Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jun 16, 2017; 9(6): 282-295
Published online Jun 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i6.282
Published online Jun 16, 2017. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i6.282
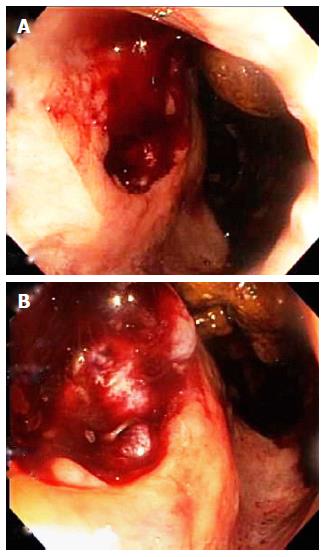
Figure 2 Colonoscopy reveals, just above the anorectal margin (line between pale skin and red mucosa), a multinodular, friable, 2.
5-cm-wide, hemorrhagic, mass that replaces the normal prostate and overlying rectum (A, B). Tissue surrounding the lesion appears to be normal. Biopsy of this mass revealed bladder urothelial carcinoma. The finding of bladder urothelial carcinoma in the normal location of the prostate and overlying rectum, just inferior to the bladder cancer, is consistent with direct extension of bladder urothelial carcinoma into the immediately adjacent prostate and its overlying rectal mucosa. This cancer location is highly consistent with the abdominopelvic computed tomography findings (Figure 1).
- Citation: Aneese AM, Manuballa V, Amin M, Cappell MS. Bladder urothelial carcinoma extending to rectal mucosa and presenting with rectal bleeding. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017; 9(6): 282-295
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v9/i6/282.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v9.i6.282