Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2025; 17(7): 106795
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106795
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106795
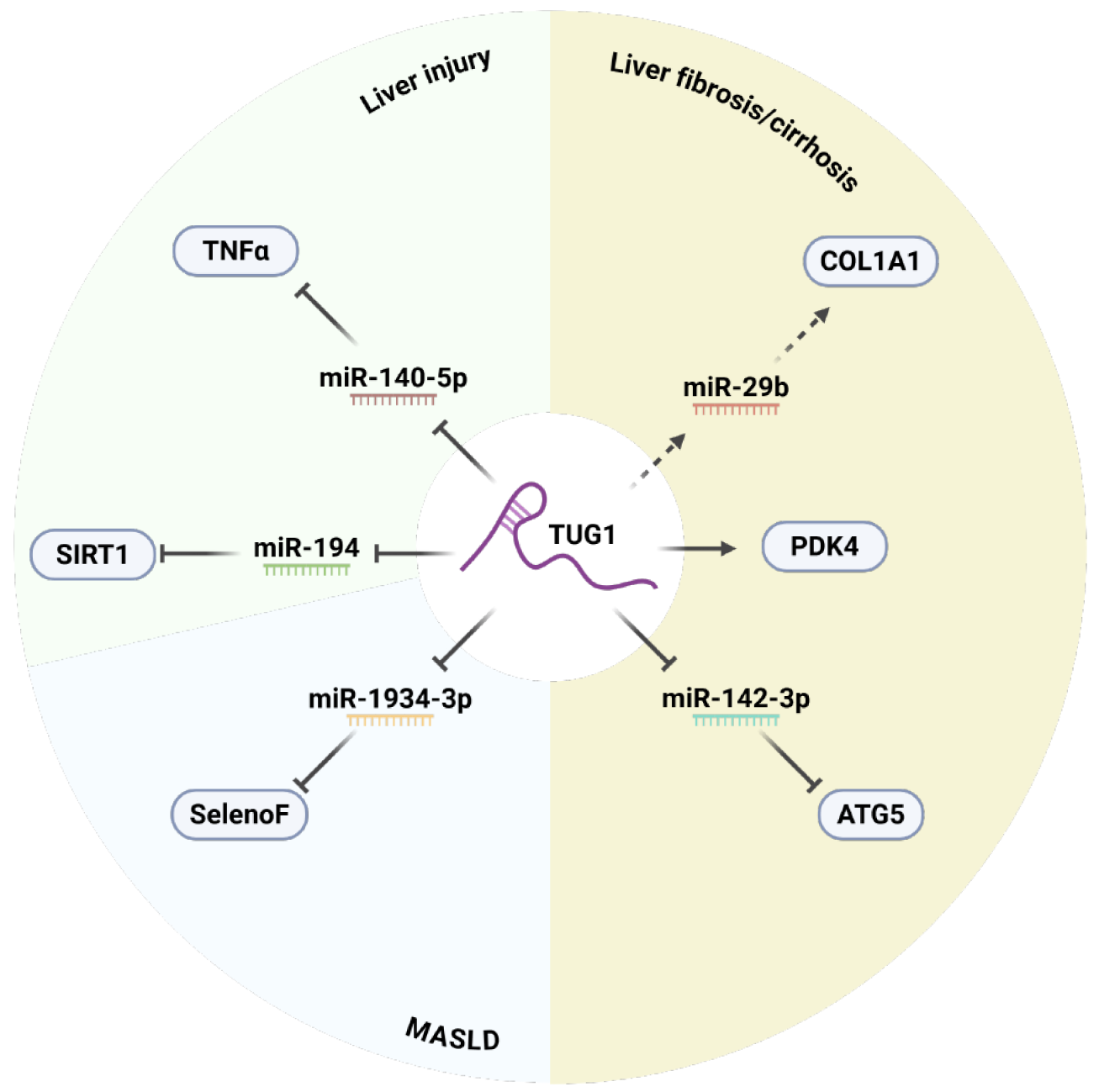
Figure 3 Taurine-upregulated gene 1's involvement in liver pathology.
This diagram illustrates the multifaceted role of taurine-upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) in liver injury, fibrosis/cirrhosis, and metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). TUG1 interacts with various molecules, including microRNAs (miRNAs) (miR-140-5p, miR-29b, miR-194, miR-1934-3p, miR-142-3p), proteins [tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, collagen type I alpha 1 (COL1A1), sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), selenoprotein F, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4), autophagy protein 5 (ATG5)], and cellular processes, contributing to the progression of liver diseases. In liver injury, TUG1 is shown to influence TNF-α signaling and SIRT1 activity. In liver fibrosis/cirrhosis, TUG1 affects the expression of COL1A1. In MASLD, TUG1 modulates the expression of PDK4 and ATG5, which are key players in metabolic pathways. T-bars indicate repression, and arrows indicate activation or positive regulation (created in BioRender). ATG5: Autophagy protein 5; COL1A1: Collagen type I alpha 1; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease; MiRNAs: MicroRNAs; PDK4: Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4; SelenoF: Selenoprotein F; SIRT1: Sirtuin 1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; TUG1: Taurine upregulated gene 1.
- Citation: Boonto T, Ariyachet C. Deciphering the role of taurine-upregulated gene 1 in liver diseases: Mechanisms, clinical relevance, and emerging therapeutic opportunities. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(7): 106795
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i7/106795.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106795