Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. May 28, 2015; 7(9): 1258-1264
Published online May 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i9.1258
Published online May 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i9.1258
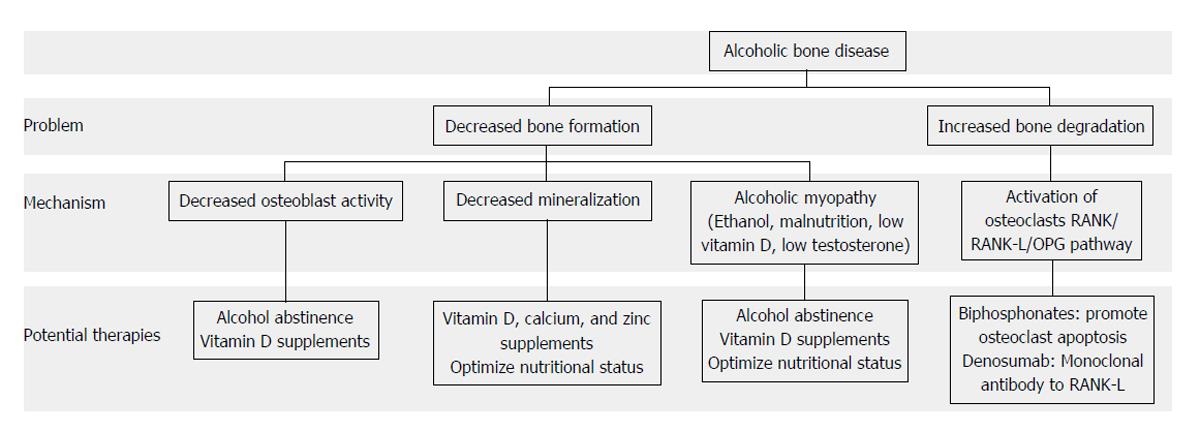
Figure 2 Pathogenesis of alcoholic bone disease and potential therapies.
Bone disease in alcoholic patients is due basically to decreased bone formation (decreased osteoblast activity and poor mineralization) and increased bone degradation (increased osteoclast activity). Potential therapies should counteract these effects but the mainstay of treatment should be alcohol abstinence. RANK: Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B; RANK-L: RANK ligand; OPG: Osteoprotegerin.
- Citation: González-Reimers E, Quintero-Platt G, Rodríguez-Rodríguez E, Martínez-Riera A, Alvisa-Negrín J, Santolaria-Fernández F. Bone changes in alcoholic liver disease. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(9): 1258-1264
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i9/1258.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i9.1258