Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2023; 15(10): 1091-1108
Published online Oct 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i10.1091
Published online Oct 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i10.1091
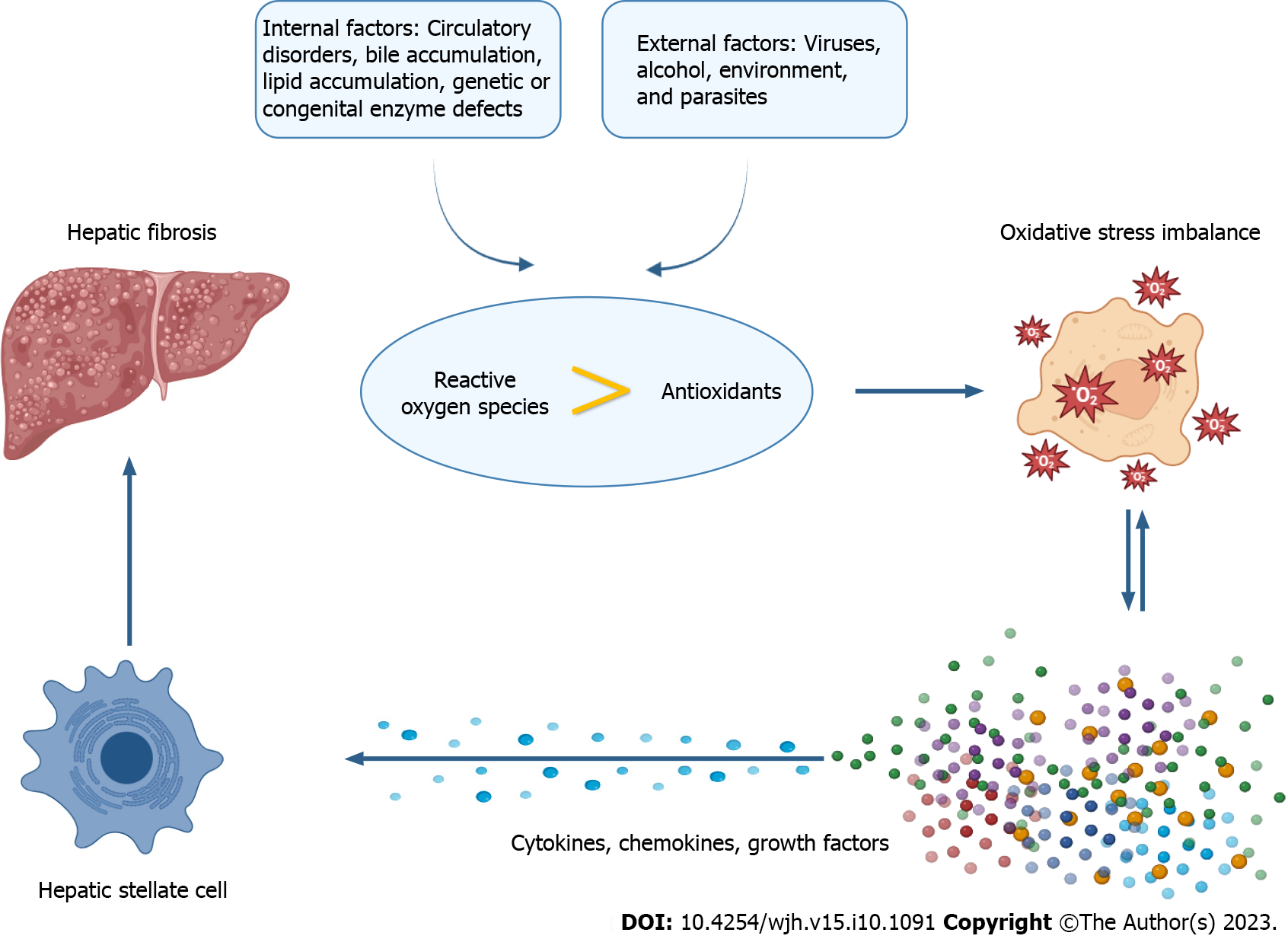
Figure 2 The mechanism of oxidative stress-mediated hepatic fibrosis.
Circulatory disorders, bile accumulation, lipid accumulation, genetic or congenital enzyme defects, as well as factors such as viruses, alcohol, environment, and parasites, can all contribute to an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and the body’s ability to remove them, resulting in oxidative stress. This imbalance can further stimulate the secretion of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors, which in turn activate hepatic stellate cells and contribute to the development of hepatic fibrosis.
- Citation: Li Z, Zhu JF, Ouyang H. Progress on traditional Chinese medicine in improving hepatic fibrosis through inhibiting oxidative stress. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(10): 1091-1108
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i10/1091.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i10.1091