Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2014; 6(5): 526-539
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.526
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.526
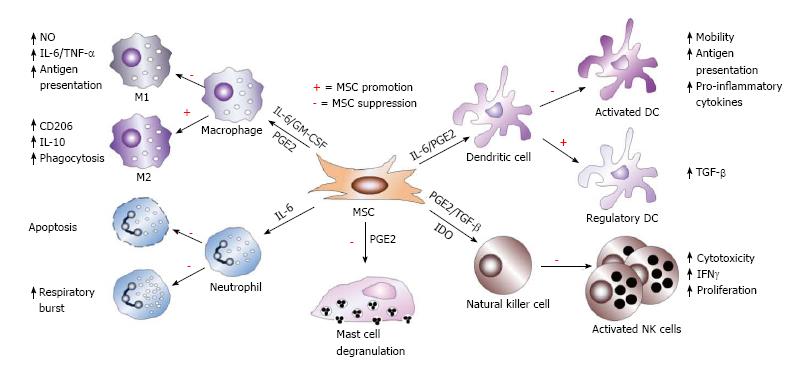
Figure 3 Mesenchymal stem cell immunosuppression of innate immune cells.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) utilize diverse molecular mechanisms to suppress innate immune cells. MSCs suppress macrophage polarization to M1, though favors M2 polarization. MSCs inhibit mast cell degranulation of histamine-containing granules and inhibit NK cell and DC activation, differentiation, and effector functions. MSC-derived PGE2 contributes to all of these effects. MSC-produced IL-6 suppresses neutrophil apoptosis and respiratory burst and also contributes to inhibition of DC function. In the presence of IL-6 and GM-CSF, MSCs also affect macrophage function, while TGF-β and IDO suppress NK cell function. In addition, MSCs also favor the generation of regulatory DCs.
- Citation: Glenn JD, Whartenby KA. Mesenchymal stem cells: Emerging mechanisms of immunomodulation and therapy. World J Stem Cells 2014; 6(5): 526-539
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v6/i5/526.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.526