Copyright
©2012 Baishideng.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2012; 4(7): 71-79
Published online Jul 26, 2012. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i7.71
Published online Jul 26, 2012. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i7.71
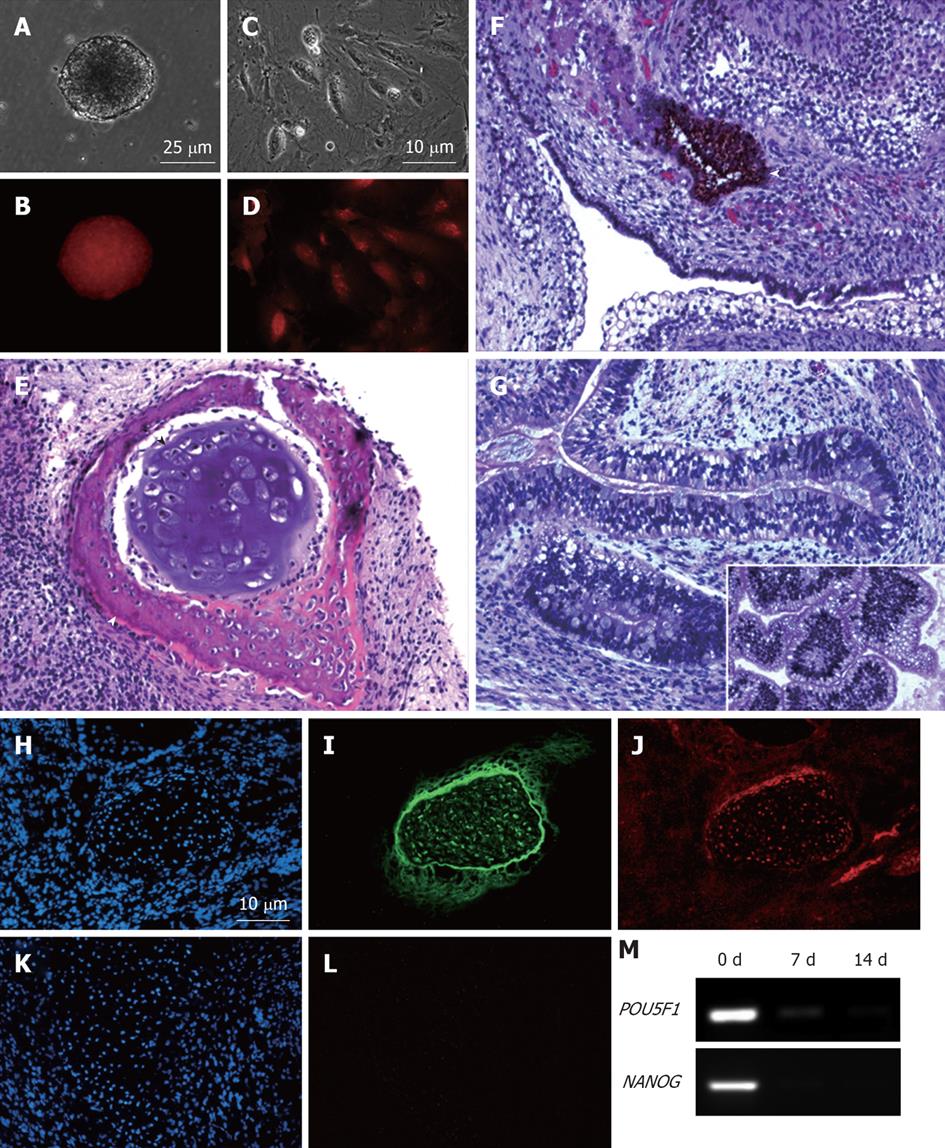
Figure 5 MEL2-mCherry line is capable of full-spectrum differentiation and retains high levels of mCherry fluorescence.
(A) Brightfield and (B) Red fluorescence images of a typical EB derived from the MEL2-mCherry line showing robust uniform fluorescence. (C) Brightfield image and (D) Red mCherry fluorescence of cells dissociated from MEL2-mCherry human embryonic stem cell (hESC) derived embryoid bodies. (E-G) Teratoma sections showing the presence of derivatives of all three major germ layer: (E) Mesoderm-derived cartilage (black arrowhead) and bone (white arrowhead); (F) Ectodermally-derived neural epithelium, including melanised retinal epithelium-like structures and (G) Endodermally-derived gut-like epithelium and (inset shows transverse section through the intestinal crypt-like structures). (J) Immunofluorescent detection of the mCherry protein in teratoma cryosections reveals uniform red fluorescence in all cells, including for instance, differentiated chondrocytes expressing high levels of the type II collagen (I). DAPI staining shows blue fluorescence of all nuclei in the sections (H and K). (L) Red fluorescence image of a cryosection incubated with an isotype control. (M) RT-PCR analysis showing down-regulation of pluripotency-associated genes POU5F1/OCT4 and NANOG mRNA expression in EBs following 1 and 2 wk withdrawal of the pluripotency-maintaining factors.
- Citation: Ovchinnikov DA, Turner JP, Titmarsh DM, Thakar NY, Sin DC, Cooper-White JJ, Wolvetang EJ. Generation of a human embryonic stem cell line stably expressing high levels of the fluorescent protein mCherry. World J Stem Cells 2012; 4(7): 71-79
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v4/i7/71.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v4.i7.71