Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
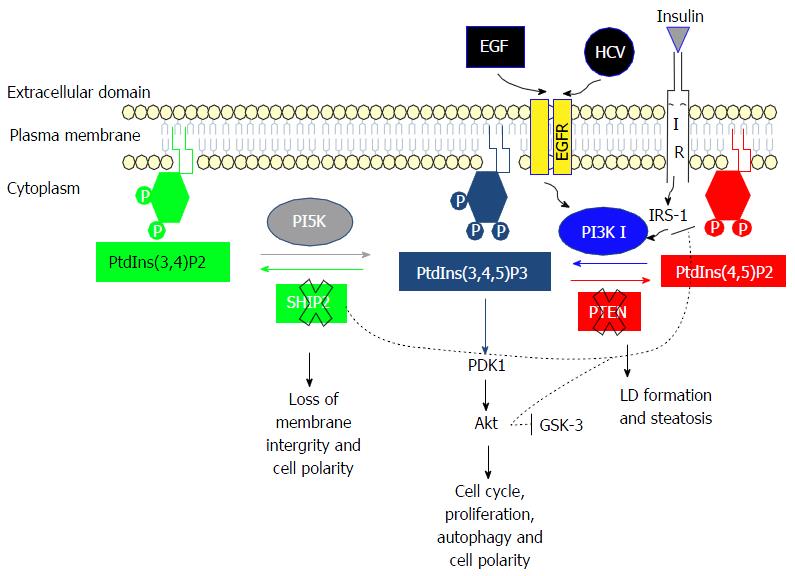
Figure 3 PI3K/Akt pathway and its activation by hepatitis C virus infection.
When EGF binds to EGFR this will activate PI3K I. PI3K activation will increase the level of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 to phosphorylate Akt and induce cell proliferation and cell polarity. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is able to bind EGFR at its entry into a cell, thus increasing PI3K activation and the level of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3, the latter being sustained by the down-regulation of SHIP2 and PTEN. The down-regulation of SHIP2 by HCV induces a loss of membrane integrity and cell polarity, while the down regulation of PTEN induces lipid droplet (LD) formation and steatosis. PtdIns: Phosphatidylinositol; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; SHIP2: SH2-containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor.
- Citation: Awad A, Gassama-Diagne A. PI3K/SHIP2/PTEN pathway in cell polarity and hepatitis C virus pathogenesis. World J Hepatol 2017; 9(1): 18-29
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v9/i1/18.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v9.i1.18