Copyright
©2012 Baishideng.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2012; 4(7): 71-79
Published online Jul 26, 2012. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i7.71
Published online Jul 26, 2012. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i7.71
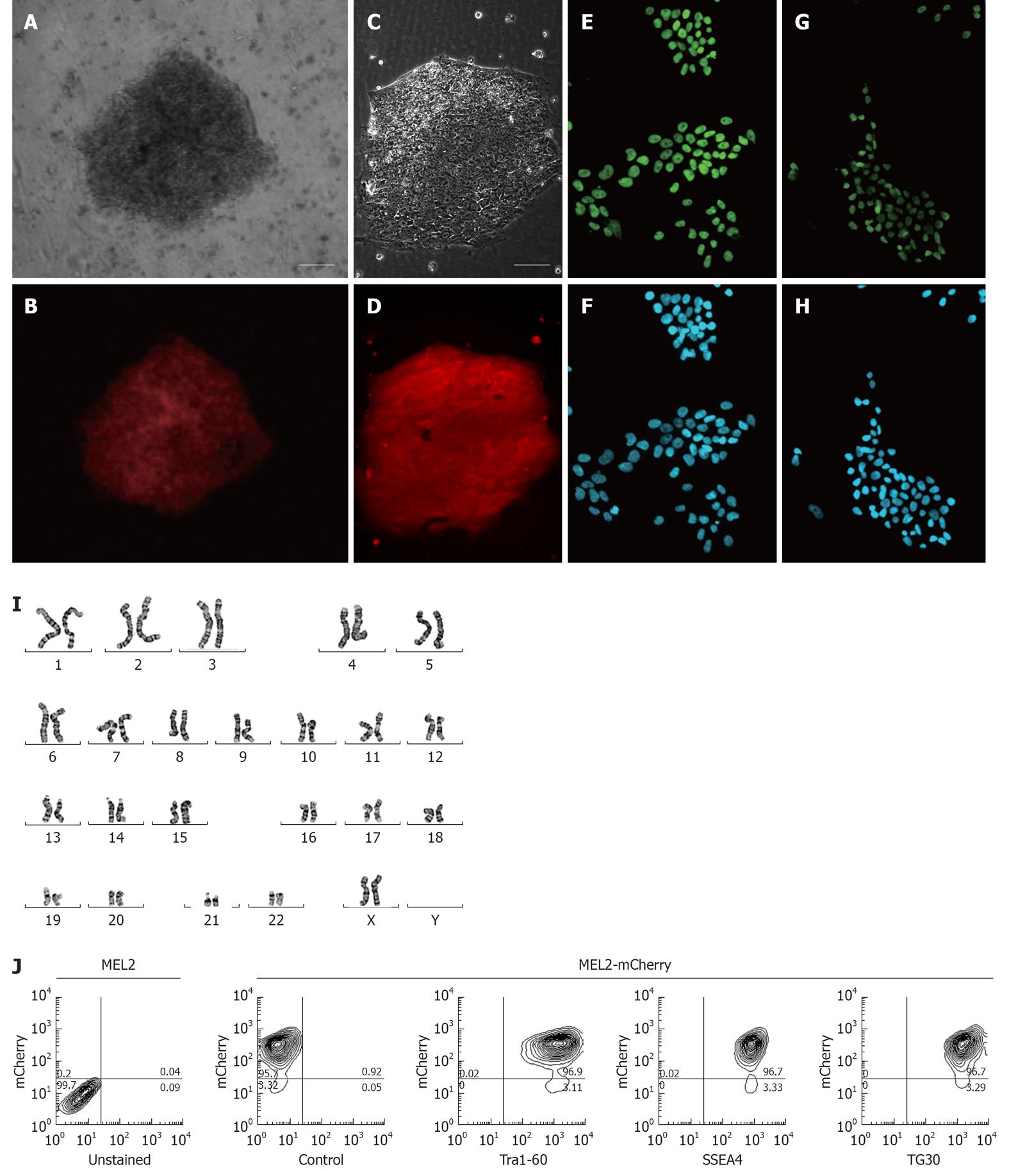
Figure 3 Characterization of the MEL2-mCherry human embryonic stem cell line.
(A) Brightfield and (B) red mCherry fluorescence of a colony of MEL2 human embryonic stem cell (hESC) transfected with Ef1a-mCherry plasmid 12 d after Blasticidin selection (scale bar = 100 μm). (C) Brightfield and (D) red mCherry fluorescence of a colony of single-cell passaging-adapted MEL2-mCherry hESC grown on Matrigel (scale bar = 100 μm). (E) POU5F1/OCT4 expression and (F) corresponding DAPI nuclear staining of MEL2-mCherry hESC. (G) NANOG protein expression and (H) corresponding DAPI nuclear staining in nuclei of MEL2-mCherry cells. (I) Normal human female karyotype of MEL2-mCherry hESC at passage 15 (Giemsa stain of a representative metaphase chromosome spread shown). (J) FACS analysis showing high levels of mCherry fluorescence (95.7%, i.e.,) and the presence of high levels of pluripotency-associated surface antigens Tra1-60, SSEA4 and TG30(CD9). Control-a representative primary isotype control antibody staining.
- Citation: Ovchinnikov DA, Turner JP, Titmarsh DM, Thakar NY, Sin DC, Cooper-White JJ, Wolvetang EJ. Generation of a human embryonic stem cell line stably expressing high levels of the fluorescent protein mCherry. World J Stem Cells 2012; 4(7): 71-79
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v4/i7/71.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v4.i7.71