Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. May 27, 2025; 17(5): 106124
Published online May 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.106124
Published online May 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.106124
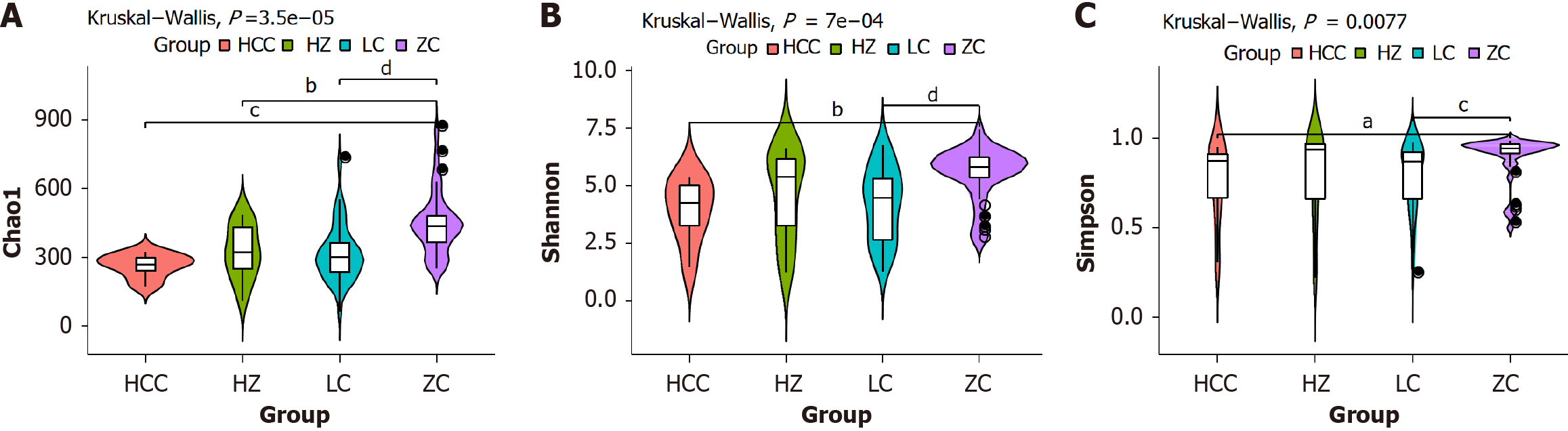
Figure 2 Analysis of gut microbiota diversity in healthy control group and C chronic liver disease liver disease groups.
The P value in the top left corner is derived from the Wilcoxon rank-sum test conducted across all groups depicted in the figure. Significant differences between pairwise groups are indicated by aP < 0.05, bP = 0.01, cP < 0.01, and dP < 0.01, while “ns” denotes no significant difference. A: The Chao1 index mainly reflects the number of species contained in the community, and the higher the value, the higher the estimated species richness in the community; B: The Shannon index mainly reflects the richness and evenness of species, and the larger the value, the higher the richness and evenness in the community; C: The Simpson index mainly reflects the diversity of species, and the higher the value, the higher the species diversity in the community. ZC: Healthy control group; HZ: Chronic hepatitis B group; LC: Liver cirrhosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Ma C, Yang J, Fu XN, Luo JY, Liu P, Zeng XL, Li XY, Zhang SL, Zheng S. Microbial characteristics of gut microbiome dysbiosis in patients with chronic liver disease. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(5): 106124
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i5/106124.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i5.106124