Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jun 16, 2021; 13(6): 170-183
Published online Jun 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i6.170
Published online Jun 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i6.170
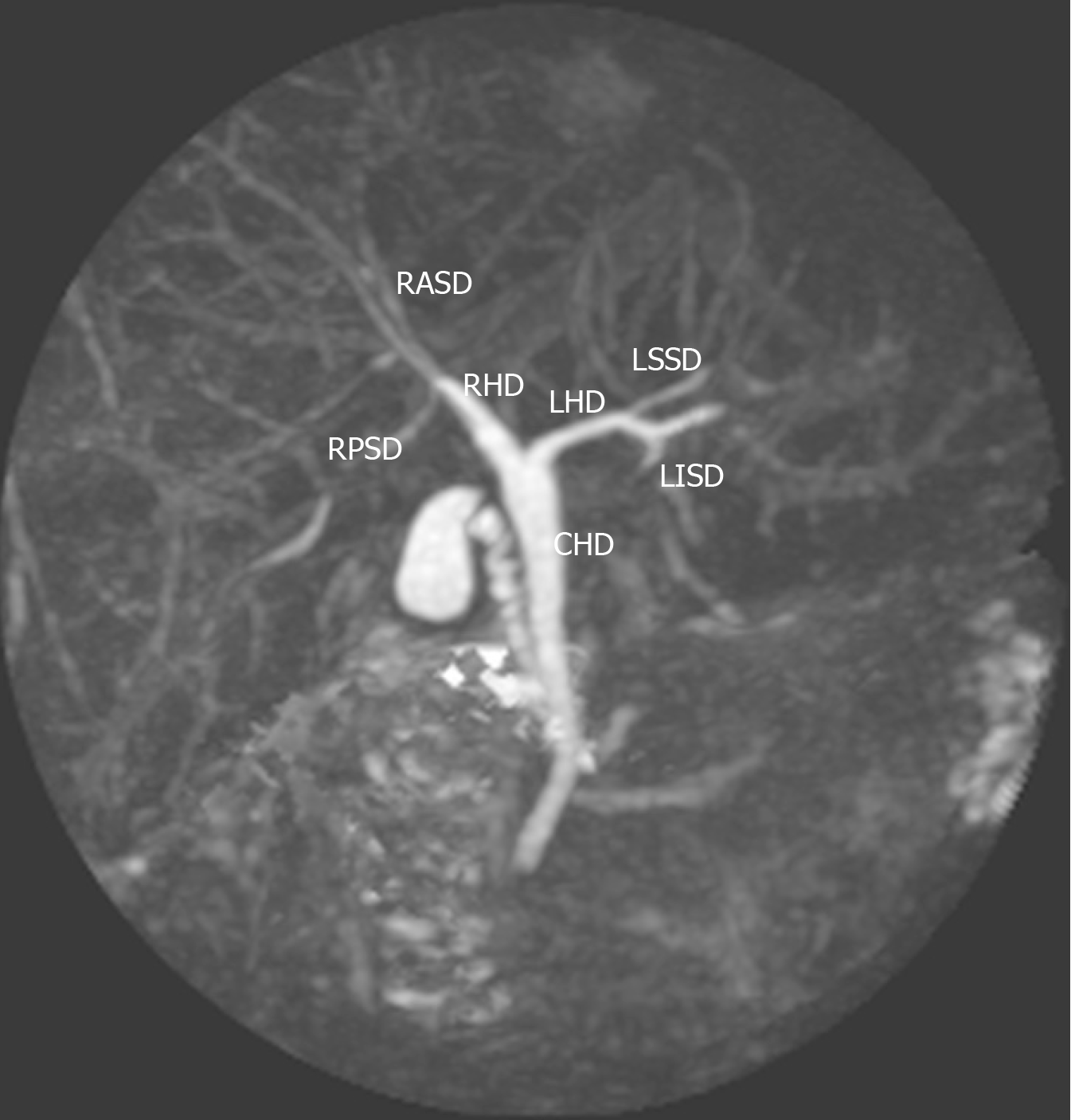
Figure 1 Type 1 (classic) variant.
In this system, the right hepatic duct (RHD) is formed by two tributaries: the right posterior sectional duct that drains segments VI and VII coursing in a horizontal plane and the right anterior sectional duct draining segments V and VIII and coursing in a vertical plane. The left hepatic duct (LHD) is formed by two tributaries: the left superior sectional duct that drains segment IVa joins the left inferior sectional duct that drains segment II, III and Ivb. The RHD and LHD then join to form the common hepatic duct (CHD). RASD: Right anterior sectional duct; RPSD: Right posterior sectional duct; RHD: Right hepatic duct; LHD: Left hepatic duct; CHD: Common hepatic duct; LSSD: Left superior sectional duct; LISD: Left inferior sectional duct.
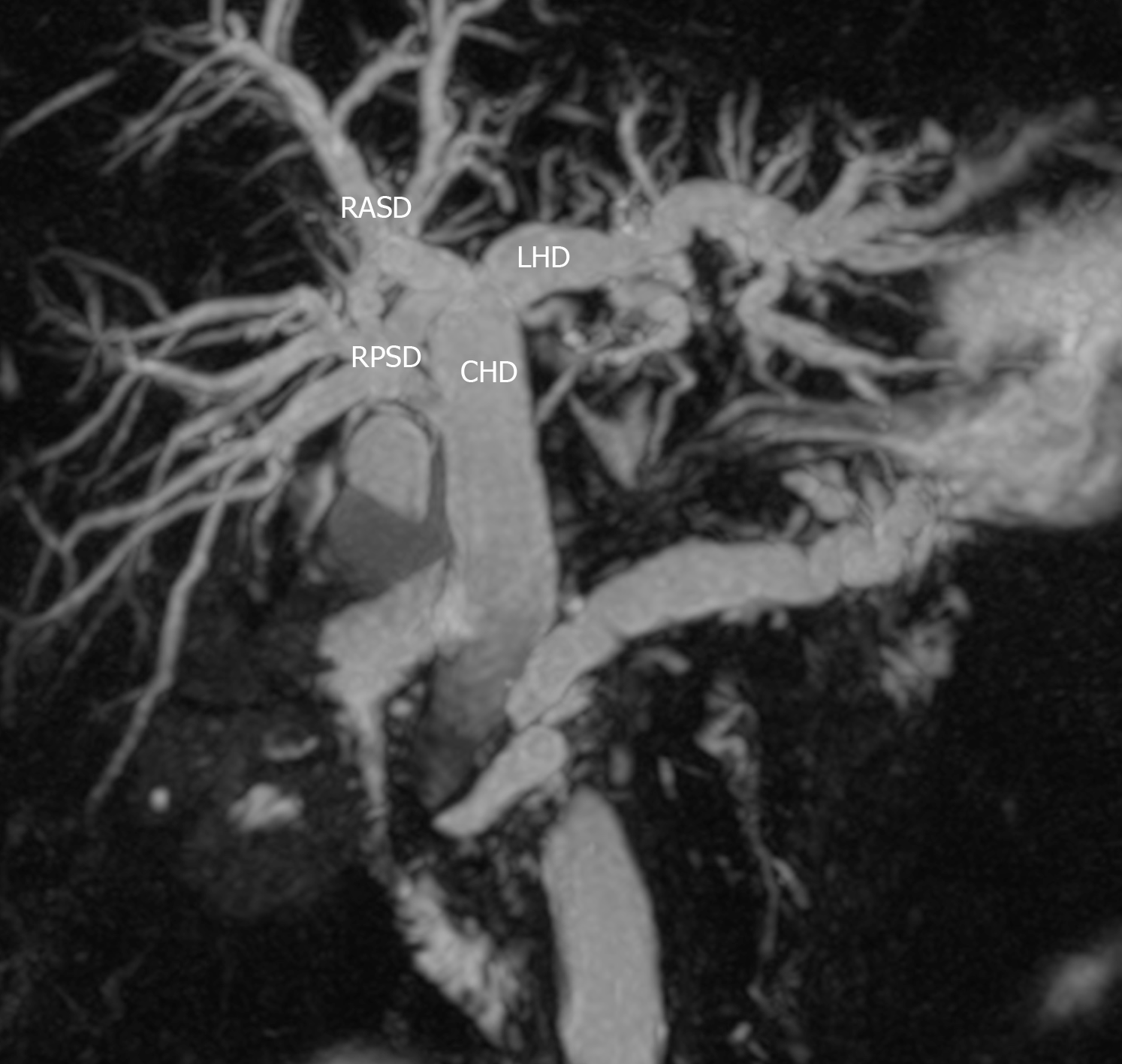
Figure 2 Type 2 variant.
A trifurcation that is formed by the union of the right anterior sectoral duct, right posterior sectoral duct and the left hepatic duct. RASD: Right anterior sectional duct; RPSD: Right posterior sectional duct; LHD: Left hepatic duct; CHD: Common hepatic duct.
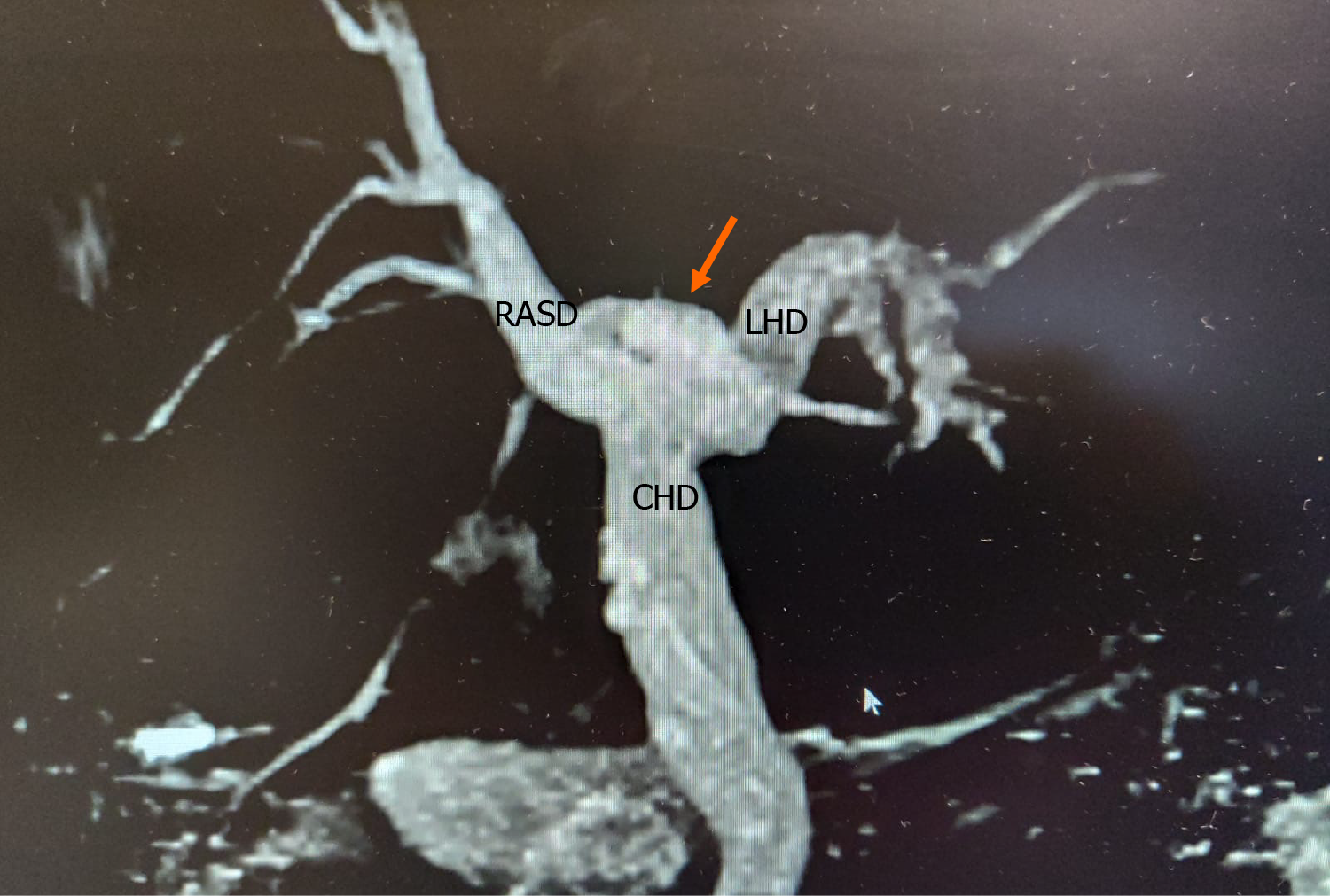
Figure 3 Type 3 variant.
The right posterior sectoral duct (arrow) drains directly into left hepatic duct. RASD: Right anterior sectional duct; LHD: Left hepatic duct; CHD: Common hepatic duct.
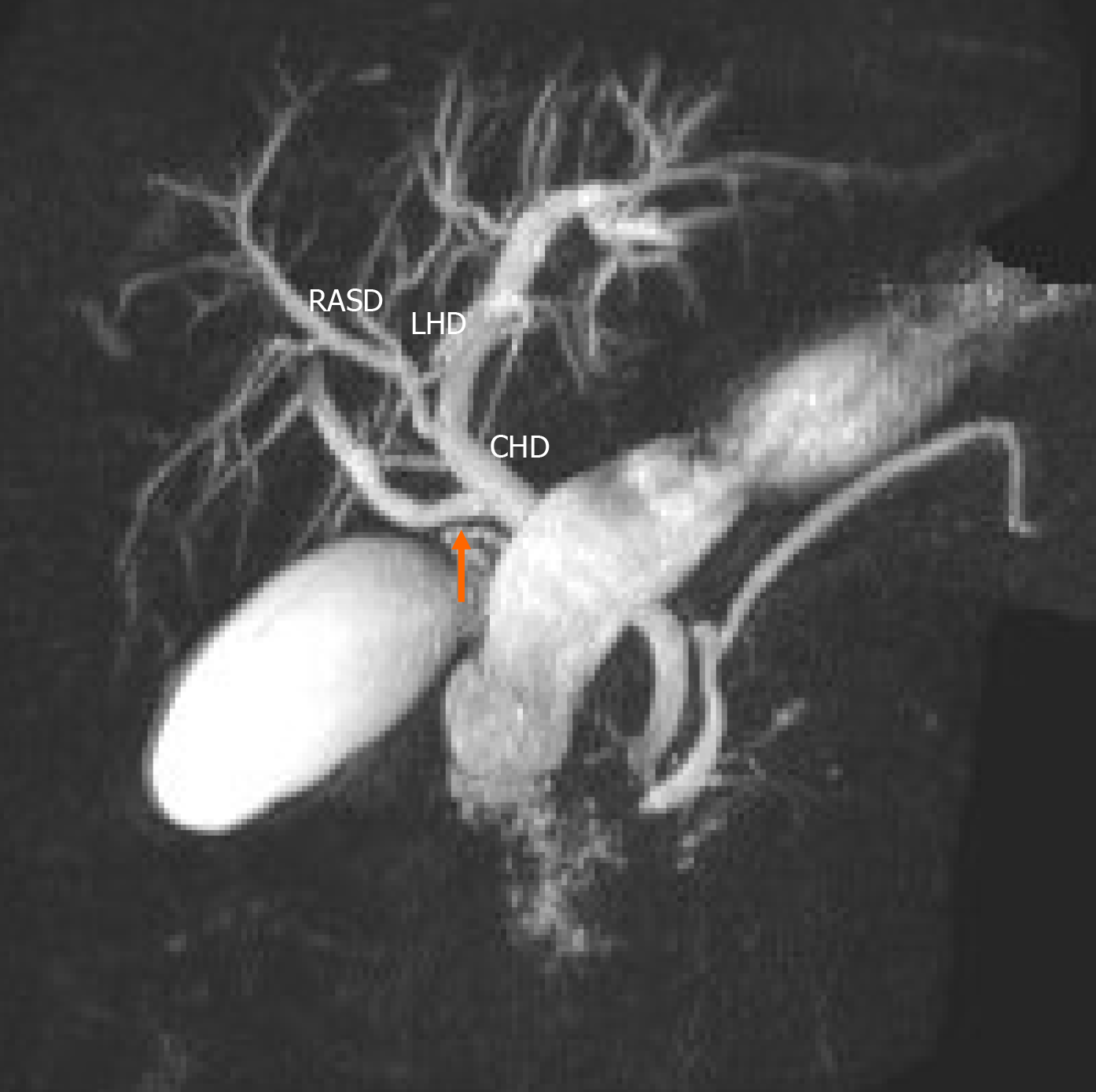
Figure 4 Type 4 variant.
An aberrant right posterior sectoral duct (arrow) can be seen emptying directly into the common hepatic duct. RASD: Right anterior sectional duct; LHD: Left hepatic duct; CHD: Common hepatic duct.
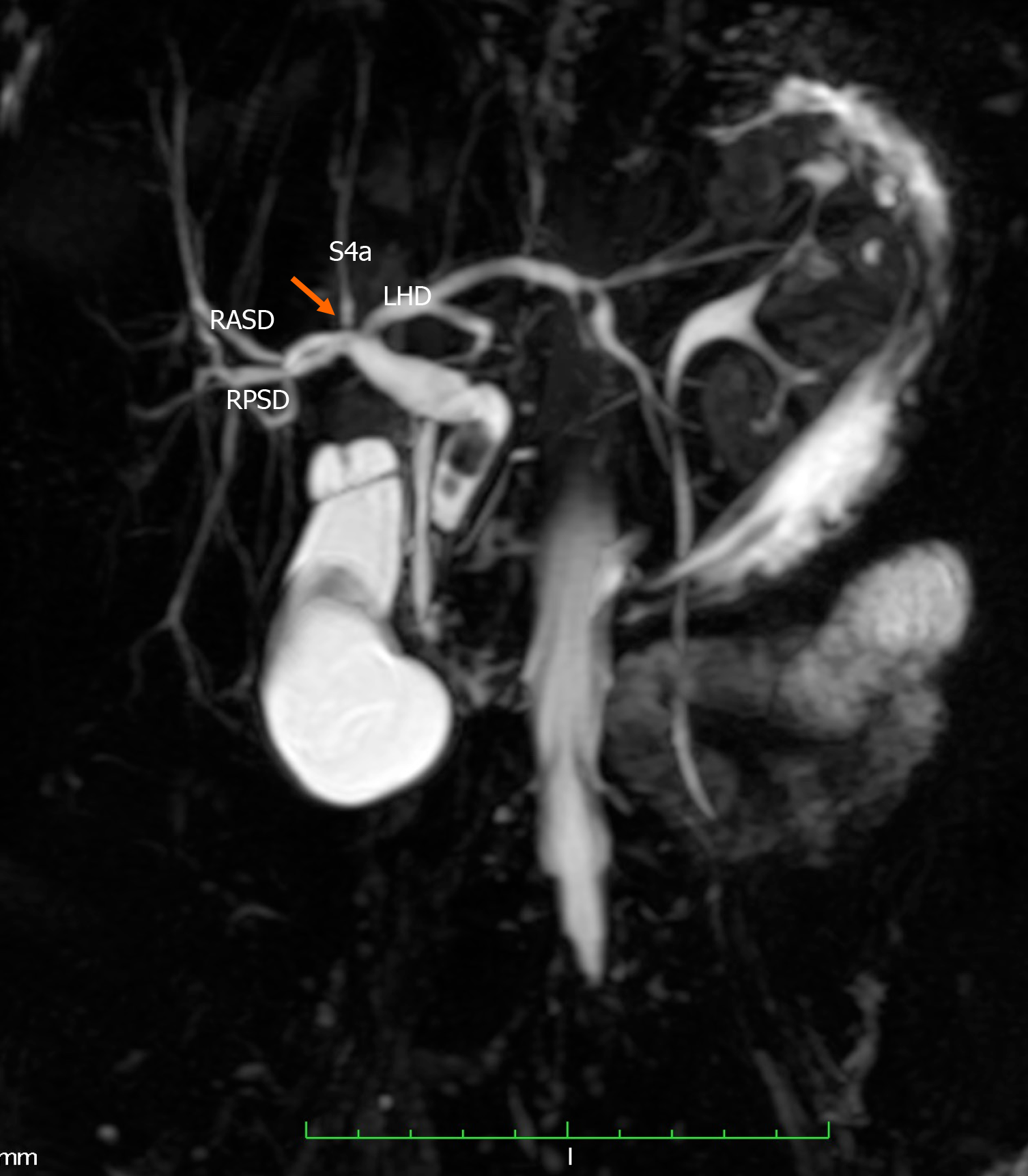
Figure 5 Undefined variant.
The image shows a quadrification (arrow) that is formed by the union of the right anterior sectoral duct, right posterior sectoral duct, segment IVa duct (S4a) and the left hepatic duct (LHD). RASD: Right anterior sectional duct; RPSD: Right posterior sectional duct; LHD: Left hepatic duct; S4a: Segment Iva.
- Citation: Cawich SO, Sinanan A, Deshpande RR, Gardner MT, Pearce NW, Naraynsingh V. Anatomic variations of the intra-hepatic biliary tree in the Caribbean: A systematic review. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 13(6): 170-183
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v13/i6/170.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v13.i6.170