Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. May 27, 2025; 17(5): 106124
Published online May 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.106124
Published online May 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.106124
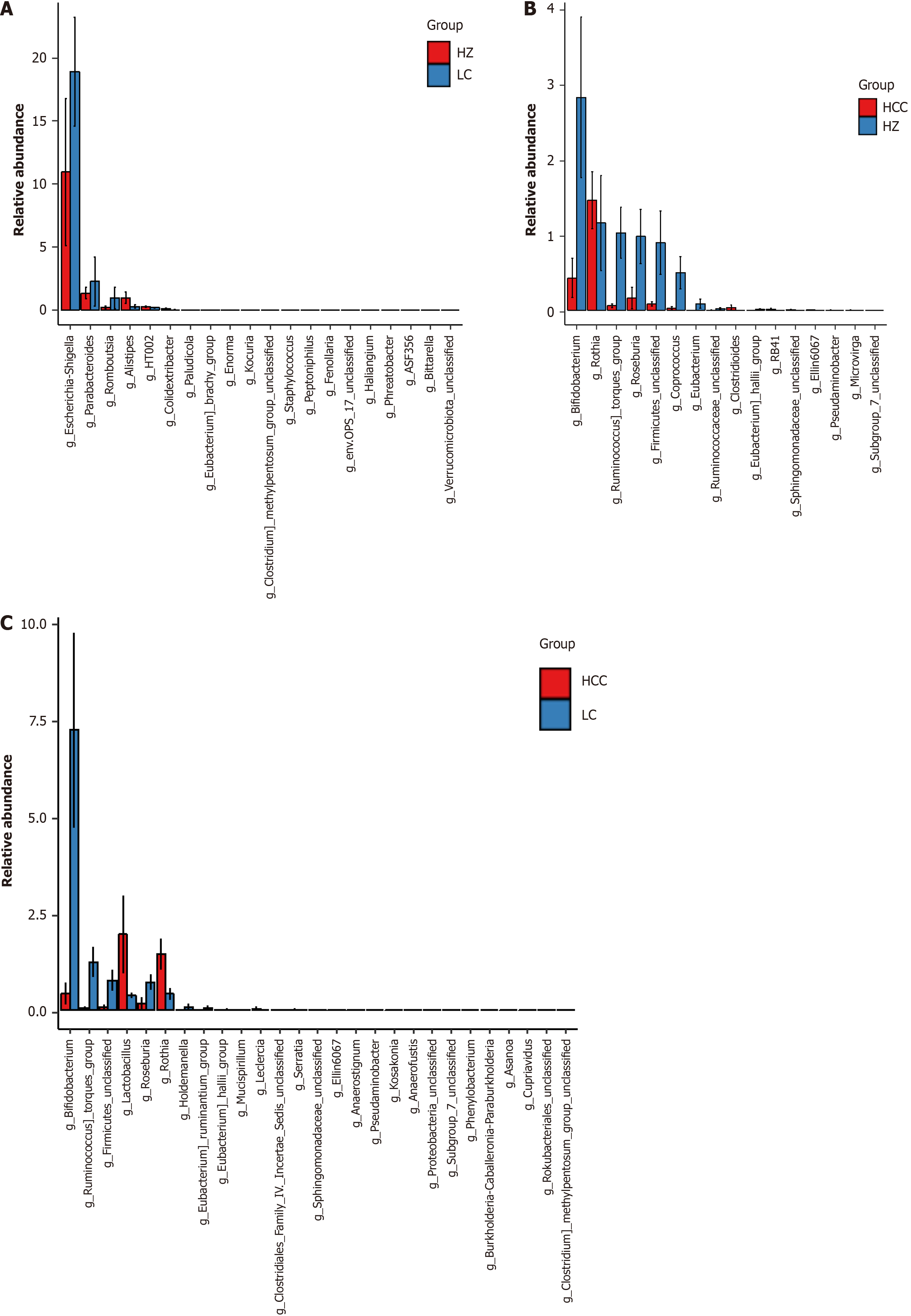
Figure 6 Analysis of differential species at genus level in chronic hepatitis B, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma groups.
A: Differential species analysis at the genus level between the chronic hepatitis B group and the cirrhosis group. In the figure, the X-axis lists differential species, arranged from left to right in order of decreasing abundance, and the Y-axis displays the relative abundance. The height of the bars visually quantifies the abundance of each differential species across the various groups; B: Differential species analysis at the genus level between the chronic hepatitis B group and the hepatocellular carcinoma group; C: Differential species analysis at the genus level between the hepatocellular carcinoma group and the liver cirrhosis group. HZ: Chronic hepatitis B group; LC: Liver cirrhosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Ma C, Yang J, Fu XN, Luo JY, Liu P, Zeng XL, Li XY, Zhang SL, Zheng S. Microbial characteristics of gut microbiome dysbiosis in patients with chronic liver disease. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(5): 106124
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i5/106124.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.106124