Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Apr 27, 2024; 16(4): 537-549
Published online Apr 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i4.537
Published online Apr 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i4.537
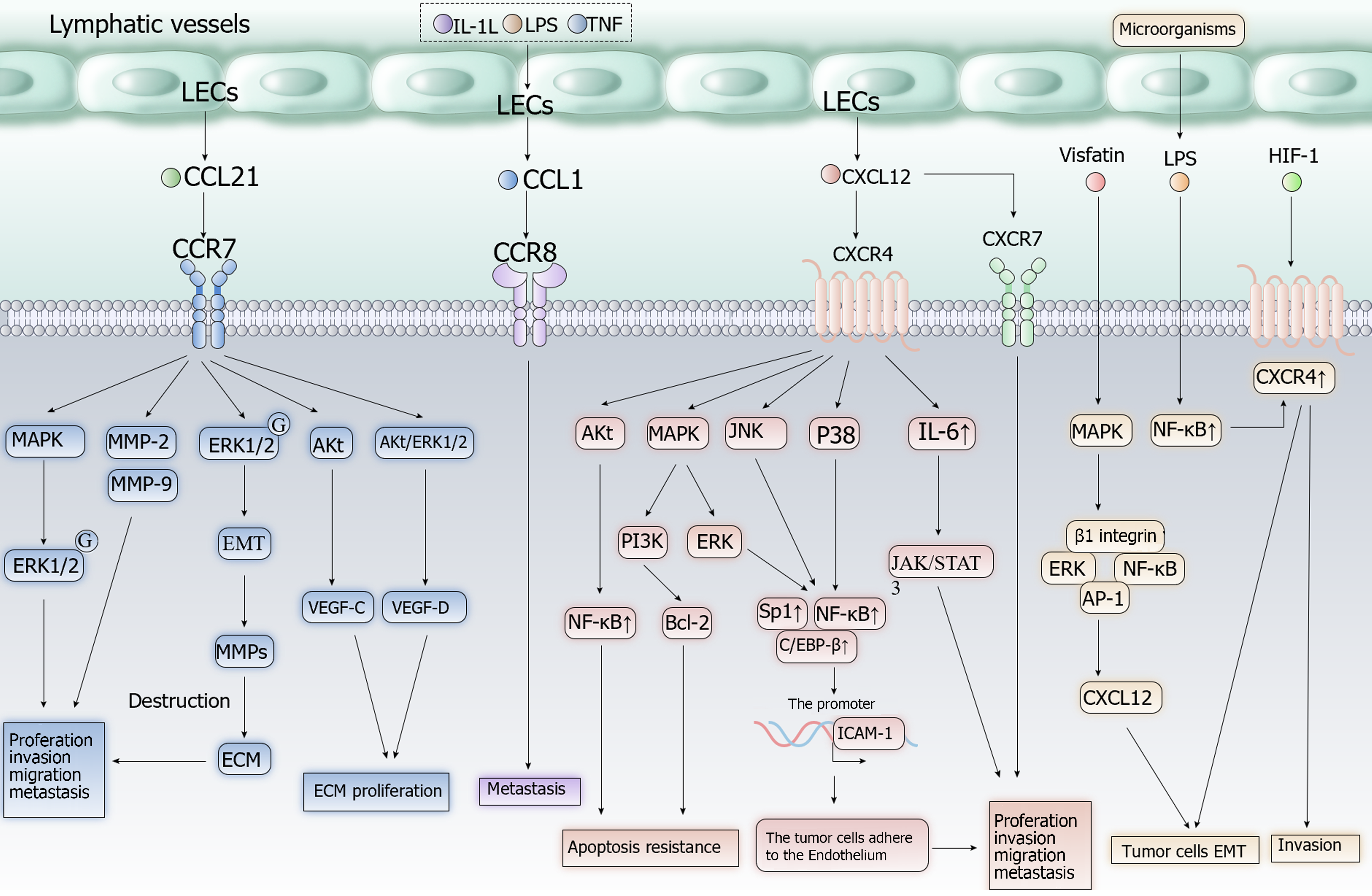
Figure 2 Cell signaling pathways of CXCL12/CXCR4, CCL21/CCR7, CCL1/CCR8 axis in tumor cells.
Proinflammatory mediators increase the production of CCL1 by lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) and enhance the migration of tumor cells towards LECs. CCL1/CCR8 Axis is involved in recruiting Treg cells into the tumor microenvironment and converting CD4+ T cells into Treg cells. CXCR4 expression caused by products of the microbiota and chronic hypoxia stimulates tumor proliferation and migration of LECs into lymphatic vessels. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor can enhances the effect of CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis. The CCL21/CCR7 axis induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes proliferation of tumor cells, LECs and extracellular matrix. Akt: Serine/threonine kinase; AP-1: Activated protein 1; Bcl-2: Anti-apoptotic gene; ECM: Extracellular matrix; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; HIF-1: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IL-1L: Interleukin 1L; IL-6: Interleukin 6; JAK/STAT: Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription; JNK: Jun N-terminal kinase; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
- Citation: Li JJ, Mao JX, Zhong HX, Zhao YY, Teng F, Lu XY, Zhu LY, Gao Y, Fu H, Guo WY. Multifaceted roles of lymphatic and blood endothelial cells in the tumor microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive review. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(4): 537-549
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i4/537.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i4.537