Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jul 26, 2025; 17(7): 106194
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.106194
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.106194
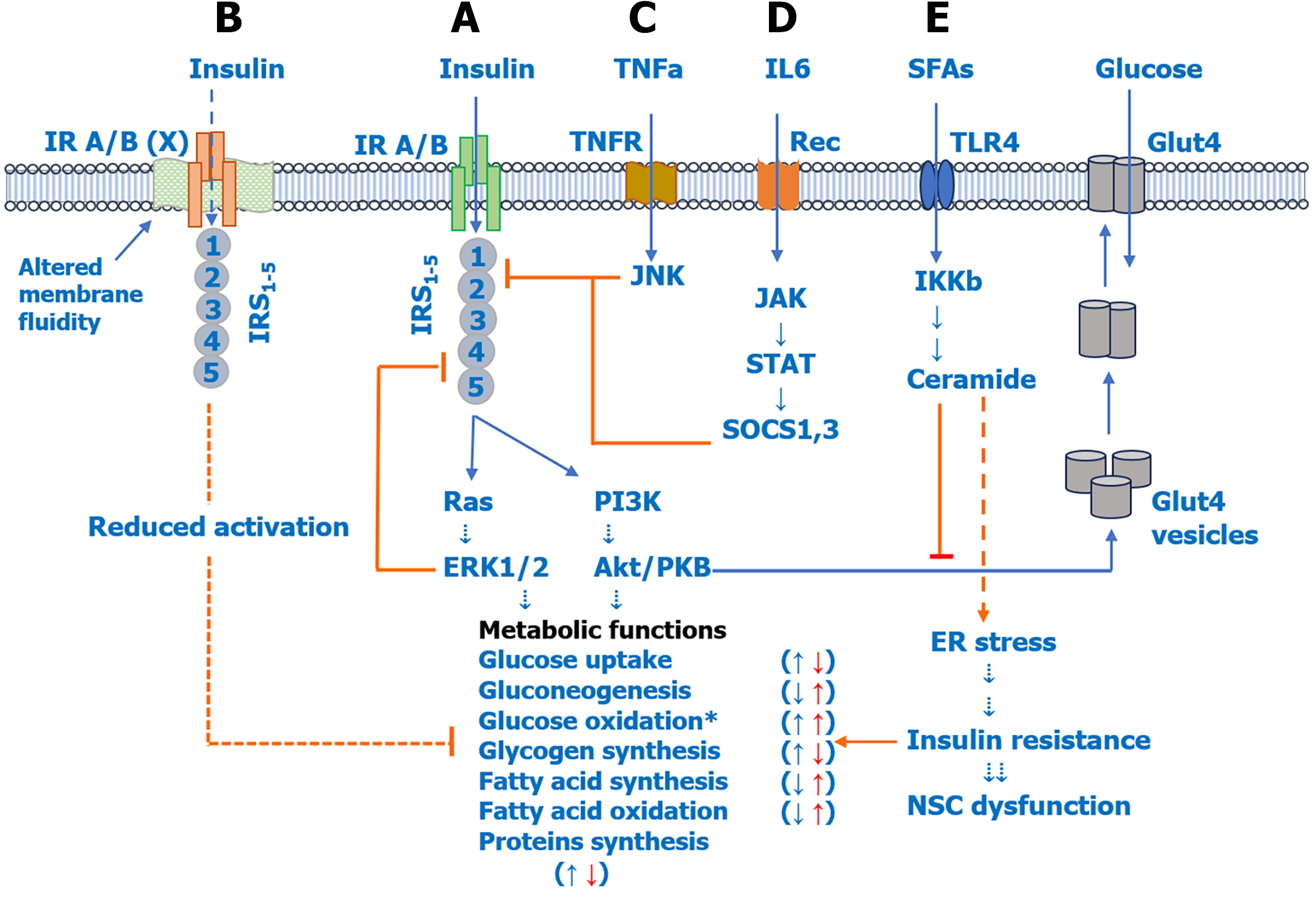
Figure 2 Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines and saturated fatty acids in insulin resistance and neural stem cell dysfunction in psychiatric disorders.
A: Insulin activates insulin receptor (IR) A/B, IR substrate 1-5 (IRS1-5), and downstream rat sarcoma-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and phosphoinositide 3 kinase-Akt/protein kinase B pathways to regulate various metabolic functions including glucose uptake (↑), glucose oxidation/glycolysis (↑), gluconeogenesis (↓), glycogen synthesis (↑), fatty acid synthesis (↓), fatty acid oxidation (↓), and protein synthesis (↑); B: Enhanced de novo lipogenesis can reduce membrane fluidity, which has been shown to reduce IR A/B activity and downstream phosphorylation of IRSs and associated metabolic functions; C and D: Elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor alpha (C) and interleukin-6 (D), can activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase and Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription pathways, respectively, which reduce IRS activation and downstream metabolic functions, indicating insulin resistance; E: Elevated saturated fatty acids can directly induce insulin resistance by activating the membrane toll-like receptor 2/4 receptor and inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress or by increasing de novo biosynthesis of ceramides. Elevated ceramides can induce insulin resistance by inhibiting Akt, which increases glucose uptake by increasing membrane expression of glucose transporter 4, and also by increasing endoplasmic reticulum stress. IR A/B: Insulin receptor A/B; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; SFAs: Saturated fatty acids; TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor; Rec: Receiver; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; Glut4: Glucose transporter 4; IRS1-5: Insulin receptor substrate 1-5; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; JAK: Janus kinase; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; SOCS: Suppressor of cytokine signaling; IKKβ: Inhibitory kappa B kinase beta; Ras: Rat sarcoma; ERK1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3 kinase; PKB: Protein kinase B; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; NSC: Neural stem cell.
- Citation: Khan MM, Khan ZA, Khan MA, Pandey G. Childhood insulin resistance and neural stem cell dysfunction in psychiatric disorders: Role of de novo lipogenesis and treatment perspectives. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(7): 106194
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i7/106194.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.106194