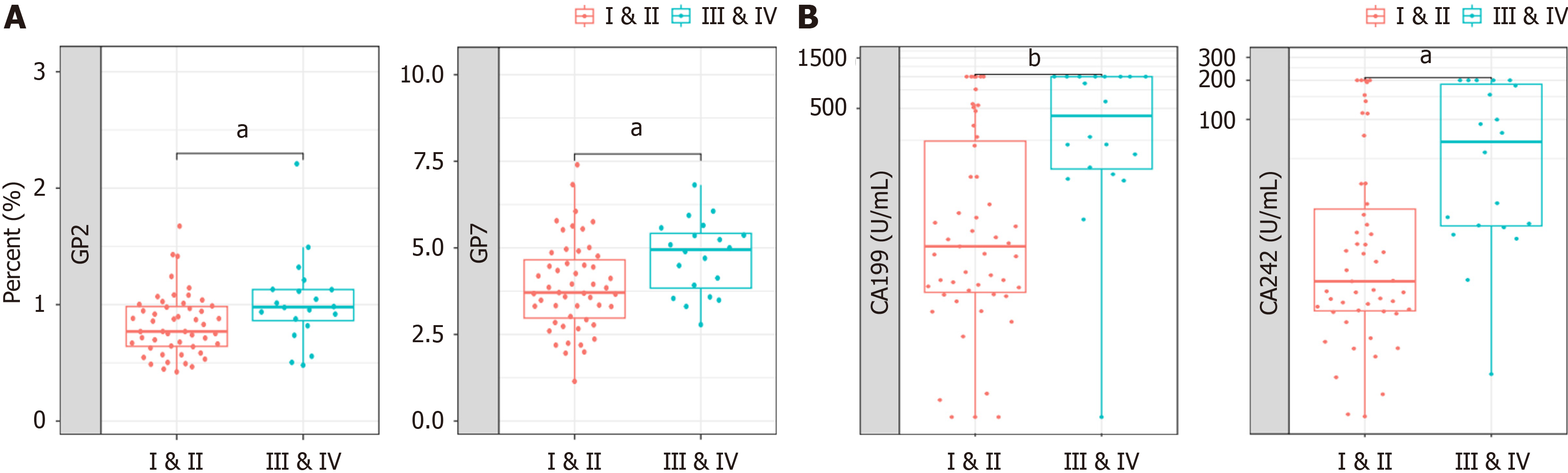
Figure 4 Comparative analysis of early-stage and advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
A: Serum glycan peak (GP)2 and GP7 levels differ significantly between early (stage I and II) and advanced (stage III and IV) pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; B: Serum cancer antigen (CA)19-9 and CA242 levels differ significantly between early (stage I and II) and advanced (stage III and IV) pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. GPs: Glycan peaks; CA19-9: Cancer antigen 19-9.
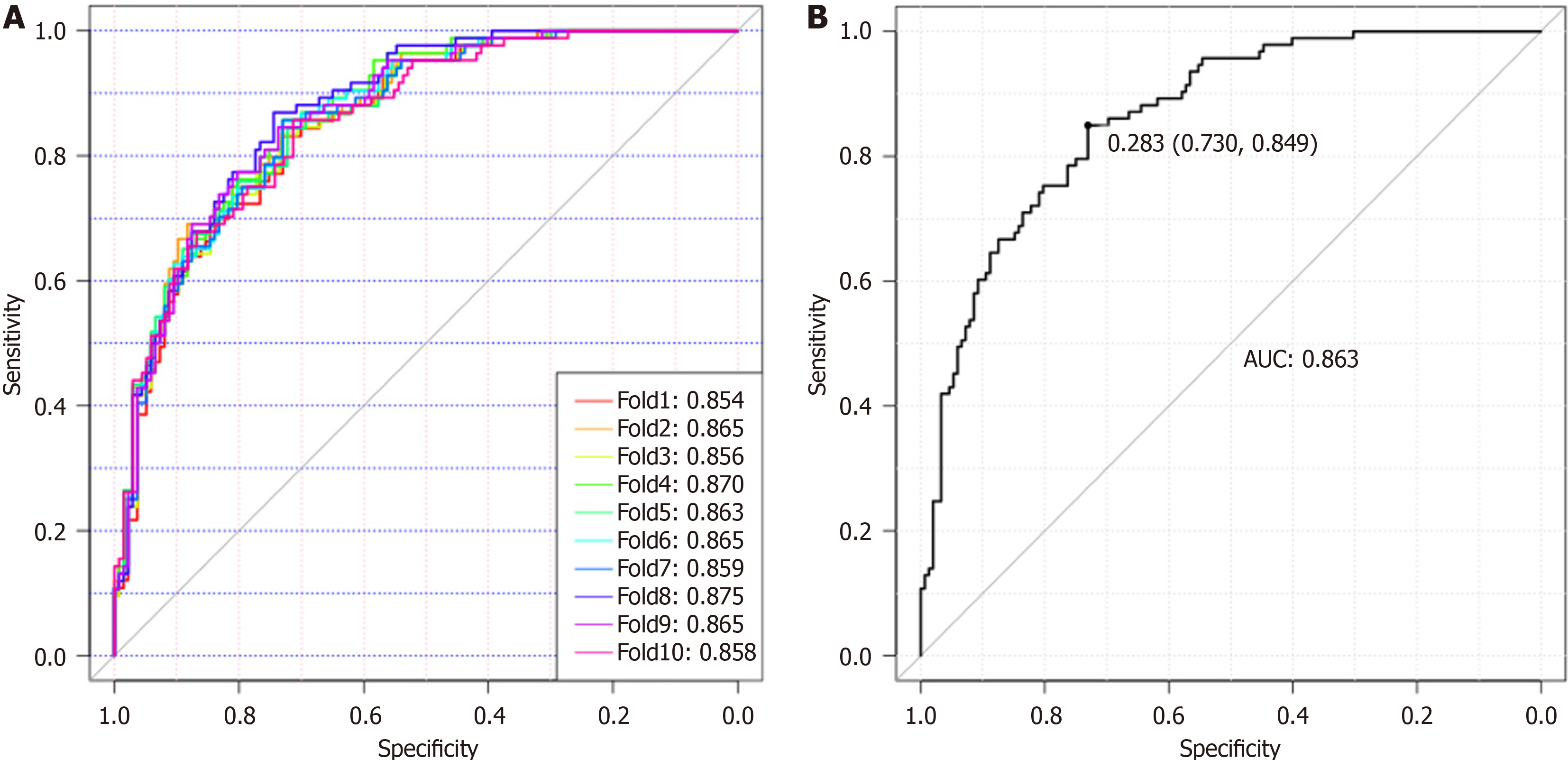
Figure 5 Glyco-model for detecting patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
A: Diagnostic model for detecting patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) using the 10-fold cross-validation diagnostic model; B: The diagnostic values for Glyco-model to distinguish patients with PDAC from those of non-PDAC. AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Wen YR, Lin XW, Zhou YW, Xu L, Zhang JL, Chen CY, He J. N-glycan biosignatures as a potential diagnostic biomarker for early-stage pancreatic cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(3): 659-669
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i3/659.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i3.659