Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2025; 17(6): 107931
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.107931
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.107931
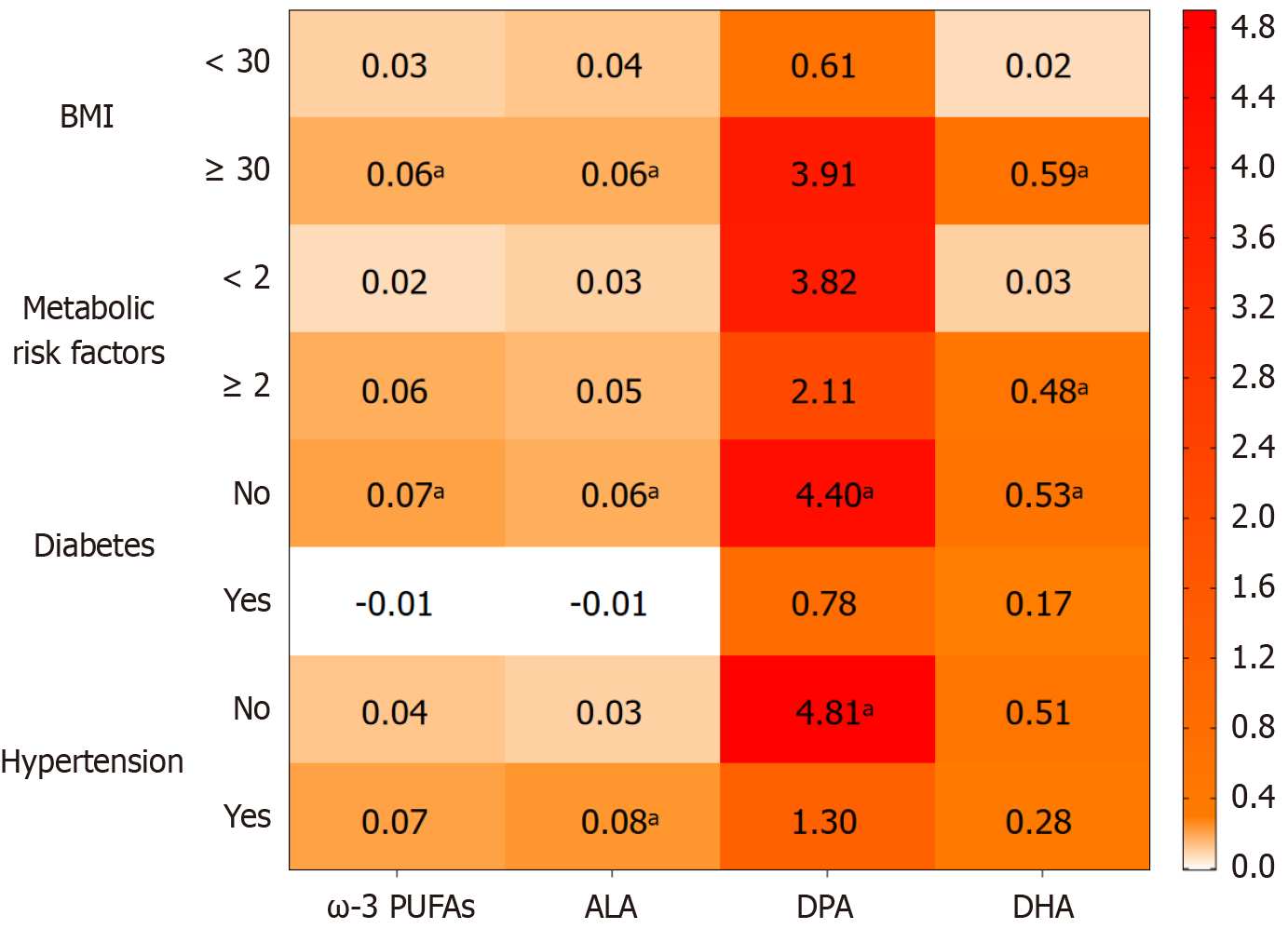
Figure 2 Association between dietary ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids intake and appendicular skeletal muscle mass index was stratified by body mass index, metabolic risk factors, diabetes status and hypertension status for adults from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2018.
Adjusted for age, sex, body mass index race and ethnicity, education status, marital status, income to poverty ratio, current smoker and current drinker.aThe correlation results were statistically significant. PUFAs: Polyunsaturated fatty acids; ASMI: Appendicular skeletal muscle mass index; ALA: α-Linolenic acid; DPA: Docosapentaenoic acid; DHA: Docosahexaenoic acid; BMI: Body mass index; PIR: Income to poverty ratio.
- Citation: Bie LZ, Wu C, Wang JL. Dietary ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake improves skeletal muscle mass in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: A nationwide cross-sectional study. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(6): 107931
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i6/107931.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.107931