Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Jan 28, 2016; 8(3): 162-182
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i3.162
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i3.162
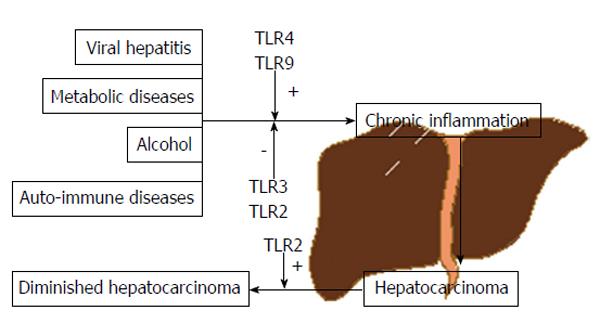
Figure 6 Toll-like receptors influence on the pathway to hepatocarcinoma.
Several factors are known to contribute to the carcinogenic process including viral hepatitis, alcohol, auto-immune or metabolic diseases, among others and the link between all this factors is chronic inflammation which, in turn, is an important hepatocarcinoma’s percursor. Moreover, innate immunity represents an important player in this equation with TLRs such as 4 and 9 having, mainly, a positive contribution to hepatocarcinogenesis and TLR3, essentially, a negative/protective one. TLR2 still presents an ambiguous role, possibly depending on liver’s stage in the inflammation-cirrhosis-carcinoma axis to exert its pro-tumorigenic or anti-tumorigenic capacity. TLR: Toll-like receptor.
- Citation: Lopes JAG, Borges-Canha M, Pimentel-Nunes P. Innate immunity and hepatocarcinoma: Can toll-like receptors open the door to oncogenesis? World J Hepatol 2016; 8(3): 162-182
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i3/162.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i3.162