Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Aug 27, 2025; 17(8): 107456
Published online Aug 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i8.107456
Published online Aug 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i8.107456
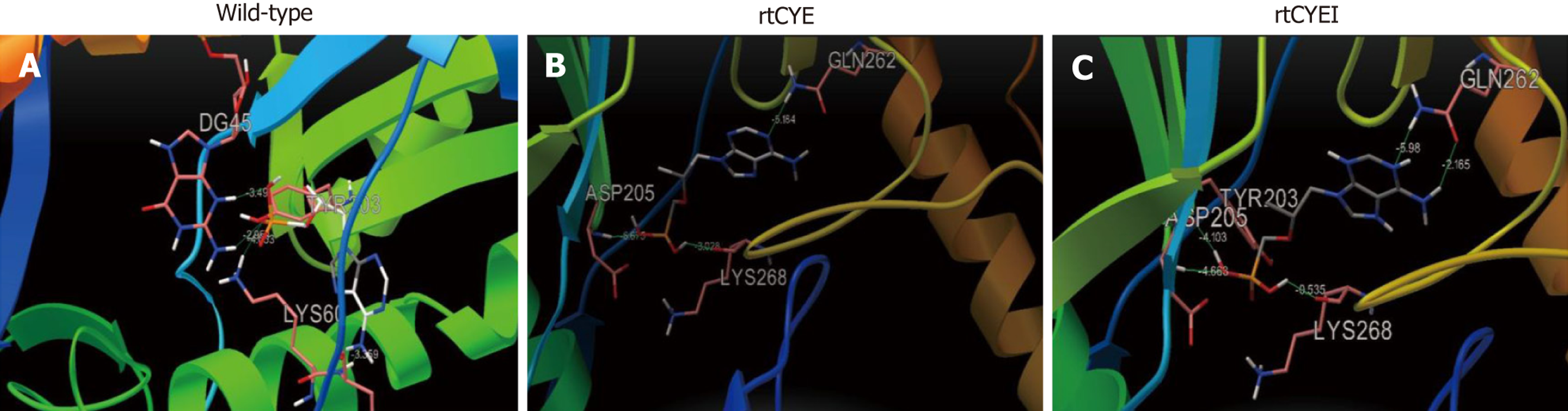
Figure 3 Three-dimensional structures of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-binding domains of viral reverse-transcriptase.
The effects of rtS106C+H126Y+D134E (rtCYE), and rtS106C+H126Y+D134E+L269I (rtCYEI) mutations on the binding ability of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) reverse transcriptase (RT) region to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) were evaluated using a homology model constructed based on the crystal structure of human immunodeficiency virus RT. A: The binding domains of the wild-type with TDF; B: The rtCYE mutant with TDF; C: The rtCYEI mutant with TDF. TDF ligand and interacting residues are shown in stick format. rtCYE: rtS106C+H126Y+D134E; rtCYEI: rtS106C+H126Y+D134E+L269I.
- Citation: Si LL, Fan ZP, Liu WH, Chen RJ, Chen XY, Ji D, Li L, Chen C, Liao H, Wang J, Xu DP, Zhao J, Liu Y. Hepatitis B virus rtCYE/rtCYEI mutations may contribute limited tenofovir resistance: Analysis of a large sample of Chinese patients. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(8): 107456
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i8/107456.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i8.107456